Science Literacy 2006 school release materials - NAP
Science Literacy 2006 school release materials - NAP
Science Literacy 2006 school release materials - NAP
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
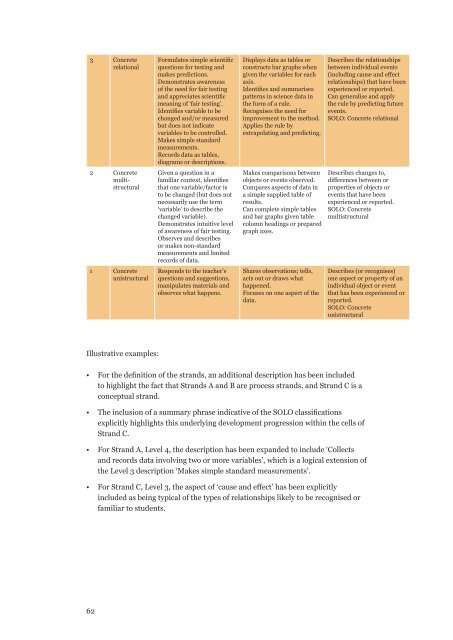
3 ConcreterelationalFormulates simple scientificquestions for testing andmakes predictions.Demonstrates awarenessof the need for fair testingand appreciates scientificmeaning of ‘fair testing’.Identifies variable to bechanged and/or measuredbut does not indicatevariables to be controlled.Makes simple standardmeasurements.Records data as tables,diagrams or descriptions.Given a question in afamiliar context, identifiesthat one variable/factor isto be changed (but does notnecessarily use the term‘variable’ to describe thechanged variable).Demonstrates intuitive levelof awareness of fair testing.Observes and describesor makes non-standardmeasurements and limitedrecords of data.Responds to the teacher’squestions and suggestions,manipulates <strong>materials</strong> andobserves what happens.Displays data as tables orconstructs bar graphs whengiven the variables for eachaxis.Identifies and summarisespatterns in science data inthe form of a rule.Recognises the need forimprovement to the method.Applies the rule byextrapolating and predicting.Describes the relationshipsbetween individual events(including cause and effectrelationships) that have beenexperienced or reported.Can generalise and applythe rule by predicting futureevents.SOLO: Concrete relational2 ConcretemultistructuralMakes comparisons betweenobjects or events observed.Compares aspects of data ina simple supplied table ofresults.Can complete simple tablesand bar graphs given tablecolumn headings or preparedgraph axes.Describes changes to,differences between orproperties of objects orevents that have beenexperienced or reported.SOLO: Concretemultistructural1 ConcreteunistructuralShares observations; tells,acts out or draws whathappened.Focuses on one aspect of thedata.Describes (or recognises)one aspect or property of anindividual object or eventthat has been experienced orreported.SOLO: ConcreteunistructuralIllustrative examples:• For the definition of the strands, an additional description has been includedto highlight the fact that Strands A and B are process strands, and Strand C is aconceptual strand.• The inclusion of a summary phrase indicative of the SOLO classificationsexplicitly highlights this underlying development progression within the cells ofStrand C.• For Strand A, Level 4, the description has been expanded to include ‘Collectsand records data involving two or more variables’, which is a logical extension ofthe Level 3 description ‘Makes simple standard measurements’.• For Strand C, Level 3, the aspect of ‘cause and effect’ has been explicitlyincluded as being typical of the types of relationships likely to be recognised orfamiliar to students.62