- Page 2:
Gene Cloning
- Page 5 and 6:
Published by: Taylor & Francis Grou
- Page 7 and 8:
vi Contents 3.14 Designing PCR Prim
- Page 9 and 10:
viii Contents 8.3 Identifying Eukar
- Page 12 and 13:
1 Introduction 1.1 The Beginning of
- Page 14 and 15:
Introduction 3 which also conveys a
- Page 16 and 17:
Introduction 5 thought, or the brin
- Page 18 and 19:
2 Genome Organization Learning outc
- Page 20 and 21:
Genome Organization 9 and not quite
- Page 22 and 23:
Genome Organization 11 both of whic
- Page 24 and 25:
Genome Organization 13 relative com
- Page 26 and 27:
Genome Organization 15 Box 2.2 Inte
- Page 28 and 29:
Genome Organization 17 Table 2.2 Hu
- Page 30 and 31:
Genome Organization 19 close to oth
- Page 32 and 33:
Genome Organization 21 individual g
- Page 34 and 35:
slower rate than junk DNA. (To be m
- Page 36 and 37:
Genome Organization 25 kb 0 2 4 6 8
- Page 38 and 39:
Genome Organization 27 cloning pred
- Page 40 and 41:
Genome Organization 29 (a) 1 2 3 4
- Page 42 and 43:
Genome Organization 31 interphase a
- Page 44 and 45:
Genome Organization 33 A2.3. Chromo
- Page 46 and 47:
3 Key Tools for Gene Cloning Learni
- Page 48 and 49:
Key Tools for Gene Cloning 37 repli
- Page 50 and 51:
Key Tools for Gene Cloning 39 Box 3
- Page 52 and 53:
Key Tools for Gene Cloning 41 (a) (
- Page 54 and 55:
Key Tools for Gene Cloning 43 then,
- Page 56 and 57:
Key Tools for Gene Cloning 45 Figur
- Page 58 and 59:
Key Tools for Gene Cloning 47 Clear
- Page 60 and 61:
Key Tools for Gene Cloning 49 that
- Page 62 and 63:
Key Tools for Gene Cloning 51 same
- Page 64 and 65:
3.9 More About Vectors Detecting su
- Page 66 and 67:
Key Tools for Gene Cloning 55 in th
- Page 68 and 69:
Key Tools for Gene Cloning 57 Q3.13
- Page 70 and 71:
Key Tools for Gene Cloning 59 alway
- Page 72 and 73:
Key Tools for Gene Cloning 61 Figur
- Page 74 and 75:
Key Tools for Gene Cloning 63 (a) C
- Page 76 and 77:
Key Tools for Gene Cloning 65 Box 3
- Page 78 and 79:
Key Tools for Gene Cloning 67 simpl
- Page 80 and 81:
Key Tools for Gene Cloning 69 (a) 5
- Page 82 and 83:
Key Tools for Gene Cloning 71 92 92
- Page 84 and 85:
Key Tools for Gene Cloning 73 polym
- Page 86 and 87:
Key Tools for Gene Cloning 75 (a) T
- Page 88 and 89:
Key Tools for Gene Cloning 77 DNA s
- Page 90 and 91:
Key Tools for Gene Cloning 79 Q3.7.
- Page 92 and 93:
Key Tools for Gene Cloning 81 A3.15
- Page 94:
Key Tools for Gene Cloning 83 A3.20
- Page 97 and 98:
86 Gene Cloning you extract DNA fro
- Page 99 and 100:
88 Gene Cloning Box 4.1 Preparation
- Page 101 and 102:
90 Gene Cloning which is 6.3 Mb, to
- Page 103 and 104:
92 Gene Cloning Also, if all the fr
- Page 105 and 106:
94 Gene Cloning (a) (b) Bacterial s
- Page 107 and 108:
96 Gene Cloning (a) Insertion vecto
- Page 109 and 110:
98 Gene Cloning The strictly define
- Page 111 and 112:
100 Gene Cloning BamHI Ap r Tet r p
- Page 113 and 114:
102 Gene Cloning parB Cm r parA rep
- Page 115 and 116:
104 Gene Cloning (a) TTTTT AAAAA TT
- Page 117 and 118:
106 Gene Cloning Box 4.3 Converting
- Page 119 and 120:
108 Gene Cloning of your gene is. A
- Page 121 and 122:
110 Gene Cloning A4.2. Extract chro
- Page 123 and 124:
112 Gene Cloning A4.8. See Section
- Page 125 and 126:
114 Gene Cloning Q4.15. What are th
- Page 127 and 128:
116 Gene Cloning dystrophin gene is
- Page 129 and 130:
118 Gene Cloning it is still a form
- Page 131 and 132:
120 Gene Cloning One obvious proble
- Page 133 and 134:
122 Gene Cloning The main difficult
- Page 135 and 136:
124 Gene Cloning (a) Labeled single
- Page 137 and 138:
126 Gene Cloning N terminus Phe Val
- Page 139 and 140:
128 Gene Cloning Box 5.3 Types of D
- Page 141 and 142:
130 Gene Cloning Box 5.4 Methods fo
- Page 143 and 144:
132 Gene Cloning the DNA probe. Bot
- Page 145 and 146:
134 Gene Cloning a b c d e f g h 1
- Page 147 and 148:
136 Gene Cloning S. cerevisiae, and
- Page 149 and 150:
138 Gene Cloning Q5.7. Would you ex
- Page 151 and 152:
140 Gene Cloning use your genomic c
- Page 153 and 154:
142 Gene Cloning diseases, where th
- Page 155 and 156:
144 Gene Cloning (a) Replicative Ta
- Page 157 and 158:
146 Gene Cloning where the transpos
- Page 159 and 160:
148 Gene Cloning DNA fragment in th
- Page 161 and 162:
150 Gene Cloning Bacteria transform
- Page 163 and 164:
152 Gene Cloning Wild-type gene Mut
- Page 165 and 166:
154 Gene Cloning molecule using PCR
- Page 167 and 168:
156 Gene Cloning digesting chromoso
- Page 169 and 170:
158 Gene Cloning + + Ac Avr Avr cf-
- Page 171 and 172:
160 Gene Cloning which are very clo
- Page 173 and 174:
162 Gene Cloning Box 6.3 Restrictio
- Page 175 and 176:
164 Gene Cloning Initial region clo
- Page 177 and 178:
166 Gene Cloning Box 6.4 Nonsense S
- Page 179 and 180:
168 Gene Cloning 6.10 Cloning of th
- Page 181 and 182:
170 Gene Cloning are two possible o
- Page 183 and 184:
172 Gene Cloning Isolation of the t
- Page 185 and 186:
174 Gene Cloning Two approaches wer
- Page 187 and 188:
176 Gene Cloning synthesize DNA de
- Page 189 and 190:
178 Gene Cloning Box 7.1 Denaturing
- Page 191 and 192:
180 Gene Cloning G A T C Figure 7.4
- Page 193 and 194:
182 Gene Cloning although other con
- Page 195 and 196:
184 Gene Cloning A large DNA fragme
- Page 197 and 198:
186 Gene Cloning chain reaction, fl
- Page 199 and 200:
188 Gene Cloning rounds of amplific
- Page 201 and 202:
190 Gene Cloning Contig 2 Clone 12
- Page 203 and 204:
192 Gene Cloning λ Clone Scaffold
- Page 205 and 206:
194 Gene Cloning Genomic DNA (a) Cl
- Page 207 and 208:
196 Gene Cloning therefore sequence
- Page 209 and 210:
198 Gene Cloning Tag sequence CGTGT
- Page 211 and 212:
200 Gene Cloning Genomic DNA (a) Ad
- Page 213 and 214: 202 Gene Cloning bases. The light s
- Page 215 and 216: 204 Gene Cloning A7.3. (a) The dide
- Page 218 and 219: 8 Bioinformatics Learning outcomes:
- Page 220 and 221: Bioinformatics 209 Table 8.1 The ge
- Page 222 and 223: Bioinformatics 211 5' accgcgcatggtg
- Page 224 and 225: Bioinformatics 213 Correlation Scor
- Page 226 and 227: Bioinformatics 215 AGG T R A G T C
- Page 228 and 229: Bioinformatics 217 conjunction with
- Page 230 and 231: Bioinformatics 219 (c) V S V K L Q
- Page 232 and 233: Bioinformatics 221 Tiny P Small Ali
- Page 234 and 235: Bioinformatics 223 Matrix: EBLOSUM6
- Page 236 and 237: Bioinformatics 225 Box 8.2 DNA and
- Page 238 and 239: Bioinformatics 227 (a) DB:ID Source
- Page 240 and 241: Bioinformatics 229 (a) Sequences pr
- Page 242 and 243: Bioinformatics 231 list is also of
- Page 244 and 245: Bioinformatics 233 this relates to
- Page 246 and 247: Bioinformatics 235 common functiona
- Page 248 and 249: Bioinformatics 237 These two regula
- Page 250 and 251: Bioinformatics 239 three-dimensiona
- Page 252 and 253: Bioinformatics 241 Neisseria mening
- Page 254 and 255: Bioinformatics 243 A8.1. The triple
- Page 256 and 257: Bioinformatics 245 Q8.11. Which gro
- Page 258: Bioinformatics 247 EMBL Nucleotide
- Page 261 and 262: 250 Gene Cloning What sorts of stud
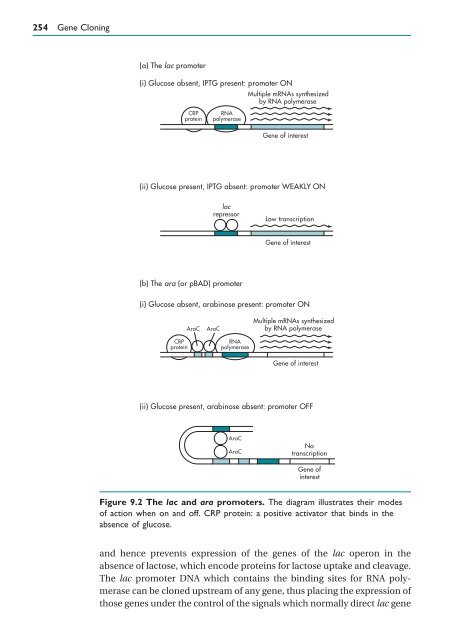
- Page 263: 252 Gene Cloning 9.2 Requirements f
- Page 267 and 268: 256 Gene Cloning lac: CCAGGCTTTACAC
- Page 269 and 270: 258 Gene Cloning phage (such as T7)
- Page 271 and 272: 260 Gene Cloning 9.4 Some Problems
- Page 273 and 274: 262 Gene Cloning Figure 9.6 Inclusi
- Page 275 and 276: 264 Gene Cloning Box 9.1 Translatio
- Page 277 and 278: 266 Gene Cloning Box 9.2 Signal Seq
- Page 279 and 280: 268 Gene Cloning Ribosome Cytosol P
- Page 281 and 282: 270 Gene Cloning Other yeast specie
- Page 283 and 284: 272 Gene Cloning (turned on by an i
- Page 285 and 286: 274 Gene Cloning 9.6 A Final Word A
- Page 287 and 288: 276 Gene Cloning study, as they wil
- Page 290 and 291: 10 Gene Cloning in the Functional A
- Page 292 and 293: Gene Cloning in the Functional Anal
- Page 294 and 295: Gene Cloning in the Functional Anal
- Page 296 and 297: Gene Cloning in the Functional Anal
- Page 298 and 299: Gene Cloning in the Functional Anal
- Page 300 and 301: Gene Cloning in the Functional Anal
- Page 302 and 303: Gene Cloning in the Functional Anal
- Page 304 and 305: Gene Cloning in the Functional Anal
- Page 306 and 307: Gene Cloning in the Functional Anal
- Page 308 and 309: Gene Cloning in the Functional Anal
- Page 310 and 311: Gene Cloning in the Functional Anal
- Page 312 and 313: Gene Cloning in the Functional Anal
- Page 314 and 315:
Gene Cloning in the Functional Anal
- Page 316 and 317:
Gene Cloning in the Functional Anal
- Page 318 and 319:
Gene Cloning in the Functional Anal
- Page 320 and 321:
Gene Cloning in the Functional Anal
- Page 322 and 323:
Gene Cloning in the Functional Anal
- Page 324:
Gene Cloning in the Functional Anal
- Page 327 and 328:
316 Gene Cloning genomic sequences
- Page 329 and 330:
318 Gene Cloning the first exon of
- Page 331 and 332:
320 Gene Cloning Box 11.1 End Label
- Page 333 and 334:
322 Gene Cloning mRNA 5' 3' 3' 5' S
- Page 335 and 336:
324 Gene Cloning mRNA 5' 3' 3' 5' G
- Page 337 and 338:
326 Gene Cloning cloning step. RACE
- Page 339 and 340:
328 Gene Cloning Prepare RNA from c
- Page 341 and 342:
330 Gene Cloning Gene A condition 1
- Page 343 and 344:
332 Gene Cloning (a) (b) (c) Immobi
- Page 345 and 346:
334 Gene Cloning tat and one in whi
- Page 347 and 348:
336 Gene Cloning Box 11.3 Examples
- Page 349 and 350:
338 Gene Cloning (a) MCS for promot
- Page 351 and 352:
340 Gene Cloning important regulato
- Page 353 and 354:
342 Gene Cloning (a) F DP DPA DNA-t
- Page 355 and 356:
344 Gene Cloning DNA alone DNA-prot
- Page 357 and 358:
346 Gene Cloning [FNR] GA - + -90 -
- Page 359 and 360:
348 Gene Cloning (a) 1 2 3 4 5 Prom
- Page 361 and 362:
350 Gene Cloning bind the transcrip
- Page 363 and 364:
352 Gene Cloning Target sequence Ye
- Page 365 and 366:
354 Gene Cloning have been develope
- Page 367 and 368:
356 Gene Cloning detected by autora
- Page 369 and 370:
358 Gene Cloning vide a complete li
- Page 371 and 372:
360 Gene Cloning MS 503 750 1400 16
- Page 373 and 374:
362 Gene Cloning Q11.3. Why is it e
- Page 375 and 376:
364 Gene Cloning (transcriptomics o
- Page 377 and 378:
366 Gene Cloning Figure 12.1 Transg
- Page 379 and 380:
368 Gene Cloning Herbicide Non-tran
- Page 381 and 382:
370 Gene Cloning that has been used
- Page 383 and 384:
372 Gene Cloning tumors with high f
- Page 385 and 386:
374 Gene Cloning Transgene encoding
- Page 387 and 388:
376 Gene Cloning placed on the mark
- Page 389 and 390:
378 Gene Cloning Gene A: a gene whi
- Page 391 and 392:
380 Gene Cloning Isolate the gene o
- Page 393 and 394:
382 Gene Cloning Box 12.1 Recombina
- Page 395 and 396:
384 Gene Cloning damage to the DNA
- Page 397 and 398:
386 Gene Cloning Box 12.2 The Produ
- Page 399 and 400:
388 Gene Cloning as to whether the
- Page 401 and 402:
390 Gene Cloning transformed. The i
- Page 403 and 404:
392 Gene Cloning 1. Gene of interes
- Page 405 and 406:
394 Gene Cloning Showing that the D
- Page 407 and 408:
396 Gene Cloning complete plants by
- Page 409 and 410:
398 Gene Cloning 12.5 Knockout Mice
- Page 411 and 412:
400 Gene Cloning introduced back in
- Page 413 and 414:
402 Gene Cloning Chromosome Constru
- Page 415 and 416:
404 Gene Cloning cells, and one has
- Page 417 and 418:
406 Gene Cloning mapped by inverse
- Page 419 and 420:
408 Gene Cloning traditional method
- Page 421 and 422:
410 Gene Cloning Further Reading Th
- Page 423 and 424:
412 Gene Cloning (a) Maternal chrom
- Page 425 and 426:
414 Gene Cloning chromosomes togeth
- Page 427 and 428:
416 Gene Cloning Box 13.1 DNA Profi
- Page 429 and 430:
418 Gene Cloning Although forensic
- Page 431 and 432:
420 Gene Cloning Dye terminators (a
- Page 433 and 434:
422 Gene Cloning With the advent of
- Page 435 and 436:
424 Gene Cloning Box 13.2 Genetic A
- Page 437 and 438:
426 Gene Cloning Box 13.3 Methods o
- Page 439 and 440:
428 Gene Cloning (a) PCR primer seq
- Page 441 and 442:
430 Gene Cloning (a) Target specifi
- Page 443 and 444:
432 Gene Cloning (a) R Q 5' 3' (b)
- Page 445 and 446:
434 Gene Cloning liquid chromatogra
- Page 447 and 448:
436 Gene Cloning such as pre-implan
- Page 449 and 450:
438 Gene Cloning attack there is a
- Page 451 and 452:
440 Gene Cloning and also because l
- Page 453 and 454:
442 Gene Cloning John Mary Ann Pete
- Page 455 and 456:
444 Gene Cloning monitoring the pro
- Page 457 and 458:
446 Gene Cloning Codon Three nucleo
- Page 459 and 460:
448 Gene Cloning Homologous recombi
- Page 461 and 462:
450 Gene Cloning Phenotype The obse
- Page 463 and 464:
452 Gene Cloning Vector A self-repl
- Page 465 and 466:
454 Gene Cloning Capillary electrop
- Page 467 and 468:
456 Gene Cloning EST see expressed
- Page 469 and 470:
458 Gene Cloning Metallothionein, 3
- Page 471 and 472:
460 Gene Cloning Protein addition o
- Page 473:
462 Gene Cloning Transcription, ide