Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
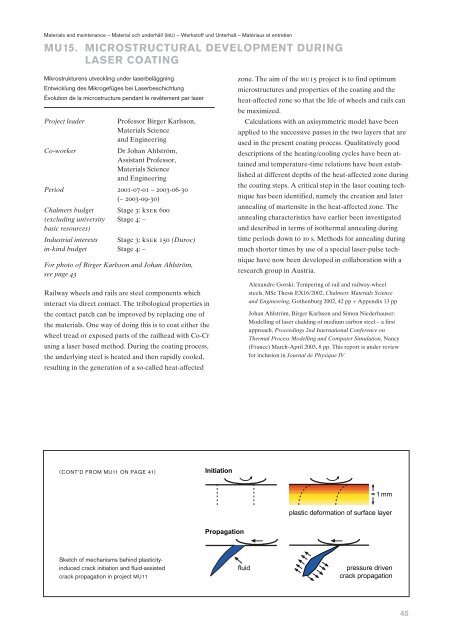
Materials and maintenance – Material och underhåll (MU) – Werkstoff und Unterhalt – Matériaux et entretienMU15. MICROSTRUCTURAL DEVELOPMENT DURINGLASER COATINGMikrostrukturens utveckling under laserbeläggningEntwicklung des Mikrogefüges bei LaserbeschichtungÉvolution de la microstructure pendant le revêtement par laserProject leaderProfessor Birger Karlsson,Materials Scienceand EngineeringCo-workerDr Johan Ahlström,Assistant Professor,Materials Scienceand EngineeringPeriod 2001-07-01 – <strong>2003</strong>-06-30(– <strong>2003</strong>-09-30)Chalmers budget Stage 3: ksek 600(excluding university Stage 4: –basic resources)Industrial interests Stage 3: ksek 150 (Duroc)in-kind budget Stage 4: –For photo of Birger Karlsson and Johan Ahlström,see page 43Railway wheels and rails are steel components whichinteract via direct contact. The tribological properties inthe contact patch can be improved by replacing one ofthe materials. One way of doing this is to coat either thewheel tread or exposed parts of the railhead with Co-Crusing a laser based method. During the coating process,the underlying steel is heated and then rapidly cooled,resulting in the generation of a so-called heat-affectedzone. The aim of the mu15 project is to find optimummicrostructures and properties of the coating and theheat-affected zone so that the life of wheels and rails canbe maximized.Calculations with an axisymmetric model have beenapplied to the successive passes in the two layers that areused in the present coating process. Qualitatively gooddescriptions of the heating/cooling cycles have been attainedand temperature-time relations have been establishedat different depths of the heat-affected zone duringthe coating steps. A critical step in the laser coating techniquehas been identified, namely the creation and laterannealing of martensite in the heat-affected zone. Theannealing characteristics have earlier been investigatedand described in terms of isothermal annealing duringtime periods down to 10 s. Methods for annealing duringmuch shorter times by use of a special laser-pulse techniquehave now been developed in collaboration with aresearch group in Austria.Alexandre Gorski: Tempering of rail and railway-wheelsteels, MSc Thesis EX16/2002, Chalmers Materials Scienceand Engineering, Gothenburg 2002, 42 pp + Appendix 13 ppJohan Ahlström, Birger Karlsson and Simon Niederhauser:Modelling of laser cladding of medium carbon steel – a firstapproach, Proceedings 2nd International Conference onThermal Process Modelling and Computer Simulation, Nancy(France) March-April <strong>2003</strong>, 8 pp. This report is under reviewfor inclusion in Journal de Physique IV(CONT’D FROM MU11 ON PAGE 41)Sketch of mechanisms behind plasticityinducedcrack initiation and fluid-assistedcrack propagation in project MU1145