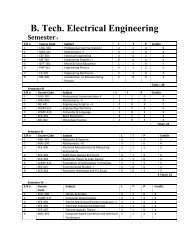
B. Tech. Production & Industrial Engineering - Shiats.edu.in
B. Tech. Production & Industrial Engineering - Shiats.edu.in
B. Tech. Production & Industrial Engineering - Shiats.edu.in
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
2. Conventional energy resources and their utilization; thermal, nuclear and hydro-electric power plants, useof diesel eng<strong>in</strong>es and gas turb<strong>in</strong>es for power generation. Comb<strong>in</strong>ed cycles for efficient power generation.3. Non-conventional energy resources and their utilization: solar , geothermal, w<strong>in</strong>d, wave, biomass andocean-thermal energy conversion and their limitations. Energy storage techniques.4. Energy conservation: energy audit<strong>in</strong>g, process energy and gross energy requirement, energy recovery:<strong>in</strong>sulation, heat recovery heat exchangers, heat-pumps, comb<strong>in</strong>ed heat and power plants (cogeneration),efficient light<strong>in</strong>g and energy conservation <strong>in</strong> build<strong>in</strong>gs.5. Environmental aspects of energy resource utilization: combustion generated air pollution, global warm<strong>in</strong>g,acid ra<strong>in</strong>, fly ash disposal, radioactive pollution and nuclear waste disposal.REFERENCES:(A) ‘Energy for a susta<strong>in</strong>able world’ by Goldemberg et al. Wiley Eastern Limited. 1988.(B) ‘Power Plant <strong>Tech</strong>nology’ by M.M.El-Wakil. McGraw-Hill. 1984.(C) ‘Manag<strong>in</strong>g energy <strong>in</strong> commerce and <strong>in</strong>dustry’ by Gordon A Payne. Butterworths, 1984.FLUID MACHINERYCourse Code (CE-576) Credit 4(2-1-1)1. Jet Theory: Introduction to hydro dynamic thrust of a jet on a fixed and mov<strong>in</strong> g suface (flat, curve),effect of <strong>in</strong>cl<strong>in</strong>ation of jet with the surface.2. Hydraulic Turb<strong>in</strong>es:Pelton Wheel, Francis and Kaplan turb<strong>in</strong>es classification of turb<strong>in</strong>es, work<strong>in</strong>gpr<strong>in</strong>ciples, work done, efficiency, draft tube theory, cavitations <strong>in</strong> turb<strong>in</strong>es, performance, test<strong>in</strong>g ofturb<strong>in</strong>es, model test<strong>in</strong>g, selection of a turb<strong>in</strong>es, stability of a turb<strong>in</strong>e (Static & dynamic),performance curves, constant efficeiency curves, Muschel curves, govern<strong>in</strong>g of turb<strong>in</strong>es, specificspeeds.3. Pumps:Centrifugal pumps, classifications, work done by impeller, efficiencies of centrifugal pumps,prim<strong>in</strong>g, specific speed, cavitations and separation, surg<strong>in</strong>g, check<strong>in</strong>g, model test<strong>in</strong>g, performancecharacteristics, reciprocat<strong>in</strong>g pumps, classification, work done (s<strong>in</strong>gle and double act<strong>in</strong>g), slip,variation of pressure, work saved by fitt<strong>in</strong>g air vessels, multicyl<strong>in</strong>der pumps, comparison ofcentrifugal and reciprocat<strong>in</strong>g pumps, design aspects.4. Hydraulic mach<strong>in</strong>es:Hydraulic systems, hydraulic press, cranks, jacks, accumulator, <strong>in</strong>tensifier, ram,fluid coupl<strong>in</strong>g, fluid torque converter, water hammer, jet pumps and air lift pumps.5. Gas Turb<strong>in</strong>es and Jet propulsion:Introduction, work<strong>in</strong>g cycle, different types of gas turb<strong>in</strong>es, jetpropulsion, thrust power and propulsion efficiency.References:1. Hydraulic Mach<strong>in</strong>es Dr. J. Lal2. Heat Engg. V.P. Vasandani & D.S. Kumar3. Hydraulic mach<strong>in</strong>es V.P. Vasandani4. Fluid mach<strong>in</strong>ery- K.R. Arora5. Fluid mach<strong>in</strong>ery – P.N. Modi & S.M. Seth.FLUID MACHINERY LAB