Statistical models of elasticity in main chain and smectic liquid ...
Statistical models of elasticity in main chain and smectic liquid ...
Statistical models of elasticity in main chain and smectic liquid ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
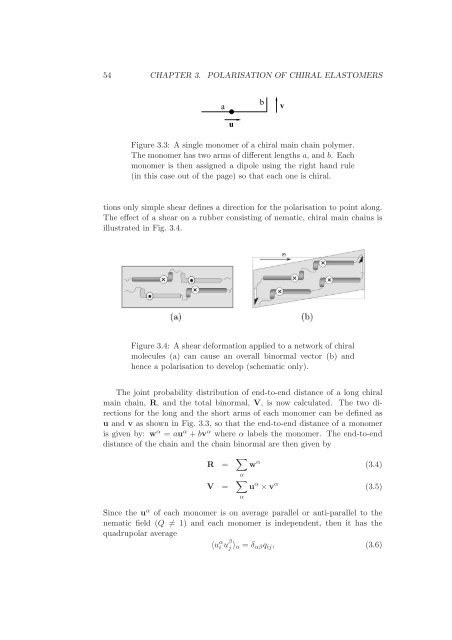
54 CHAPTER 3. POLARISATION OF CHIRAL ELASTOMERSabvuFigure 3.3: A s<strong>in</strong>gle monomer <strong>of</strong> a chiral ma<strong>in</strong> cha<strong>in</strong> polymer.The monomer has two arms <strong>of</strong> different lengths a, <strong>and</strong> b. Eachmonomer is then assigned a dipole us<strong>in</strong>g the right h<strong>and</strong> rule(<strong>in</strong> this case out <strong>of</strong> the page) so that each one is chiral.tions only simple shear def<strong>in</strong>es a direction for the polarisation to po<strong>in</strong>t along.The effect <strong>of</strong> a shear on a rubber consist<strong>in</strong>g <strong>of</strong> nematic, chiral ma<strong>in</strong> cha<strong>in</strong>s isillustrated <strong>in</strong> Fig. 3.4.Figure 3.4: A shear deformation applied to a network <strong>of</strong> chiralmolecules (a) can cause an overall b<strong>in</strong>ormal vector (b) <strong>and</strong>hence a polarisation to develop (schematic only).The jo<strong>in</strong>t probability distribution <strong>of</strong> end-to-end distance <strong>of</strong> a long chiralma<strong>in</strong> cha<strong>in</strong>, R, <strong>and</strong> the total b<strong>in</strong>ormal, V, is now calculated. The two directionsfor the long <strong>and</strong> the short arms <strong>of</strong> each monomer can be def<strong>in</strong>ed asu <strong>and</strong> v as shown <strong>in</strong> Fig. 3.3, so that the end-to-end distance <strong>of</strong> a monomeris given by: w α = au α +bv α where α labels the monomer. The end-to-enddistance <strong>of</strong> the cha<strong>in</strong> <strong>and</strong> the cha<strong>in</strong> b<strong>in</strong>ormal are then given byR = ∑ αV = ∑ αw α (3.4)u α ×v α (3.5)S<strong>in</strong>ce the u α <strong>of</strong> each monomer is on average parallel or anti-parallel to thenematic field (Q ≠ 1) <strong>and</strong> each monomer is <strong>in</strong>dependent, then it has thequadrupolar average〈u α i u β j 〉 u = δ αβ q ij , (3.6)