Download Lab Safety Manual - Integrated Nanosystems Research ...
Download Lab Safety Manual - Integrated Nanosystems Research ...
Download Lab Safety Manual - Integrated Nanosystems Research ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
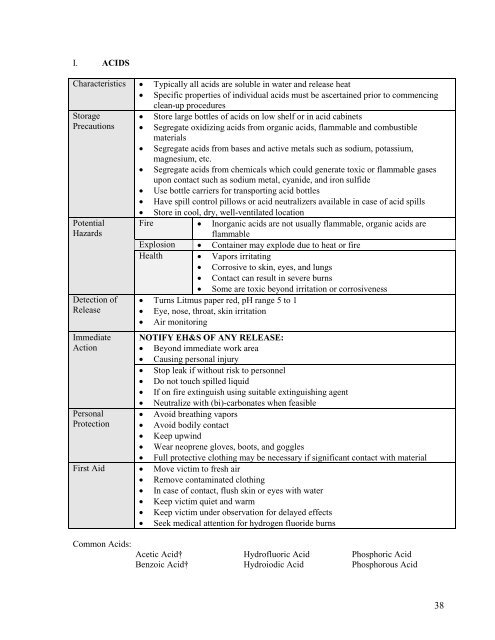
I. ACIDS<br />
Characteristics • Typically all acids are soluble in water and release heat<br />
• Specific properties of individual acids must be ascertained prior to commencing<br />
clean-up procedures<br />
Storage<br />
Precautions<br />
Potential<br />
Hazards<br />
Detection of<br />
Release<br />
Immediate<br />
Action<br />
Personal<br />
Protection<br />
• Store large bottles of acids on low shelf or in acid cabinets<br />
• Segregate oxidizing acids from organic acids, flammable and combustible<br />
materials<br />
• Segregate acids from bases and active metals such as sodium, potassium,<br />
magnesium, etc.<br />
• Segregate acids from chemicals which could generate toxic or flammable gases<br />
upon contact such as sodium metal, cyanide, and iron sulfide<br />
• Use bottle carriers for transporting acid bottles<br />
• Have spill control pillows or acid neutralizers available in case of acid spills<br />
• Store in cool, dry, well-ventilated location<br />
Fire • Inorganic acids are not usually flammable, organic acids are<br />
flammable<br />
Explosion • Container may explode due to heat or fire<br />
Health • Vapors irritating<br />
• Corrosive to skin, eyes, and lungs<br />
• Contact can result in severe burns<br />
• Some are toxic beyond irritation or corrosiveness<br />
• Turns Litmus paper red, pH range 5 to 1<br />
• Eye, nose, throat, skin irritation<br />
• Air monitoring<br />
NOTIFY EH&S OF ANY RELEASE:<br />
• Beyond immediate work area<br />
• Causing personal injury<br />
• Stop leak if without risk to personnel<br />
• Do not touch spilled liquid<br />
• If on fire extinguish using suitable extinguishing agent<br />
• Neutralize with (bi)-carbonates when feasible<br />
• Avoid breathing vapors<br />
• Avoid bodily contact<br />
• Keep upwind<br />
• Wear neoprene gloves, boots, and goggles<br />
• Full protective clothing may be necessary if significant contact with material<br />
First Aid • Move victim to fresh air<br />
• Remove contaminated clothing<br />
• In case of contact, flush skin or eyes with water<br />
• Keep victim quiet and warm<br />
• Keep victim under observation for delayed effects<br />
• Seek medical attention for hydrogen fluoride burns<br />
Common Acids:<br />
Acetic Acid†<br />
Benzoic Acid†<br />
Hydrofluoric Acid<br />
Hydroiodic Acid<br />
Phosphoric Acid<br />
Phosphorous Acid<br />
38