E-Andrew Sindt Creative Component S11.pdf
E-Andrew Sindt Creative Component S11.pdf
E-Andrew Sindt Creative Component S11.pdf
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
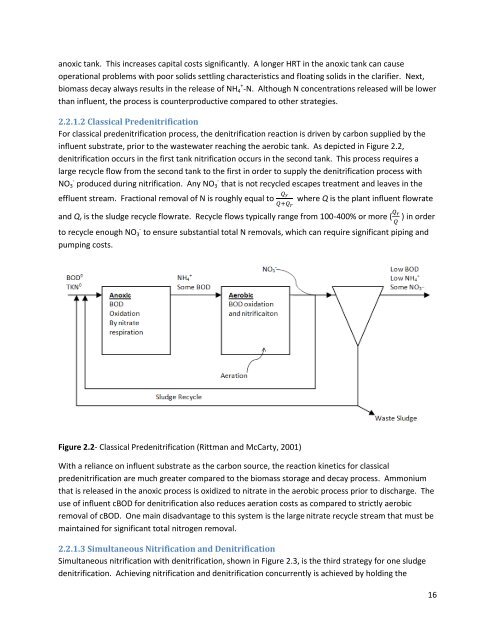
anoxic tank. This increases capital costs significantly. A longer HRT in the anoxic tank can causeoperational problems with poor solids settling characteristics and floating solids in the clarifier. Next,biomass decay always results in the release of NH 4 + -N. Although N concentrations released will be lowerthan influent, the process is counterproductive compared to other strategies.2.2.1.2 Classical PredenitrificationFor classical predenitrification process, the denitrification reaction is driven by carbon supplied by theinfluent substrate, prior to the wastewater reaching the aerobic tank. As depicted in Figure 2.2,denitrification occurs in the first tank nitrification occurs in the second tank. This process requires alarge recycle flow from the second tank to the first in order to supply the denitrification process withNO 3 - produced during nitrification. Any NO 3 - that is not recycled escapes treatment and leaves in theeffluent stream. Fractional removal of N is roughly equal towhere Q is the plant influent flowrateand Q r is the sludge recycle flowrate. Recycle flows typically range from 100-400% or more ( ) in orderto recycle enough NO 3 - to ensure substantial total N removals, which can require significant piping andpumping costs.Figure 2.2- Classical Predenitrification (Rittman and McCarty, 2001)With a reliance on influent substrate as the carbon source, the reaction kinetics for classicalpredenitrification are much greater compared to the biomass storage and decay process. Ammoniumthat is released in the anoxic process is oxidized to nitrate in the aerobic process prior to discharge. Theuse of influent cBOD for denitrification also reduces aeration costs as compared to strictly aerobicremoval of cBOD. One main disadvantage to this system is the large nitrate recycle stream that must bemaintained for significant total nitrogen removal.2.2.1.3 Simultaneous Nitrification and DenitrificationSimultaneous nitrification with denitrification, shown in Figure 2.3, is the third strategy for one sludgedenitrification. Achieving nitrification and denitrification concurrently is achieved by holding the16