- Page 1:
IE-Commerce
- Page 4 and 5:
Published by In-TehIn-TehOlajnica 1
- Page 7 and 8:
VIIWe wish to thank the reviewers o
- Page 9:
IXContentsPrefaceV1. A Conceptual F
- Page 13 and 14:
A Conceptual Framework and an Exten
- Page 15 and 16:
A Conceptual Framework and an Exten
- Page 17 and 18:
A Conceptual Framework and an Exten
- Page 19:
A Conceptual Framework and an Exten
- Page 22 and 23:
12E-CommerceThe Application Layer c
- Page 24 and 25:
14E-CommerceService description. Th
- Page 26 and 27:
16E-Commerceunderstanding about the
- Page 28 and 29:
18E-CommerceThis chapter contribute
- Page 30 and 31:
20E-CommercePorter M (2001). Strate
- Page 32 and 33:
22E-CommerceTo evaluate the e-comme
- Page 34 and 35:
24E-CommerceAa 2a a4m1 m 2 m 3m (
- Page 36 and 37:
26E-CommerceV v ij , i 1,2,...,
- Page 38 and 39:
28E-CommerceIndexFuzzy numberAltern
- Page 40 and 41:
30E-CommerceS. Mabuchi (1988). An a
- Page 42 and 43:
32E-Commercetechnology implementati
- Page 44 and 45:
34E-Commerceapplied to study an ind
- Page 46 and 47:
36E-Commerce PEOU of the public sec
- Page 48 and 49:
38E-CommerceNITC (National Informat
- Page 50 and 51:
40E-Commercewill describe the mecha
- Page 52 and 53:
42E-Commerce(2) The manner of commu
- Page 54 and 55:
44E-CommerceIf ADS is employed in a
- Page 56 and 57:
46E-Commerce4.2 Case studyThe detai
- Page 58 and 59:
48E-CommerceAs a high-speed develop
- Page 60 and 61:
50E-Commerce4.3.2 The architecture
- Page 62 and 63:
52E-Commerceone conclusion is that
- Page 64 and 65:
54E-Commerce
- Page 66 and 67:
56E-Commerceorganizations expose de
- Page 68 and 69:
58E-Commercerules. Such adapters ne
- Page 70 and 71:
60E-CommerceThe third level of inve
- Page 72 and 73:
62E-Commercecommon “language” h
- Page 74 and 75:
64E-Commercewell described in (Mül
- Page 76 and 77:
66E-Commerce3.3 Organizational Comp
- Page 78 and 79:
68E-Commercethe interaction of defi
- Page 80 and 81:
70E-CommerceAs a first step towards
- Page 82 and 83:
72E-Commerce5. Conclusion and Outlo
- Page 84 and 85:
74E-CommerceSchmid, B. F., Schroth,
- Page 86 and 87:
76E-CommerceThe following section p
- Page 88 and 89:
78E-Commerce(a) G cooc(b) G overlap
- Page 90 and 91:
80E-CommerceBetweenness centrality
- Page 92 and 93:
82E-Commerce4.1.1 Generating Networ
- Page 94 and 95:
84E-CommerceThe resultant value som
- Page 96 and 97:
86E-CommerceG shareholdershareholdi
- Page 98 and 99:
88E-Commerce17: Murata Noda Screen
- Page 100 and 101:
90E-Commerceand testing data in the
- Page 102:
92E-Commerce(c) Centrality-based ra
- Page 105 and 106:
Ranking Companies Based on Multiple
- Page 107 and 108:
Ranking Companies Based on Multiple
- Page 109 and 110:
Considering Culture in Designing We
- Page 111 and 112:
Considering Culture in Designing We
- Page 113 and 114:
Considering Culture in Designing We
- Page 115 and 116:
Considering Culture in Designing We
- Page 117 and 118:
Considering Culture in Designing We
- Page 119 and 120:
Considering Culture in Designing We
- Page 121 and 122:
Considering Culture in Designing We
- Page 123 and 124:
Consumer Responses to Colors of E-C
- Page 125 and 126:
Consumer Responses to Colors of E-C
- Page 127 and 128:
Consumer Responses to Colors of E-C
- Page 130 and 131:
120E-Commerce4. Research methodOur
- Page 132 and 133:
122E-Commerceavailable information
- Page 134 and 135:
124E-CommerceNewsvine Green. Starti
- Page 136 and 137:
126E-CommerceProcedureRespondents w
- Page 138 and 139:
128E-Commerce6. Data analysis and r
- Page 140 and 141:
130E-CommerceHue 1Newsvine Green (d
- Page 142 and 143:
132E-CommerceEffects of graphic cha
- Page 144 and 145:
134E-Commercethe consumer retains w
- Page 146 and 147:
136E-Commercemaintain, load more ra
- Page 148 and 149:
138E-CommerceBellizzi J. A. & Hite
- Page 150 and 151:
140E-CommerceHill A. & Scharff L. V
- Page 152 and 153:
142E-CommerceSpool J. M., Scanlon T
- Page 154 and 155:
144E-CommerceConsequently, we concl
- Page 156 and 157:
146E-CommerceDimensionsSystems qual
- Page 158 and 159:
148E-Commercefunction deployment (Q
- Page 160 and 161:
150E-CommerceUseful help serviceEle
- Page 162 and 163:
152E-Commerceplanning, enacting and
- Page 164 and 165:
154E-Commercecomplete and measurabl
- Page 166 and 167:
156E-Commerce There is "About us" s
- Page 168 and 169:
158E-Commerce Validation testing -
- Page 170 and 171:
160E-Commercefor the Websites (Lohs
- Page 172 and 173:
162E-CommerceSinnappan S., Carlson
- Page 174 and 175:
164E-Commercerecommendations of a t
- Page 176 and 177:
166E-Commerce3.1 Neighborhood Based
- Page 178 and 179:
168E-Commerce3.3 Significance Weigh
- Page 180 and 181:
170E-Commerce , u1 0,fR5fuR1 u2else
- Page 182 and 183:
172E-CommerceFigure 6 shows the ste
- Page 184 and 185:
174E-CommerceMAE0.750.740.730.720.7
- Page 187 and 188:
Improving performance in recommende
- Page 189 and 190:
Improving performance in recommende
- Page 191 and 192:
Improving performance in recommende
- Page 193 and 194:
Attacks on Two Buyer-Seller Waterma
- Page 195 and 196:
Attacks on Two Buyer-Seller Waterma
- Page 197 and 198:
Attacks on Two Buyer-Seller Waterma
- Page 199 and 200: Attacks on Two Buyer-Seller Waterma
- Page 201 and 202: Attacks on Two Buyer-Seller Waterma
- Page 203 and 204: Attacks on Two Buyer-Seller Waterma
- Page 205 and 206: Attacks on Two Buyer-Seller Waterma
- Page 207 and 208: Attacks on Two Buyer-Seller Waterma
- Page 209 and 210: Attacks on Two Buyer-Seller Waterma
- Page 211 and 212: Attacks on Two Buyer-Seller Waterma
- Page 213 and 214: Electronic Commerce Readinessin Dev
- Page 215 and 216: Electronic Commerce Readinessin Dev
- Page 217 and 218: Electronic Commerce Readinessin Dev
- Page 219 and 220: Electronic Commerce Readinessin Dev
- Page 221 and 222: Electronic Commerce Readinessin Dev
- Page 223 and 224: Electronic Commerce Readinessin Dev
- Page 225 and 226: Electronic Commerce Readinessin Dev
- Page 227 and 228: Electronic Commerce Readinessin Dev
- Page 229 and 230: Electronic Commerce Readinessin Dev
- Page 231 and 232: Electronic Commerce Readinessin Dev
- Page 233 and 234: Electronic Commerce Readinessin Dev
- Page 235 and 236: Electronic Commerce Readinessin Dev
- Page 237 and 238: Electronic Commerce Readinessin Dev
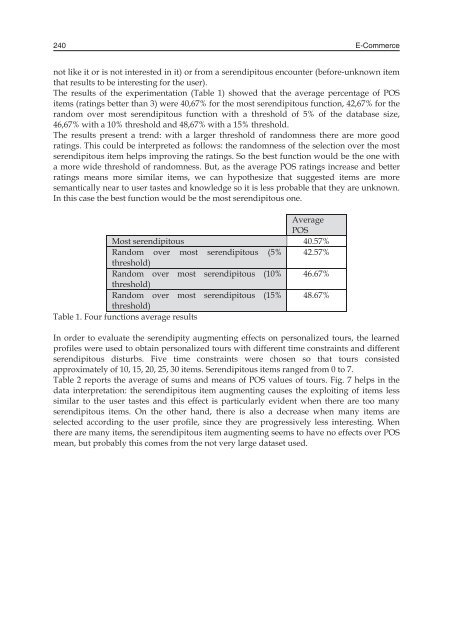
- Page 239 and 240: Can a Recommender System induce ser
- Page 241 and 242: Can a Recommender System induce ser
- Page 243 and 244: Can a Recommender System induce ser
- Page 245 and 246: Can a Recommender System induce ser
- Page 247 and 248: Can a Recommender System induce ser
- Page 249: Can a Recommender System induce ser
- Page 253 and 254: Can a Recommender System induce ser
- Page 255 and 256: Can a Recommender System induce ser
- Page 257 and 258: A Mobile Commerce Model for Automob
- Page 259 and 260: A Mobile Commerce Model for Automob
- Page 261 and 262: A Mobile Commerce Model for Automob
- Page 263 and 264: A Mobile Commerce Model for Automob
- Page 265 and 266: A Mobile Commerce Model for Automob
- Page 267 and 268: A Mobile Commerce Model for Automob
- Page 269 and 270: A Mobile Commerce Model for Automob
- Page 271 and 272: A Mobile Commerce Model for Automob
- Page 273 and 274: A Mobile Commerce Model for Automob
- Page 275 and 276: A Mobile Commerce Model for Automob
- Page 277 and 278: The Automatic Attaching Function Ba
- Page 279 and 280: The Automatic Attaching Function Ba
- Page 281 and 282: The Automatic Attaching Function Ba
- Page 283 and 284: The Automatic Attaching Function Ba
- Page 285 and 286: The Automatic Attaching Function Ba
- Page 287 and 288: The Automatic Attaching Function Ba
- Page 289 and 290: The Automatic Attaching Function Ba
- Page 291 and 292: The Automatic Attaching Function Ba
- Page 293 and 294: The Automatic Attaching Function Ba










![focuspdca.ppt [Compatibility Mode]](https://img.yumpu.com/22859457/1/190x146/focuspdcappt-compatibility-mode.jpg?quality=85)


