Treatment of pulmonary hypertension in congenital heart disease
Treatment of pulmonary hypertension in congenital heart disease
Treatment of pulmonary hypertension in congenital heart disease
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
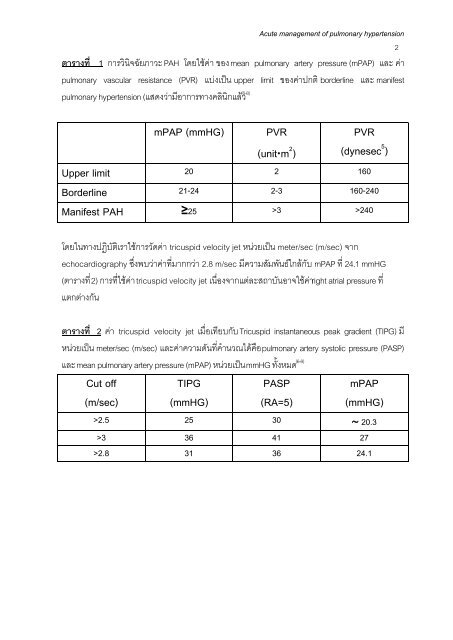
Acute management <strong>of</strong> <strong>pulmonary</strong> <strong>hypertension</strong>2ตารางที่ 1 การวินิจฉัยภาวะ PAH โดยใชคา ของ mean <strong>pulmonary</strong> artery pressure (mPAP) และ คา<strong>pulmonary</strong> vascular resistance (PVR) แบงเปน upper limit ของคาปกติ borderl<strong>in</strong>e และ manifest<strong>pulmonary</strong> <strong>hypertension</strong> (แสดงวามีอาการทางคลินิกแลว (6-8)mPAP (mmHG) PVR(unit⋅m 2 )PVR(dynesecUpper limit 20 2 160Borderl<strong>in</strong>e 21-24 2-3 160-240Manifest PAH ≥25 >3 >240โดยในทางปฏิบัติเราใชการวัดคา tricuspid velocity jet หนวยเปน meter/sec (m/sec) จากechocardiography ซึ่งพบวาคาที่มากกวา 2.8 m/sec มีความสัมพันธใกลกับ mPAP ที่ 24.1 mmHG(ตารางที่ 2) การที่ใชคา tricuspid velocity jet เนื่องจากแตละสถาบันอาจใชคา right atrial pressure ที่แตกตางกันตารางที่ 2 คา tricuspid velocity jet เมื่อเทียบกับ Tricuspid <strong>in</strong>stantaneous peak gradient (TIPG) มีหนวยเปน meter/sec (m/sec) และคาความดันที่คํานวณไดคือ <strong>pulmonary</strong> artery systolic pressure (PASP)(6-8)และ mean <strong>pulmonary</strong> artery pressure (mPAP) หนวยเปน mmHG ทั้งหมดCut <strong>of</strong>f(m/sec)TIPG(mmHG)PASP(RA=5)5 )mPAP(mmHG)>2.5 25 30 ∼ 20.3>3 36 41 27>2.8 31 36 24.1