vector
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Vectors 441<br />
Solution.<br />
<br />
<br />
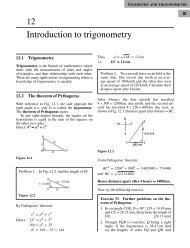
F =<br />
iˆ<br />
ˆj kˆ<br />
iˆ<br />
ˆj kˆ<br />
x y z<br />
y z x<br />
Obviously ˆn = k ˆ.<br />
Therefore<br />
<br />
( F)<br />
nˆ<br />
= (– iˆ<br />
– ˆj – kˆ). kˆ<br />
–1<br />
Hence<br />
( F)<br />
nˆ<br />
ds<br />
= ( 1) dx dy<br />
S<br />
<br />
=<br />
S<br />
<br />
S<br />
dx dy<br />
= – (1) 2 = – . (Area of circle = r 2 ) Ans.<br />
Example 92. Evaluate Fdr<br />
<br />
2 2<br />
by Stoke’s Theorem, where F y iˆ x ˆ j ( x z)<br />
kˆ<br />
and<br />
C<br />
C is the boundary of triangle with vertices at (0, 0, 0), (1, 0, 0) and (1, 1, 0).<br />
(U.P., I Semester, Winter 2000)<br />
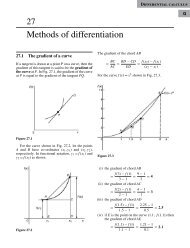
Solution. We have, curl F =<br />
=<br />
iˆ<br />
ˆj kˆ<br />
<br />
x y z<br />
2 2<br />
F <br />
0. iˆ ˆj 2( x y) kˆ<br />
.<br />
y x ( x z)<br />
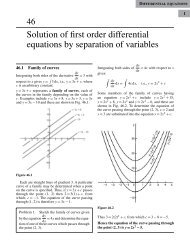
We observe that z co-ordinate of each vertex of the triangle is zero.<br />
Therefore, the triangle lies in the xy-plane.<br />
ˆn = ˆk<br />
<br />
curl Fn ˆ [ ˆj 2( x yk ) ˆ]. kˆ<br />
2( x y).<br />
In the figure, only xy-plane is considered.<br />
The equation of the line OB is y = x<br />
By Stoke’s theorem, we have<br />
C<br />
<br />
Fdr <br />
=<br />
<br />
S<br />
<br />
<br />
(curl Fnˆ<br />
) ds<br />
1 x<br />
= 2( )<br />
2<br />
1<br />
x y dx dy<br />
y <br />
x0 = 2<br />
y 0 xy<br />
dx<br />
0<br />
2 0<br />
2<br />
1 2<br />
= 2 x <br />
2<br />
x<br />
dx<br />
0<br />
2 <br />
=<br />
1 x<br />
1<br />
2 dx = 2<br />
0 2<br />
x dx <br />
3<br />
x <br />
=<br />
0 <br />
3 <br />
x<br />
1<br />
0<br />
= 1 .<br />
3<br />
Example 93. Evaluate Fdr<br />
<br />
<br />
by Stoke’s Theorem, where<br />
2 2<br />
F ( x y ) iˆ 2 xy ˆj<br />
C and C<br />
is the boundary of the rectangle x = a, y = 0 and y = b. (U.P., I Semester, Winter 2002)<br />
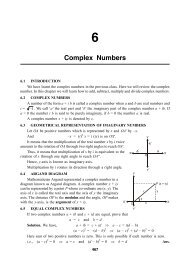
Solution. Since the z co-ordinate of each vertex of the given rectangle is zero, hence the given<br />
rectangle must lie in the xy-plane.<br />
Here, the co-ordinates of A, B, C and D are (a, 0), (a, b), (– a, b) and (– a, 0) respectively.<br />
Curl F =<br />
iˆ<br />
ˆj kˆ<br />
<br />
= – 4 y k<br />
x y z<br />
2 2<br />
x y 2xy<br />
0<br />
Ans.