Hydrogeology and Groundwater Quality of Highlands ... - USGS
Hydrogeology and Groundwater Quality of Highlands ... - USGS
Hydrogeology and Groundwater Quality of Highlands ... - USGS
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
NORTH<br />
FEET<br />
200<br />
NGVD 29<br />
200<br />
400<br />
600<br />
800<br />
1,000<br />
1,200<br />
1,400<br />
1,600<br />
1,800<br />
2,000<br />
C C ′<br />
ROMP 43xx<br />
Section A-A’<br />
?<br />
?<br />
?<br />
W-2859<br />
MIDDLE<br />
CONFINING UNIT II<br />
ROMP 29A<br />
LOWER<br />
FLORIDAN AQUIFER<br />
Vertical scale greatly exaggerated<br />
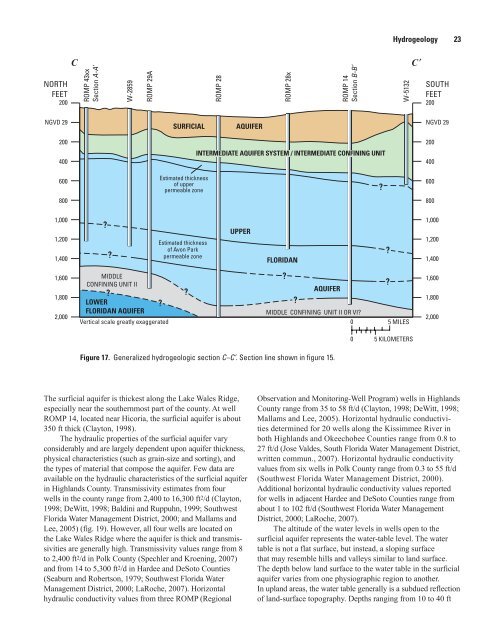
Figure 17. Generalized hydrogeologic section C–C’. Section line shown in figure 15.<br />
The surficial aquifer is thickest along the Lake Wales Ridge,<br />
especially near the southernmost part <strong>of</strong> the county. At well<br />
ROMP 14, located near Hicoria, the surficial aquifer is about<br />
350 ft thick (Clayton, 1998).<br />
The hydraulic properties <strong>of</strong> the surficial aquifer vary<br />
considerably <strong>and</strong> are largely dependent upon aquifer thickness,<br />
physical characteristics (such as grain-size <strong>and</strong> sorting), <strong>and</strong><br />
the types <strong>of</strong> material that compose the aquifer. Few data are<br />
available on the hydraulic characteristics <strong>of</strong> the surficial aquifer<br />
in Highl<strong>and</strong>s County. Transmissivity estimates from four<br />
wells in the county range from 2,400 to 16,300 ft 2/d (Clayton,<br />
1998; DeWitt, 1998; Baldini <strong>and</strong> Ruppuhn, 1999; Southwest<br />
Florida Water Management District, 2000; <strong>and</strong> Mallams <strong>and</strong><br />
Lee, 2005) (fig. 19). However, all four wells are located on<br />
the Lake Wales Ridge where the aquifer is thick <strong>and</strong> transmissivities<br />
are generally high. Transmissivity values range from 8<br />
to 2,400 ft 2/d in Polk County (Spechler <strong>and</strong> Kroening, 2007)<br />
<strong>and</strong> from 14 to 5,300 ft 2/d in Hardee <strong>and</strong> DeSoto Counties<br />
(Seaburn <strong>and</strong> Robertson, 1979; Southwest Florida Water<br />
Management District, 2000; LaRoche, 2007). Horizontal<br />
hydraulic conductivity values from three ROMP (Regional<br />
?<br />
SURFICIAL<br />
Estimated thickness<br />
<strong>of</strong> upper<br />
permeable zone<br />
Estimated thickness<br />
<strong>of</strong> Avon Park<br />
permeable zone<br />
?<br />
ROMP 28<br />
AQUIFER<br />
ROMP 28x<br />
?<br />
AQUIFER<br />
ROMP 14<br />
Section B-B’<br />
INTERMEDIATE AQUIFER SYSTEM / INTERMEDIATE CONFINING UNIT<br />
UPPER<br />
FLORIDAN<br />
?<br />
MIDDLE CONFINING UNIT II OR VI?<br />
0<br />
0<br />
<strong>Hydrogeology</strong> 23<br />
Observation <strong>and</strong> Monitoring-Well Program) wells in Highl<strong>and</strong>s<br />
County range from 35 to 58 ft/d (Clayton, 1998; DeWitt, 1998;<br />
Mallams <strong>and</strong> Lee, 2005). Horizontal hydraulic conductivities<br />
determined for 20 wells along the Kissimmee River in<br />
both Highl<strong>and</strong>s <strong>and</strong> Okeechobee Counties range from 0.8 to<br />
27 ft/d (Jose Valdes, South Florida Water Management District,<br />
written commun., 2007). Horizontal hydraulic conductivity<br />
values from six wells in Polk County range from 0.3 to 55 ft/d<br />
(Southwest Florida Water Management District, 2000).<br />
Additional horizontal hydraulic conductivity values reported<br />
for wells in adjacent Hardee <strong>and</strong> DeSoto Counties range from<br />
about 1 to 102 ft/d (Southwest Florida Water Management<br />
District, 2000; LaRoche, 2007).<br />
The altitude <strong>of</strong> the water levels in wells open to the<br />
surficial aquifer represents the water-table level. The water<br />
table is not a flat surface, but instead, a sloping surface<br />
that may resemble hills <strong>and</strong> valleys similar to l<strong>and</strong> surface.<br />
The depth below l<strong>and</strong> surface to the water table in the surficial<br />
aquifer varies from one physiographic region to another.<br />
In upl<strong>and</strong> areas, the water table generally is a subdued reflection<br />
<strong>of</strong> l<strong>and</strong>-surface topography. Depths ranging from 10 to 40 ft<br />
?<br />
?<br />
?<br />
W-5132<br />
5 MILES<br />
5 KILOMETERS<br />
SOUTH<br />
FEET<br />
200<br />
NGVD 29<br />
200<br />
400<br />
600<br />
800<br />
1,000<br />
1,200<br />
1,400<br />
1,600<br />
1,800<br />
2,000