Maize in India: Production Systems, Constraints - AgEcon Search
Maize in India: Production Systems, Constraints - AgEcon Search
Maize in India: Production Systems, Constraints - AgEcon Search
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
6<br />
Egg production<br />
7000<br />
<strong>Maize</strong> production<br />
1400<br />
Egg production<br />
2000<br />
<strong>Maize</strong> production<br />
2000<br />
6000<br />
5000<br />
4000<br />
Egg (millions)<br />
1200<br />
1000<br />
800<br />
1600<br />
1200<br />
Egg (millions)<br />
1600<br />
1200<br />
3000<br />
2000<br />
1000<br />
<strong>Maize</strong> production (000 t)<br />
600<br />
400<br />
200<br />
800<br />
400<br />
<strong>Maize</strong> production (000 t)<br />
800<br />
400<br />
0<br />
1980 1982 1984 1986 1988 1990 1992 1994 1996<br />
Year<br />
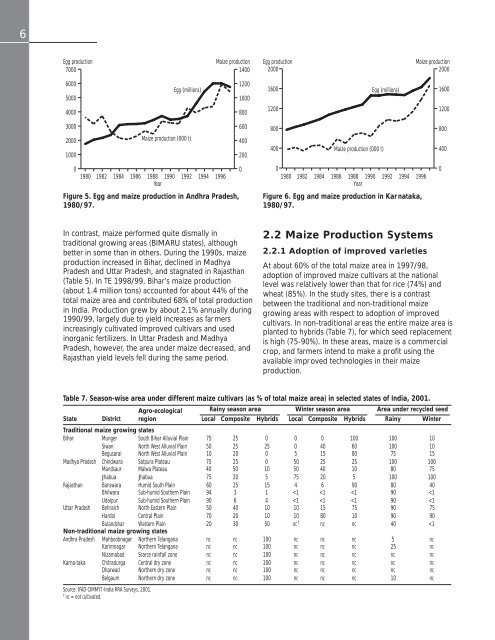
Figure 5. Egg and maize production <strong>in</strong> Andhra Pradesh,<br />
1980/97.<br />
0<br />
0<br />
1980 1982 1984 1986 1988 1990 1992 1994 1996<br />
Year<br />
Figure 6. Egg and maize production <strong>in</strong> Kar nataka,<br />
1980/97.<br />
0<br />
In contrast, maize performed quite dismally <strong>in</strong><br />
traditional grow<strong>in</strong>g areas (BIMARU states), although<br />
better <strong>in</strong> some than <strong>in</strong> others. Dur<strong>in</strong>g the 1990s, maize<br />
production <strong>in</strong>creased <strong>in</strong> Bihar, decl<strong>in</strong>ed <strong>in</strong> Madhya<br />
Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh, and stagnated <strong>in</strong> Rajasthan<br />
(Table 5). In TE 1998/99, Bihar’s maize production<br />
(about 1.4 million tons) accounted for about 44% of the<br />
total maize area and contributed 68% of total production<br />
<strong>in</strong> <strong>India</strong>. <strong>Production</strong> grew by about 2.1% annually dur<strong>in</strong>g<br />
1990/99, largely due to yield <strong>in</strong>creases as farmers<br />
<strong>in</strong>creas<strong>in</strong>gly cultivated improved cultivars and used<br />
<strong>in</strong>organic fertilizers. In Uttar Pradesh and Madhya<br />
Pradesh, however, the area under maize decreased, and<br />
Rajasthan yield levels fell dur<strong>in</strong>g the same period.<br />
2.2 <strong>Maize</strong> <strong>Production</strong> <strong>Systems</strong><br />
2.2.1 Adoption of improved varieties<br />
At about 60% of the total maize area <strong>in</strong> 1997/98,<br />
adoption of improved maize cultivars at the national<br />
level was relatively lower than that for rice (74%) and<br />
wheat (85%). In the study sites, there is a contrast<br />
between the traditional and non-traditional maize<br />
grow<strong>in</strong>g areas with respect to adoption of improved<br />
cultivars. In non-traditional ar eas the entire maize area is<br />
planted to hybrids (Table 7), for which seed replacement<br />
is high (75-90%). In these areas, maize is a commercial<br />
crop, and farmers <strong>in</strong>tend to make a profit us<strong>in</strong>g the<br />
available impr oved technologies <strong>in</strong> their maize<br />
production.<br />
Table 7. Season-wise area under different maize cultivars (as % of total maize area) <strong>in</strong> selected states of <strong>India</strong>, 2001.<br />
Agro-ecological Ra<strong>in</strong>y season area W<strong>in</strong>ter season area Area under recycled seed<br />
State District region Local Composite Hybrids Local Composite Hybrids Ra<strong>in</strong>y W<strong>in</strong>ter<br />
Traditional maize grow<strong>in</strong>g states<br />
Bihar Munger South Bihar Alluvial Pla<strong>in</strong> 75 25 0 0 0 100 100 10<br />
Siwan North West Alluvial Pla<strong>in</strong> 50 25 25 0 40 60 100 10<br />
Begusarai North West Alluvial Pla<strong>in</strong> 10 20 0 5 15 80 75 15<br />
Madhya Pradesh Ch<strong>in</strong>dwara Satpura Plateau 75 25 0 50 25 25 100 100<br />
Mandsaur Malwa Plateau 40 50 10 50 40 10 80 75<br />
Jhabua Jhabua 75 20 5 75 20 5 100 100<br />
Rajasthan Banswara Humid South Pla<strong>in</strong> 60 25 15 4 6 90 80 40<br />
Bhilwara Sub-humid Southern Pla<strong>in</strong> 94 3 1