Dalla relatività ai buchi neri - Liceo cantonale di Locarno
Dalla relatività ai buchi neri - Liceo cantonale di Locarno
Dalla relatività ai buchi neri - Liceo cantonale di Locarno
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Dalla</strong> <strong>relatività</strong> <strong>ai</strong> <strong>buchi</strong> <strong>neri</strong> 5. La <strong>relatività</strong> ristretta<br />
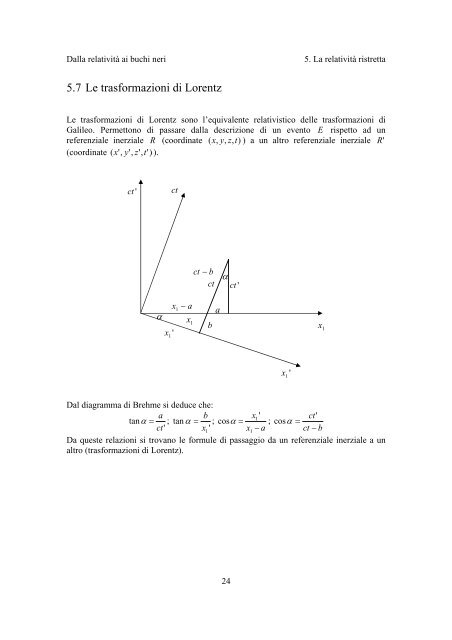
5.7 Le trasformazioni <strong>di</strong> Lorentz<br />
Le trasformazioni <strong>di</strong> Lorentz sono l’equivalente relativistico delle trasformazioni <strong>di</strong><br />
Galileo. Permettono <strong>di</strong> passare dalla descrizione <strong>di</strong> un evento E rispetto ad un<br />
referenziale inerziale R (coor<strong>di</strong>nate ( x , y,<br />
z,<br />
t)<br />
) a un altro referenziale inerziale R '<br />
(coor<strong>di</strong>nate ( x ',<br />
y',<br />
z',<br />
t')<br />
).<br />
ct '<br />
α<br />
x1'<br />
ct<br />
x1 − a<br />
x1<br />
ct − b<br />
ct<br />
b<br />
a<br />
α<br />
ct '<br />
Dal <strong>di</strong>agramma <strong>di</strong> Brehme si deduce che:<br />
a b<br />
x<br />
tanα<br />
= ; tanα<br />
= ; = 1'<br />
ct'<br />
cosα ; cosα =<br />
ct'<br />
x1'<br />
x1<br />
− a ct − b<br />
Da queste relazioni si trovano le formule <strong>di</strong> passaggio da un referenziale inerziale a un<br />
altro (trasformazioni <strong>di</strong> Lorentz).<br />
24<br />
x1<br />
'<br />
x1