Remaining Life of a Pipeline
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
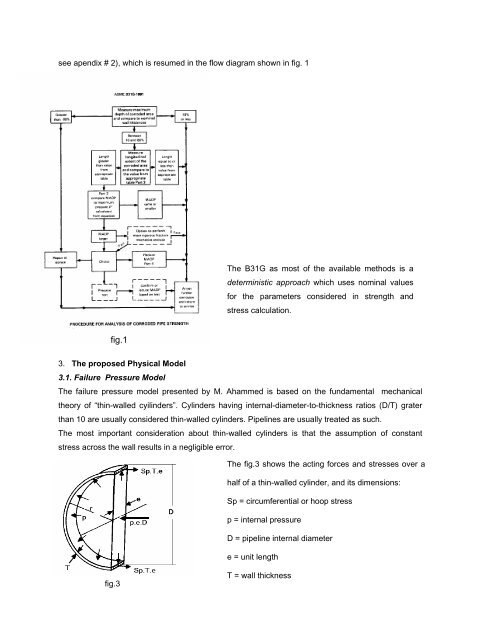
see apendix # 2), which is resumed in the flow diagram shown in fig. 1<br />
The B31G as most <strong>of</strong> the available methods is a<br />
deterministic approach which uses nominal values<br />
for the parameters considered in strength and<br />
stress calculation.<br />
fig.1<br />
3. The proposed Physical Model<br />
3.1. Failure Pressure Model<br />
The failure pressure model presented by M. Ahammed is based on the fundamental mechanical<br />
theory <strong>of</strong> “thin-walled cyilinders”. Cylinders having internal-diameter-to-thickness ratios (D/T) grater<br />
than 10 are usually considered thin-walled cylinders. <strong>Pipeline</strong>s are usually treated as such.<br />
The most important consideration about thin-walled cylinders is that the assumption <strong>of</strong> constant<br />
stress across the wall results in a negligible error.<br />
The fig.3 shows the acting forces and stresses over a<br />
half <strong>of</strong> a thin-walled cylinder, and its dimensions:<br />
Sp = circumferential or hoop stress<br />
p = internal pressure<br />
D = pipeline internal diameter<br />
e = unit length<br />
fig.3<br />
T = wall thickness<br />
4