The Extent, Nature and Effectiveness of Planned Approaches in ...
The Extent, Nature and Effectiveness of Planned Approaches in ...
The Extent, Nature and Effectiveness of Planned Approaches in ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
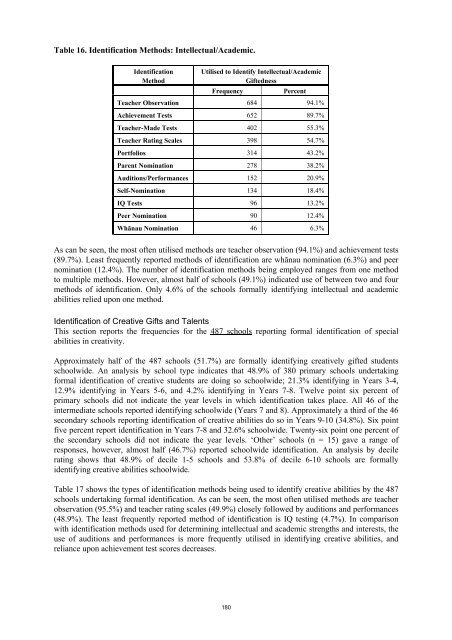
Table 16. Identification Methods: Intellectual/Academic.IdentificationMethodUtilised to Identify Intellectual/AcademicGiftednessFrequencyPercentTeacher Observation 684 94.1%Achievement Tests 652 89.7%Teacher-Made Tests 402 55.3%Teacher Rat<strong>in</strong>g Scales 398 54.7%Portfolios 314 43.2%Parent Nom<strong>in</strong>ation 278 38.2%Auditions/Performances 152 20.9%Self-Nom<strong>in</strong>ation 134 18.4%IQ Tests 96 13.2%Peer Nom<strong>in</strong>ation 90 12.4%Whänau Nom<strong>in</strong>ation 46 6.3%As can be seen, the most <strong>of</strong>ten utilised methods are teacher observation (94.1%) <strong>and</strong> achievement tests(89.7%). Least frequently reported methods <strong>of</strong> identification are whänau nom<strong>in</strong>ation (6.3%) <strong>and</strong> peernom<strong>in</strong>ation (12.4%). <strong>The</strong> number <strong>of</strong> identification methods be<strong>in</strong>g employed ranges from one methodto multiple methods. However, almost half <strong>of</strong> schools (49.1%) <strong>in</strong>dicated use <strong>of</strong> between two <strong>and</strong> fourmethods <strong>of</strong> identification. Only 4.6% <strong>of</strong> the schools formally identify<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>tellectual <strong>and</strong> academicabilities relied upon one method.Identification <strong>of</strong> Creative Gifts <strong>and</strong> TalentsThis section reports the frequencies for the 487 schools report<strong>in</strong>g formal identification <strong>of</strong> specialabilities <strong>in</strong> creativity.Approximately half <strong>of</strong> the 487 schools (51.7%) are formally identify<strong>in</strong>g creatively gifted studentsschoolwide. An analysis by school type <strong>in</strong>dicates that 48.9% <strong>of</strong> 380 primary schools undertak<strong>in</strong>gformal identification <strong>of</strong> creative students are do<strong>in</strong>g so schoolwide; 21.3% identify<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> Years 3-4,12.9% identify<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> Years 5-6, <strong>and</strong> 4.2% identify<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong> Years 7-8. Twelve po<strong>in</strong>t six percent <strong>of</strong>primary schools did not <strong>in</strong>dicate the year levels <strong>in</strong> which identification takes place. All 46 <strong>of</strong> the<strong>in</strong>termediate schools reported identify<strong>in</strong>g schoolwide (Years 7 <strong>and</strong> 8). Approximately a third <strong>of</strong> the 46secondary schools report<strong>in</strong>g identification <strong>of</strong> creative abilities do so <strong>in</strong> Years 9-10 (34.8%). Six po<strong>in</strong>tfive percent report identification <strong>in</strong> Years 7-8 <strong>and</strong> 32.6% schoolwide. Twenty-six po<strong>in</strong>t one percent <strong>of</strong>the secondary schools did not <strong>in</strong>dicate the year levels. ‘Other’ schools (n = 15) gave a range <strong>of</strong>responses, however, almost half (46.7%) reported schoolwide identification. An analysis by decilerat<strong>in</strong>g shows that 48.9% <strong>of</strong> decile 1-5 schools <strong>and</strong> 53.8% <strong>of</strong> decile 6-10 schools are formallyidentify<strong>in</strong>g creative abilities schoolwide.Table 17 shows the types <strong>of</strong> identification methods be<strong>in</strong>g used to identify creative abilities by the 487schools undertak<strong>in</strong>g formal identification. As can be seen, the most <strong>of</strong>ten utilised methods are teacherobservation (95.5%) <strong>and</strong> teacher rat<strong>in</strong>g scales (49.9%) closely followed by auditions <strong>and</strong> performances(48.9%). <strong>The</strong> least frequently reported method <strong>of</strong> identification is IQ test<strong>in</strong>g (4.7%). In comparisonwith identification methods used for determ<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>tellectual <strong>and</strong> academic strengths <strong>and</strong> <strong>in</strong>terests, theuse <strong>of</strong> auditions <strong>and</strong> performances is more frequently utilised <strong>in</strong> identify<strong>in</strong>g creative abilities, <strong>and</strong>reliance upon achievement test scores decreases.180