Treatment of pulmonary hypertension in congenital heart disease
Treatment of pulmonary hypertension in congenital heart disease
Treatment of pulmonary hypertension in congenital heart disease
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
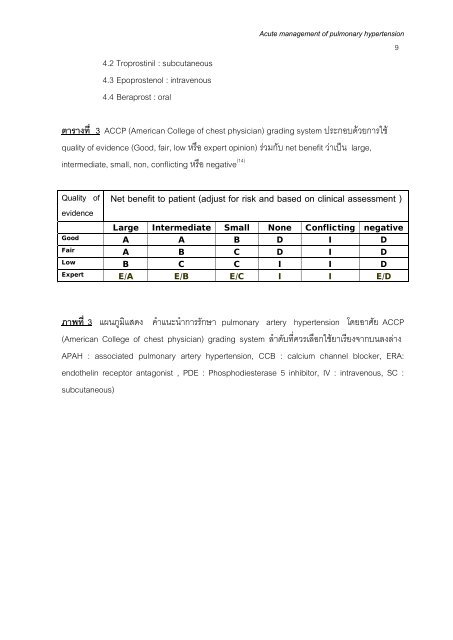
4.2 Troprost<strong>in</strong>il : subcutaneous4.3 Epoprostenol : <strong>in</strong>travenous4.4 Beraprost : oralAcute management <strong>of</strong> <strong>pulmonary</strong> <strong>hypertension</strong>9ตารางที่ 3 ACCP (American College <strong>of</strong> chest physician) grad<strong>in</strong>g system ประกอบดวยการใชquality <strong>of</strong> evidence (Good, fair, low หรือ expert op<strong>in</strong>ion) รวมกับ net benefit วาเปน large,(14)<strong>in</strong>termediate, small, non, conflict<strong>in</strong>g หรือ negativeQuality <strong>of</strong>evidenceNet benefit to patient (adjust for risk and based on cl<strong>in</strong>ical assessment )Large Intermediate Small None Conflict<strong>in</strong>g negativeGoodA A B D I DFairA B C D I DLowB C C I I DExpertE/A E/B E/C I I E/Dภาพที่ 3 แผนภูมิแสดง คําแนะนําการรักษา <strong>pulmonary</strong> artery <strong>hypertension</strong> โดยอาศัย ACCP(American College <strong>of</strong> chest physician) grad<strong>in</strong>g system ลําดับที่ควรเลือกใชยาเรียงจากบนลงลางAPAH : associated <strong>pulmonary</strong> artery <strong>hypertension</strong>, CCB : calcium channel blocker, ERA:endothel<strong>in</strong> receptor antagonist , PDE : Phosphodiesterase 5 <strong>in</strong>hibitor, IV : <strong>in</strong>travenous, SC :subcutaneous)