section 1 - The American College Online Learning Center
section 1 - The American College Online Learning Center
section 1 - The American College Online Learning Center
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
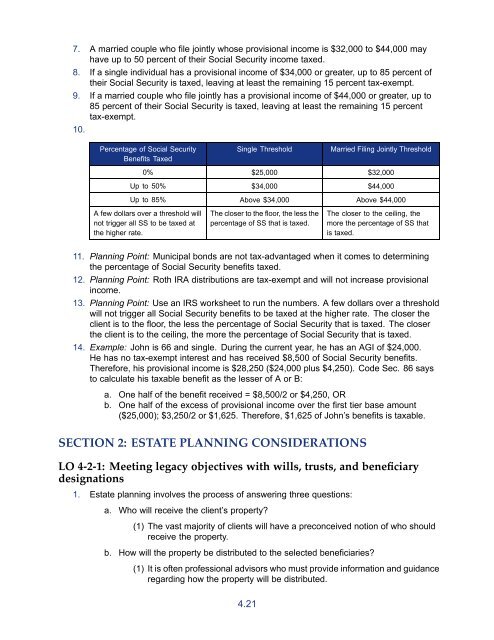
7. A married couple who file jointly whose provisional income is $32,000 to $44,000 mayhave up to 50 percent of their Social Security income taxed.8. If a single individual has a provisional income of $34,000 or greater, up to 85 percent oftheir Social Security is taxed, leaving at least the remaining 15 percent tax-exempt.9. If a married couple who file jointly has a provisional income of $44,000 or greater, up to85 percent of their Social Security is taxed, leaving at least the remaining 15 percenttax-exempt.10.Percentage of Social SecurityBenefits TaxedSingle ThresholdMarried Filing Jointly Threshold0% $25,000 $32,000Up to 50% $34,000 $44,000Up to 85% Above $34,000 Above $44,000A few dollars over a threshold willnot trigger all SS to be taxed atthe higher rate.<strong>The</strong> closer to the floor, the less thepercentage of SS that is taxed.<strong>The</strong> closer to the ceiling, themore the percentage of SS thatis taxed.11. Planning Point: Municipal bonds are not tax-advantaged when it comes to determiningthe percentage of Social Security benefits taxed.12. Planning Point: Roth IRA distributions are tax-exempt and will not increase provisionalincome.13. Planning Point: Use an IRS worksheet to run the numbers. A few dollars over a thresholdwill not trigger all Social Security benefits to be taxed at the higher rate. <strong>The</strong> closer theclient is to the floor, the less the percentage of Social Security that is taxed. <strong>The</strong> closerthe client is to the ceiling, the more the percentage of Social Security that is taxed.14. Example: John is 66 and single. During the current year, he has an AGI of $24,000.He has no tax-exempt interest and has received $8,500 of Social Security benefits.<strong>The</strong>refore, his provisional income is $28,250 ($24,000 plus $4,250). Code Sec. 86 saysto calculate his taxable benefit as the lesser of A or B:a. One half of the benefit received = $8,500/2 or $4,250, ORb. One half of the excess of provisional income over the first tier base amount($25,000); $3,250/2 or $1,625. <strong>The</strong>refore, $1,625 of John’s benefits is taxable.SECTION 2: ESTATE PLANNING CONSIDERATIONSLO 4-2-1: Meeting legacy objectives with wills, trusts, and beneficiarydesignations1. Estate planning involves the process of answering three questions:a. Who will receive the client’s property?(1) <strong>The</strong> vast majority of clients will have a preconceived notion of who shouldreceive the property.b. How will the property be distributed to the selected beneficiaries?(1) It is often professional advisors who must provide information and guidanceregarding how the property will be distributed.4.21