Maize in India: Production Systems, Constraints - AgEcon Search
Maize in India: Production Systems, Constraints - AgEcon Search
Maize in India: Production Systems, Constraints - AgEcon Search
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
3<br />
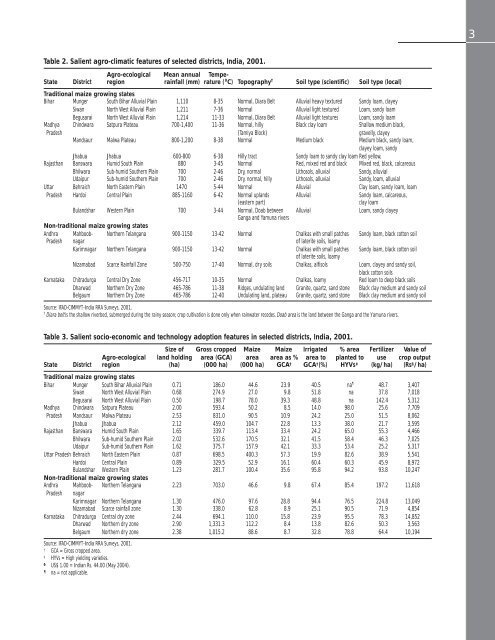
Table 2. Salient agro-climatic features of selected districts, <strong>India</strong>, 2001.<br />
Agro-ecological Mean annual Tempe-<br />
State District region ra<strong>in</strong>fall (mm) rature ( 0 C) Topography † Soil type (scientific) Soil type (local)<br />
Traditional maize grow<strong>in</strong>g states<br />
Bihar Munger South Bihar Alluvial Pla<strong>in</strong> 1,110 8-35 Normal, Diara Belt Alluvial heavy textured Sandy loam, clayey<br />
Siwan North West Alluvial Pla<strong>in</strong> 1,211 7-36 Normal Alluvial light textured Loam, sandy loam<br />
Begusarai North West Alluvial Pla<strong>in</strong> 1,214 11-33 Normal, Diara Belt Alluvial light textures Loam, sandy loam<br />
Madhya Ch<strong>in</strong>dwara Satpura Plateau 700-1,400 11-36 Normal, hilly Black clay loam Shallow medium black,<br />
Pradesh (Tamiya Block) gravelly, clayey<br />
Mandsaur Malwa Plateau 800-1,200 8-38 Normal Medium black Medium black, sandy loam,<br />
clayey loam, sandy<br />
Jhabua Jhabua 600-800 6-38 Hilly tract Sandy loam to sandy clay loam Red yellow,<br />
Rajasthan Banswara Humid South Pla<strong>in</strong> 880 3-45 Normal Red, mixed red and black Mixed red, black, calcareous<br />
Bhilwara Sub-humid Southern Pla<strong>in</strong> 700 2-46 Dry, normal Lithosols, alluvial Sandy, alluvial<br />
Udaipur Sub-humid Southern Pla<strong>in</strong> 700 2-46 Dry, normal, hilly Lithosols, alluvial Sandy, loam, alluvial<br />
Uttar Behraich North Eastern Pla<strong>in</strong> 1470 5-44 Normal Alluvial Clay loam, sandy loam, loam<br />
Pradesh Hardoi Central Pla<strong>in</strong> 885-1160 6-42 Normal uplands Alluvial Sandy loam, calcareous,<br />
(eastern part)<br />
clay loam<br />
Bulandshar Western Pla<strong>in</strong> 700 3-44 Normal, Doab between Alluvial Loam, sandy clayey<br />
Ganga and Yamuna rivers<br />
Non-traditional maize grow<strong>in</strong>g states<br />
Andhra Mahboob- Northern Telangana 900-1150 13-42 Normal Chalkas with small patches Sandy loam, black cotton soil<br />
Pradesh nagar of laterite soils, loamy<br />
Karimnagar Northern Telangana 900-1150 13-42 Normal Chalkas with small patches Sandy loam, black cotton soil<br />
of laterite soils, loamy<br />
Nizamabad Scarce Ra<strong>in</strong>fall Zone 500-750 17-40 Normal, dry soils Chalkas, alfisols Loam, clayey and sandy soil,<br />
black cotton soils<br />
Karnataka Chitradurga Central Dry Zone 456-717 10-35 Normal Chalkas, loamy Red loam to deep black soils<br />
Dharwad Northern Dry Zone 465-786 11-38 Ridges, undulat<strong>in</strong>g land Granite, quartz, sand stone Black clay medium and sandy soil<br />
Belgaum Northern Dry Zone 465-786 12-40 Undulat<strong>in</strong>g land, plateau Granite, quartz, sand stone Black clay medium and sandy soil<br />
Source: IFAD-CIMMYT-<strong>India</strong> RRA Surveys, 2001.<br />
†<br />
Diara belt is the shallow riverbed, submerged dur<strong>in</strong>g the ra<strong>in</strong>y season; crop cultivation is done only when ra<strong>in</strong>water recedes. Doab area is the land between the Ganga and the Yamuna rivers.<br />
Table 3. Salient socio-economic and technology adoption features <strong>in</strong> selected districts, <strong>India</strong>, 2001.<br />
Size of Gross cropped <strong>Maize</strong> <strong>Maize</strong> Irrigated % area Fertilizer Value of<br />
Agro-ecological land hold<strong>in</strong>g area (GCA) area area as % area to planted to use crop output<br />
State District region (ha) (000 ha) (000 ha) GCA † GCA † (%) HYVs ‡ (kg/ha) (Rs § /ha)<br />
Traditional maize grow<strong>in</strong>g states<br />
Bihar Munger South Bihar Alluvial Pla<strong>in</strong> 0.71 186.0 44.6 23.9 40.5 na 48.7 3,407<br />
Siwan North West Alluvial Pla<strong>in</strong> 0.68 274.9 27.0 9.8 51.8 na 37.8 7,018<br />
Begusarai North West Alluvial Pla<strong>in</strong> 0.50 198.7 78.0 39.3 48.8 na 142.4 5,312<br />
Madhya Ch<strong>in</strong>dwara Satpura Plateau 2.00 593.4 50.2 8.5 14.0 98.0 25.6 7,709<br />
Pradesh Mandsaur Malwa Plateau 2.53 831.0 90.5 10.9 24.2 25.0 51.5 8,062<br />
Jhabua Jhabua 2.12 459.0 104.7 22.8 13.3 38.0 21.7 3,595<br />
Rajasthan Banswara Humid South Pla<strong>in</strong> 1.65 339.7 113.4 33.4 24.2 65.0 55.3 4,466<br />
Bhilwara Sub-humid Southern Pla<strong>in</strong> 2.02 532.6 170.5 32.1 41.5 58.4 46.3 7,025<br />
Udaipur Sub-humid Southern Pla<strong>in</strong> 1.62 375.7 157.9 42.1 33.3 53.4 25.2 5,317<br />
Uttar Pradesh Behraich North Eastern Pla<strong>in</strong> 0.87 698.5 400.3 57.3 19.9 82.6 38.9 5,541<br />
Hardoi Central Pla<strong>in</strong> 0.89 329.5 52.9 16.1 60.4 60.3 45.9 8,972<br />
Bulandshar Western Pla<strong>in</strong> 1.23 281.7 100.4 35.6 95.8 94.2 93.8 10,247<br />
Non-traditional maize grow<strong>in</strong>g states<br />
Andhra Mahboob- Northern Telangana 2.23 703.0 46.6 9.8 67.4 85.4 197.2 11,618<br />
Pradesh nagar<br />
Karimnagar Northern Telangana 1.30 476.0 97.6 28.8 94.4 76.5 224.8 13,049<br />
Nizamabad Scarce ra<strong>in</strong>fall zone 1.30 338.0 62.8 8.9 25.1 90.5 71.9 4,854<br />
Karnataka Chitradurga Central dry zone 2.44 694.1 110.0 15.8 23.9 95.5 78.3 14,852<br />
Dharwad Northern dry zone 2.90 1,331.3 112.2 8.4 13.8 82.6 50.3 3,563<br />
Belgaum Northern dry zone 2.38 1,015.2 88.6 8.7 32.8 78.8 64.4 10,194<br />
Source: IFAD-CIMMYT-<strong>India</strong> RRA Surveys, 2001.<br />
†<br />
GCA = Gross cropped area.<br />
‡<br />
HYVs = High yield<strong>in</strong>g varieties.<br />
§<br />
US$ 1.00 = <strong>India</strong>n Rs. 44.00 (May 2004).<br />
<br />
na = not applicable.