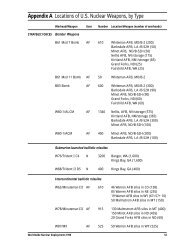
US Nuclear Weapons in Europe - Natural Resources Defense Council
US Nuclear Weapons in Europe - Natural Resources Defense Council
US Nuclear Weapons in Europe - Natural Resources Defense Council
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
U.S. <strong>Nuclear</strong> <strong>Weapons</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>Europe</strong> • Hans M. Kristensen/<strong>Natural</strong> <strong>Resources</strong> <strong>Defense</strong> <strong>Council</strong>, 2005<br />
change to <strong>in</strong>stead reaffirm the importance of widely dispersed forward-deployed nuclear<br />
weapons to <strong>Europe</strong>’s security. In do<strong>in</strong>g so, it rejected the denuclearization of <strong>Europe</strong>.<br />
Accord<strong>in</strong>g to then NATO General Secretary Manfred Woerner:<br />
“<strong>Nuclear</strong> arms cannot be dis<strong>in</strong>vented. We live <strong>in</strong> a world <strong>in</strong> which there<br />
rema<strong>in</strong> many such weapons, and I cannot imag<strong>in</strong>e situations <strong>in</strong> which<br />
<strong>Europe</strong> can be denuclearized.” 80<br />
With a new numerical warhead level<br />
set, NATO moved and consolidated<br />
weapons at the various bases. For<br />
example, the 402 nd Munitions Support<br />
Squadron (MUNSS) at Rim<strong>in</strong>i <strong>in</strong> Italy<br />
was <strong>in</strong>activated on August 1, 1993. 81<br />
But the nuclear weapons were not<br />
returned to the United States but <strong>in</strong>stead<br />
moved to the second Italian base at<br />
Ghedi Torre, <strong>in</strong>creas<strong>in</strong>g the number of<br />
B61 nuclear bombs to 40, stored <strong>in</strong> 11<br />
vaults.<br />
The Rim<strong>in</strong>i <strong>in</strong>activation followed the<br />
transfer of the 401 st Fighter W<strong>in</strong>g from<br />
Torrejon Air Base <strong>in</strong> Spa<strong>in</strong> to Aviano<br />
Air Base <strong>in</strong> May 1992. After arriv<strong>in</strong>g at<br />
the base, the w<strong>in</strong>g began receiv<strong>in</strong>g<br />
nuclear weapons certification tra<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g.<br />
Interest<strong>in</strong>gly, the nuclear mission <strong>in</strong>terfered with the w<strong>in</strong>g’s conventional responsibilities<br />
<strong>in</strong> the Balkans, so <strong>US</strong>AFE asked for a 180-day waiver of the 18-month nuclear surety<br />
<strong>in</strong>spection <strong>in</strong>terval for the 401 st W<strong>in</strong>g. The burden of ma<strong>in</strong>ta<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g nuclear proficiency<br />
was considerable: Between January 1993 and March 1994, the 401 st W<strong>in</strong>g conducted a<br />
total of seven local <strong>Nuclear</strong> Surety Inspection (NSI) exercises. Even amid the urgent nonnuclear<br />
requirements <strong>in</strong> post–Cold War <strong>Europe</strong>, the U.S. Air Force <strong>in</strong>sisted that nuclear<br />
proficiency was so important that it turned down the request and granted only a 60-day<br />
waiver. In the next <strong>in</strong>spection <strong>in</strong> November 1994, however, only facilities would be<br />
<strong>in</strong>spected exclud<strong>in</strong>g all areas perta<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g to aircrew performance and weapons load<strong>in</strong>g. 82<br />
Later, <strong>in</strong> April 1994, the 401 st Fighter W<strong>in</strong>g was redesignated the 31 st Fighter W<strong>in</strong>g.<br />
<strong>Nuclear</strong> Reductions Trigger Security Problems<br />
While NATO issued assurances about the safe storage of its nuclear weapons, the U.S.<br />
Air Force was urgently try<strong>in</strong>g to correct deficiencies. In October 1992, General Merrill<br />
McPeak, the U.S. Air Force chief of staff, warned about the worsen<strong>in</strong>g practices<br />
regard<strong>in</strong>g the safe handl<strong>in</strong>g and storage of nuclear weapons and directed commanders at<br />
every level to review surety programs to ensure that performance standards were<br />
rigorously ma<strong>in</strong>ta<strong>in</strong>ed.<br />
34<br />
Figure 12:<br />
Italian F-104 at Rim<strong>in</strong>i Air Base<br />
Italian F-104 fighter-bomber of the 6 th Stormo W<strong>in</strong>g at<br />
Rim<strong>in</strong>i Air Base. When the United States withdrew its<br />
Munitions Support Squadron <strong>in</strong> 1993, the nuclear<br />
weapons were moved to Ghedi Torre Air Base.<br />
Source: Italian Air Force.