census
census
census
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
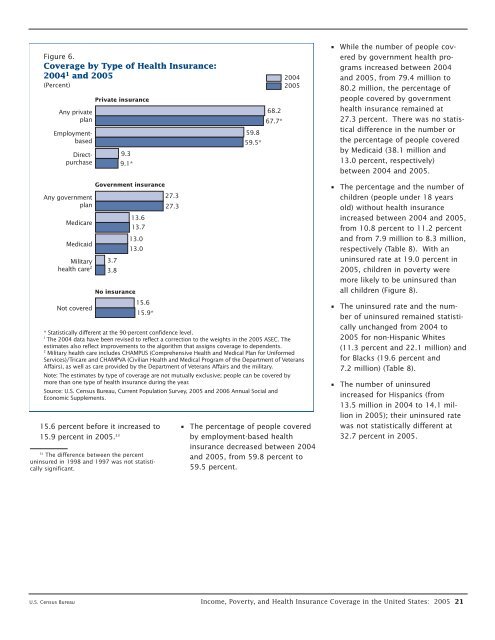
Figure 6.<br />
Coverage by Type of Health Insurance:<br />
2004 1 and 2005<br />
(Percent)<br />
Any private<br />
plan<br />
Directpurchase<br />
Employmentbased<br />
Private insurance<br />
9.3<br />
9.1*<br />
59.8<br />
59.5*<br />
68.2<br />
67.7*<br />
2004<br />
2005<br />
• While the number of people covered<br />
by government health programs<br />
increased between 2004<br />
and 2005, from 79.4 million to<br />
80.2 million, the percentage of<br />
people covered by government<br />
health insurance remained at<br />
27.3 percent. There was no statistical<br />
difference in the number or<br />
the percentage of people covered<br />
by Medicaid (38.1 million and<br />
13.0 percent, respectively)<br />
between 2004 and 2005.<br />
Any government<br />
plan<br />
Medicare<br />
Medicaid<br />
Military<br />
health care 2<br />
Not covered<br />
Government insurance<br />
3.7<br />
3.8<br />
No insurance<br />
13.6<br />
13.7<br />
13.0<br />
13.0<br />
15.6<br />
15.9*<br />
27.3<br />
27.3<br />
* Statistically different at the 90-percent confidence level.<br />
1<br />
The 2004 data have been revised to reflect a correction to the weights in the 2005 ASEC. The<br />
estimates also reflect improvements to the algorithm that assigns coverage to dependents.<br />
2 Military health care includes CHAMPUS (Comprehensive Health and Medical Plan for Uniformed<br />
Services)/Tricare and CHAMPVA (Civilian Health and Medical Program of the Department of Veterans<br />
Affairs), as well as care provided by the Department of Veterans Affairs and the military.<br />
Note: The estimates by type of coverage are not mutually exclusive; people can be covered by<br />
more than one type of health insurance during the year.<br />
Source: U.S. Census Bureau, Current Population Survey, 2005 and 2006 Annual Social and<br />
Economic Supplements.<br />
15.6 percent before it increased to • The percentage of people covered<br />
15.9 percent in 2005. 33 by employment-based health<br />
33<br />
The difference between the percent<br />
uninsured in 1998 and 1997 was not statistically<br />
significant.<br />
insurance decreased between 2004<br />
and 2005, from 59.8 percent to<br />
59.5 percent.<br />
• The percentage and the number of<br />
children (people under 18 years<br />
old) without health insurance<br />
increased between 2004 and 2005,<br />
from 10.8 percent to 11.2 percent<br />
and from 7.9 million to 8.3 million,<br />
respectively (Table 8). With an<br />
uninsured rate at 19.0 percent in<br />
2005, children in poverty were<br />
more likely to be uninsured than<br />
all children (Figure 8).<br />
• The uninsured rate and the number<br />
of uninsured remained statistically<br />
unchanged from 2004 to<br />
2005 for non-Hispanic Whites<br />
(11.3 percent and 22.1 million) and<br />
for Blacks (19.6 percent and<br />
7.2 million) (Table 8).<br />
• The number of uninsured<br />
increased for Hispanics (from<br />
13.5 million in 2004 to 14.1 million<br />
in 2005); their uninsured rate<br />
was not statistically different at<br />
32.7 percent in 2005.<br />
U.S. Census Bureau Income, Poverty, and Health Insurance Coverage in the United States: 2005 21