DOTcvpSB: a Matlab Toolbox for Dynamic Optimization in Systems ...
DOTcvpSB: a Matlab Toolbox for Dynamic Optimization in Systems ...
DOTcvpSB: a Matlab Toolbox for Dynamic Optimization in Systems ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
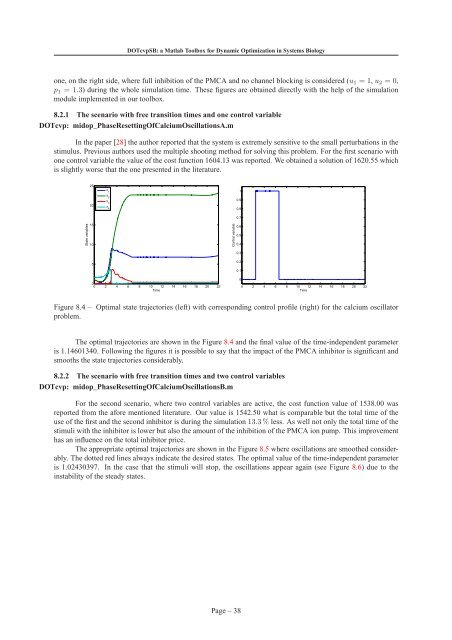
<strong>DOTcvpSB</strong>: a <strong>Matlab</strong> <strong>Toolbox</strong> <strong>for</strong> <strong>Dynamic</strong> <strong>Optimization</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>Systems</strong> Biologyone, on the right side, where full <strong>in</strong>hibition of the PMCA and no channel block<strong>in</strong>g is considered (u 1 = 1, u 2 = 0,p 1 = 1.3) dur<strong>in</strong>g the whole simulation time. These figures are obta<strong>in</strong>ed directly with the help of the simulationmodule implemented <strong>in</strong> our toolbox.8.2.1 The scenario with free transition times and one control variableDOTcvp: midop_PhaseResett<strong>in</strong>gOfCalciumOscillationsA.mIn the paper [28] the author reported that the system is extremely sensitive to the small perturbations <strong>in</strong> thestimulus. Previous authors used the multiple shoot<strong>in</strong>g method <strong>for</strong> solv<strong>in</strong>g this problem. For the first scenario withone control variable the value of the cost function 1604.13 was reported. We obta<strong>in</strong>ed a solution of 1620.55 whichis slightly worse that the one presented <strong>in</strong> the literature.2520x 1x 2x 310.90.8State variables1510x 40 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 220.7Control variable0.60.50.40.350.20.100 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22Time0TimeFigure 8.4 – Optimal state trajectories (left) with correspond<strong>in</strong>g control profile (right) <strong>for</strong> the calcium oscillatorproblem.The optimal trajectories are shown <strong>in</strong> the Figure 8.4 and the f<strong>in</strong>al value of the time-<strong>in</strong>dependent parameteris 1.14601340. Follow<strong>in</strong>g the figures it is possible to say that the impact of the PMCA <strong>in</strong>hibitor is significant andsmooths the state trajectories considerably.8.2.2 The scenario with free transition times and two control variablesDOTcvp: midop_PhaseResett<strong>in</strong>gOfCalciumOscillationsB.mFor the second scenario, where two control variables are active, the cost function value of 1538.00 wasreported from the a<strong>for</strong>e mentioned literature. Our value is 1542.50 what is comparable but the total time of theuse of the first and the second <strong>in</strong>hibitor is dur<strong>in</strong>g the simulation 13.3% less. As well not only the total time of thestimuli with the <strong>in</strong>hibitor is lower but also the amount of the <strong>in</strong>hibition of the PMCA ion pump. This improvementhas an <strong>in</strong>fluence on the total <strong>in</strong>hibitor price.The appropriate optimal trajectories are shown <strong>in</strong> the Figure 8.5 where oscillations are smoothed considerably.The dotted red l<strong>in</strong>es always <strong>in</strong>dicate the desired states. The optimal value of the time-<strong>in</strong>dependent parameteris 1.02430397. In the case that the stimuli will stop, the oscillations appear aga<strong>in</strong> (see Figure 8.6) due to the<strong>in</strong>stability of the steady states.Page – 38