COMPUTING
Second Edition - Orchard Publications
Second Edition - Orchard Publications
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
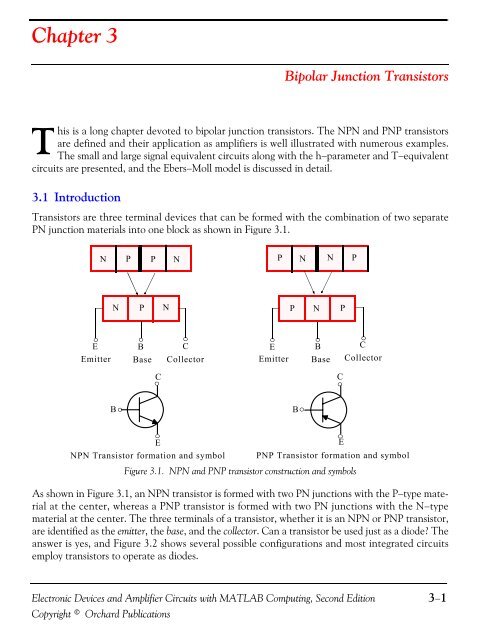
Chapter 3Bipolar Junction TransistorsThis is a long chapter devoted to bipolar junction transistors. The NPN and PNP transistorsare defined and their application as amplifiers is well illustrated with numerous examples.The small and large signal equivalent circuits along with the h−parameter and T−equivalentcircuits are presented, and the Ebers−Moll model is discussed in detail.3.1 IntroductionTransistors are three terminal devices that can be formed with the combination of two separatePN junction materials into one block as shown in Figure 3.1.NPPNPNNPNPNPNPE B CE B CEmitter Base CollectorEmitter Base CollectorCCBBENPN Transistor formation and symbolPNP Transistor formation and symbolFigure 3.1. NPN and PNP transistor construction and symbolsAs shown in Figure 3.1, an NPN transistor is formed with two PN junctions with the P−type materialat the center, whereas a PNP transistor is formed with two PN junctions with the N−typematerial at the center. The three terminals of a transistor, whether it is an NPN or PNP transistor,are identified as the emitter, the base, and the collector. Can a transistor be used just as a diode? Theanswer is yes, and Figure 3.2 shows several possible configurations and most integrated circuitsemploy transistors to operate as diodes.EElectronic Devices and Amplifier Circuits with MATLAB Computing, Second EditionCopyright © Orchard Publications3−1