Remaining Life of a Pipeline
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
The method to find the most suitable probability distribution function <strong>of</strong> “E”, ( pdf(E)) will be described<br />
in step #3.<br />
In a similar fashion, the limit wall thickness “E lim “ which has been traditionally considered as a<br />
deterministic value, can also be considered as having its own probability distribution, as the one<br />
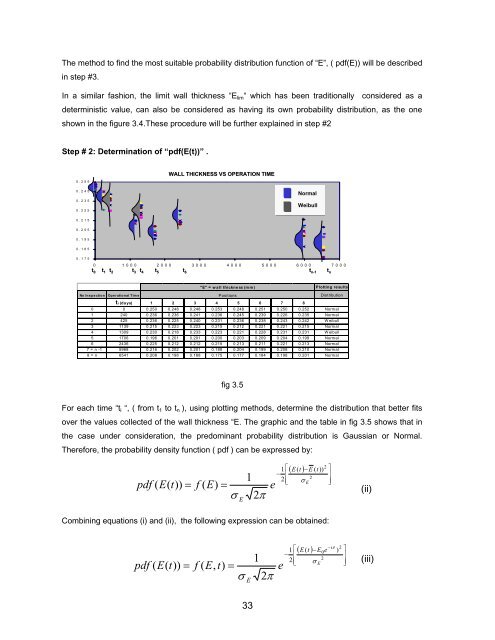
shown in the figure 3.4.These procedure will be further explained in step #2<br />
Step # 2: Determination <strong>of</strong> “pdf(E(t))” .<br />
0.255<br />
WALL THICKNESS VS OPERATION TIME<br />
0.245<br />
0.235<br />
0.225<br />
Normal<br />
Weibull<br />
0.215<br />
0.205<br />
0.195<br />
0.185<br />
0.175<br />
0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 7000<br />
t 0 t 1 t 2 t 3 t 4 t 5 t 6<br />
t n-1<br />
t n<br />
"E" = wall thickness (mm)<br />
Plotting results<br />
No Inspection Operational Tim e Positions<br />
Distribution<br />
ti (days) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8<br />
0 0 0.250 0.248 0.248 0.253 0.248 0.251 0.250 0.252 Normal<br />
1 240 0.236 0.236 0.241 0.236 0.245 0.239 0.226 0.235 Normal<br />
2 425 0.236 0.225 0.240 0.231 0.236 0.238 0.243 0.242 W eibull<br />
3 1139 0.215 0.223 0.223 0.215 0.212 0.221 0.221 0.215 Normal<br />
4 1309 0.230 0.218 0.233 0.223 0.221 0.228 0.231 0.231 W eibull<br />
5 1706 0.196 0.201 0.201 0.200 0.203 0.209 0.204 0.199 Normal<br />
6 2436 0.225 0.212 0.212 0.215 0.213 0.211 0.221 0.213 Normal<br />
7 = n -1 5968 0.216 0.202 0.201 0.188 0.204 0.199 0.208 0.210 Normal<br />
8 = n 6541 0.208 0.198 0.188 0.175 0.177 0.184 0.198 0.201 Normal<br />
fig 3.5<br />
For each time “t i “, ( from t 1 to t n ), using plotting methods, determine the distribution that better fits<br />
over the values collected <strong>of</strong> the wall thickness “E. The graphic and the table in fig 3.5 shows that in<br />
the case under consideration, the predominant probability distribution is Gaussian or Normal.<br />
Therefore, the probability density function ( pdf ) can be expressed by:<br />
pdf<br />
1<br />
E(<br />
t))<br />
= f ( E)<br />
=<br />
σ 2π<br />
1 ⎡<br />
− ⎢<br />
2 ⎢⎣<br />
( E(<br />
t )<br />
2<br />
σ E<br />
( e<br />
E<br />
−E<br />
( t))<br />
2<br />
⎤<br />
⎥<br />
⎥⎦<br />
(ii)<br />
Combining equations (i) and (ii), the following expression can be obtained:<br />
pdf<br />
1 ⎡<br />
− ⎢<br />
2 ⎢⎣<br />
( E(<br />
t )<br />
−υt<br />
2<br />
−E0 e )<br />
1<br />
2<br />
σ E<br />
( E(<br />
t))<br />
= f ( E,<br />
t)<br />
= e<br />
σ<br />
E<br />
2π<br />
⎤<br />
⎥<br />
⎥⎦<br />
(iii)<br />
33