Statistical models of elasticity in main chain and smectic liquid ...
Statistical models of elasticity in main chain and smectic liquid ...
Statistical models of elasticity in main chain and smectic liquid ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
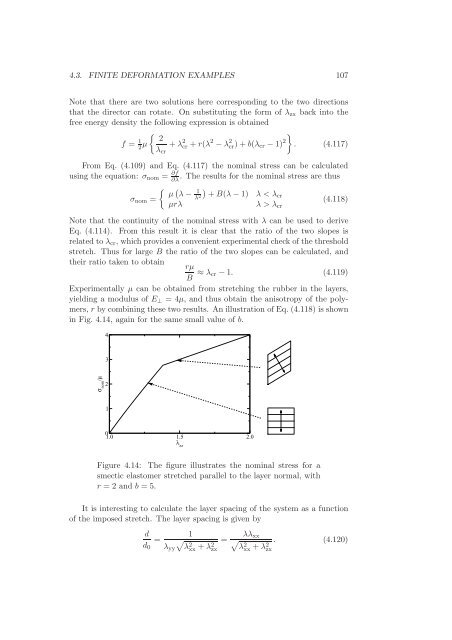
4.3. FINITE DEFORMATION EXAMPLES 107Note that there are two solutions here correspond<strong>in</strong>g to the two directionsthat the director can rotate. On substitut<strong>in</strong>g the form <strong>of</strong> λ zx back <strong>in</strong>to thefree energy density the follow<strong>in</strong>g expression is obta<strong>in</strong>ed{ }2f = 1 2 µ +λ 2 cr +r(λ 2 −λ 2λcr)+b(λ cr −1) 2 . (4.117)crFrom Eq. (4.109) <strong>and</strong> Eq. (4.117) the nom<strong>in</strong>al stress can be calculatedus<strong>in</strong>g the equation: σ nom = ∂f∂λ. The results for the nom<strong>in</strong>al stress are thus{ ( )µ λ−1σ nom = λ +B(λ−1) λ < 2 λcr(4.118)µrλ λ > λ crNote that the cont<strong>in</strong>uity <strong>of</strong> the nom<strong>in</strong>al stress with λ can be used to deriveEq. (4.114). From this result it is clear that the ratio <strong>of</strong> the two slopes isrelated toλ cr , whichprovidesaconvenient experimental check <strong>of</strong> thethresholdstretch. Thus for large B the ratio <strong>of</strong> the two slopes can be calculated, <strong>and</strong>their ratio taken to obta<strong>in</strong>rµB ≈ λ cr −1. (4.119)Experimentally µ can be obta<strong>in</strong>ed from stretch<strong>in</strong>g the rubber <strong>in</strong> the layers,yield<strong>in</strong>g a modulus <strong>of</strong> E ⊥ = 4µ, <strong>and</strong> thus obta<strong>in</strong> the anisotropy <strong>of</strong> the polymers,r by comb<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g these two results. An illustration <strong>of</strong> Eq. (4.118) is shown<strong>in</strong> Fig. 4.14, aga<strong>in</strong> for the same small value <strong>of</strong> b.43σ nom/µ2101.0 1.5 2.0λ zzFigure 4.14: The figure illustrates the nom<strong>in</strong>al stress for a<strong>smectic</strong> elastomer stretched parallel to the layer normal, withr = 2 <strong>and</strong> b = 5.It is <strong>in</strong>terest<strong>in</strong>g to calculate the layer spac<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> the system as a function<strong>of</strong> the imposed stretch. The layer spac<strong>in</strong>g is given bydd 0=1λ yy√λ 2 xx +λ 2 zx=λλ√ xx. (4.120)λ 2 xx +λ 2 zx