Antibiotic Classification and Modes of Action - bioMerieux
Antibiotic Classification and Modes of Action - bioMerieux
Antibiotic Classification and Modes of Action - bioMerieux
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Customer Education <strong>Antibiotic</strong> <strong>Classification</strong><br />
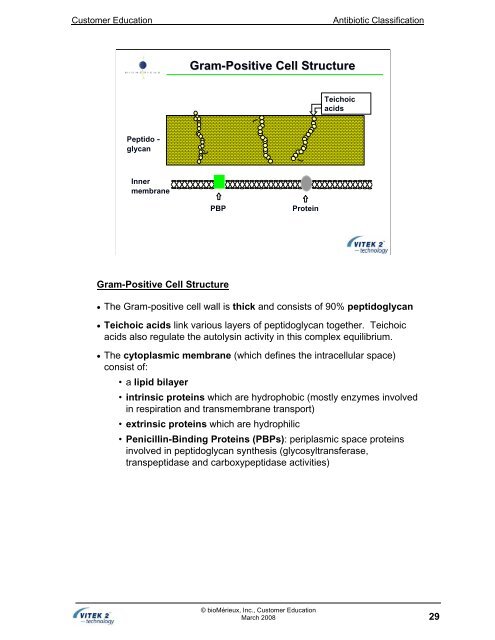
Peptido -<br />
glycan<br />
Inner<br />
membrane<br />
Gram-Positive Cell Structure<br />
Gram-Positive Gram Positive Cell Structure<br />
PBP Protein<br />
© bioMérieux, Inc., Customer Education<br />
March 2008<br />
Teichoic<br />
acids<br />
• The Gram-positive cell wall is thick <strong>and</strong> consists <strong>of</strong> 90% peptidoglycan<br />
• Teichoic acids link various layers <strong>of</strong> peptidoglycan together. Teichoic<br />
acids also regulate the autolysin activity in this complex equilibrium.<br />
• The cytoplasmic membrane (which defines the intracellular space)<br />
consist <strong>of</strong>:<br />
•a lipid bilayer<br />
• intrinsic proteins which are hydrophobic (mostly enzymes involved<br />
in respiration <strong>and</strong> transmembrane transport)<br />
• extrinsic proteins which are hydrophilic<br />
• Penicillin-Binding Proteins (PBPs): periplasmic space proteins<br />
involved in peptidoglycan synthesis (glycosyltransferase,<br />
transpeptidase <strong>and</strong> carboxypeptidase activities)<br />
29