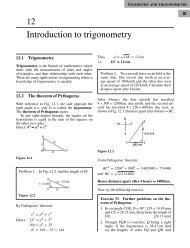
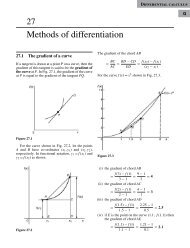
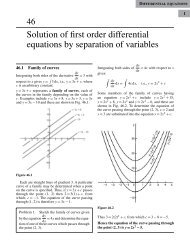
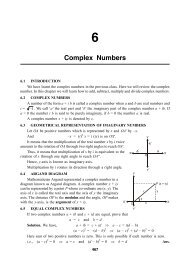
vector
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
444 Vectors<br />
2 2<br />
= [(2 x – y) dx – yz dy – y z dz]<br />
C<br />
= (2 x – y) dx,<br />
C<br />
since on C, z = 0 and 2z = 0<br />
2<br />
dx 2<br />
= (2cos t –sin t) dt (2cos t –sin t)(–sin t)<br />
dt<br />
0 dt<br />
0<br />
2 2<br />
2 1–cos 2t<br />
<br />
= (– sin 2t sin t) dt – sin 2t dt<br />
0 <br />
0<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
2 <br />
2<br />
cos 2t t sin 2t<br />
1 1<br />
= – –<br />
2 2 4<br />
<br />
<br />
0 2 2<br />
iˆ<br />
ˆj kˆ<br />
...(1)<br />
<br />
Curl F =<br />
<br />
x y z = (– 2yz 2 yz) iˆ<br />
(0–0) ˆj (01)<br />
kˆ kˆ<br />
2 x – y<br />
2<br />
– yz<br />
2<br />
– y z<br />
<br />
Z<br />
Curl F . nˆ<br />
= kˆ. nˆ<br />
nk ˆ.<br />
ˆ<br />
<br />
Curl F.<br />
nds ˆ = ˆ. ˆ ˆ. ˆ dx dy<br />
. .<br />
S nkds nk<br />
S R ˆ ˆ<br />
Where R is the projection of S on xy-plane.<br />
O<br />
Y<br />
=<br />
2<br />
1 1– x<br />
dx dy =<br />
2<br />
–1 – 1– x<br />
<br />
1 2 1 2<br />
2 1– x dx 4 1– x dx<br />
–1 0<br />
1<br />
2 –1<br />
x<br />
1 1<br />
<br />
= 4 1– x sin x 4 .<br />
2 2<br />
<br />
0 2 2<br />
<br />
<br />
From (1) and (2), we have<br />
<br />
<br />
F . dr = Curl F . nds ˆ which is the Stoke's theorem.<br />
C <br />
<br />
Example 97. Verify Stoke’s Theorem for 2 ˆ ˆ<br />
2<br />
F ( x y 4) i 3 xyj (2 xz z ) kˆ<br />
over the surface of hemisphere x 2 + y 2 + z 2 = 16 above the xy-plane.<br />
<br />
Solution. Fdr , where c is the boundary of the circle x 2 + y 2 + z 2 = 16<br />
c<br />
(bounding the hemispherical surface)<br />
2 2 ˆ<br />
= [( x y 4) iˆ 3 xyj ˆ (2 xz z ) k]( idx ˆ ˆjdy)<br />
Putting<br />
<br />
<br />
c<br />
2<br />
= [( x y 4) dx 3 xy dy)]<br />
c<br />
x = 4 cos , y = 4 sin , dx = – 4 sin d , dy = 4 cos d <br />
=<br />
<br />
2<br />
2 2<br />
0<br />
<br />
[(16 cos 4sin 4) ( 4sin d ) (192 sin cos d )]<br />
2 2 2 2<br />
= 16 [ 4cos sin sin sin 12 sin cos ] d <br />
<br />
<br />
0<br />
2<br />
2 2<br />
= 16 (8 sin cos sin sin ) d <br />
=<br />
=<br />
0<br />
<br />
2<br />
16 sin d<br />
<br />
0<br />
2<br />
<br />
2 2<br />
=<br />
0<br />
16 4 sin d<br />
<br />
To evaluate surface integral<br />
F <br />
=<br />
1<br />
<br />
64 = – 16 .<br />
22 <br />
iˆ<br />
ˆj kˆ<br />
<br />
x y z<br />
X<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
2 2<br />
x y 4 3xy 2 xz z<br />
<br />
<br />
2<br />
0<br />
2<br />
0<br />
C<br />
...(2)<br />
Ans.<br />
n<br />
sin cos d0<br />
<br />
<br />
<br />
n<br />
cos sin d<br />
0