- Page 1 and 2: TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY OF DENMARK (DT
- Page 3 and 4: Preface The present dissertation su
- Page 5 and 6: the carboxylic acid, ceria inhibite
- Page 7 and 8: Resume Denne afhandling giver indle
- Page 9 and 10: hvorimod mængden af katalysator ku
- Page 11 and 12: 2.3.8 Oxidation of sulfides .......
- Page 13 and 14: 5.3.5 Macroscopic mass transport in
- Page 15 and 16: Chapter 1 Introduction With its gre
- Page 17 and 18: 1. Introduction Scheme 1‐1: High
- Page 19 and 20: 1. Introduction Figure 1‐2: Phase
- Page 21 and 22: 1. Introduction [28] S. Bawaked, N.
- Page 23: 2.1 Introduction 2.1 Introduction E
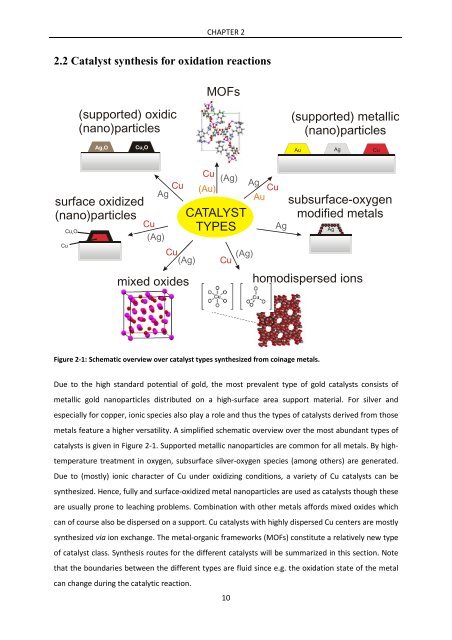
- Page 27 and 28: 2.2 Catalyst synthesis for oxidatio
- Page 29 and 30: 2.2 Catalyst synthesis for oxidatio
- Page 31 and 32: 2.3 Selective liquid‐phase oxidat
- Page 33 and 34: Table 2-1: Overview over alcohol ox
- Page 35 and 36: 2.3 Selective liquid‐phase oxidat
- Page 37 and 38: 2.3 Selective liquid‐phase oxidat
- Page 39 and 40: 2.3 Selective liquid‐phase oxidat
- Page 41 and 42: 2.3 Selective liquid‐phase oxidat
- Page 43 and 44: 2.3 Selective liquid‐phase oxidat
- Page 45 and 46: Ph O O Ph (4) (5) 2.3 Selective liq
- Page 47 and 48: 2.3 Selective liquid‐phase oxidat
- Page 49 and 50: 2.3 Selective liquid‐phase oxidat
- Page 51 and 52: Table 2-4: Side-chain oxidation of
- Page 53 and 54: 2.3.4 Oxidation of cyclohexane 2.3
- Page 55 and 56: Table 2-5: Oxidatin of cyclohexane.
- Page 57 and 58: 2.3 Selective liquid‐phase oxidat
- Page 59 and 60: Table 2-6: Ring hydroxylation of ar
- Page 61 and 62: 2.3 Selective liquid‐phase oxidat
- Page 63 and 64: Table 2-7: Aerobic oxidation of ami
- Page 65 and 66: Table 2-8: Oxidation of hydroquinon
- Page 67 and 68: 2.3 Selective liquid‐phase oxidat
- Page 69 and 70: Table 2-9: Oxidation of silanes wit
- Page 71 and 72: Table 2-10: Oxidation reactions cat
- Page 73 and 74: 2.4 Strengths and opportunities of
- Page 75 and 76:
2.4 Strengths and opportunities of
- Page 77 and 78:
2.4 Strengths and opportunities of
- Page 79 and 80:
2.4 Strengths and opportunities of
- Page 81 and 82:
2.6 References 2.6 References [1] M
- Page 83 and 84:
2.6 References [56] H. Tumma, N. Na
- Page 85 and 86:
2.6 References [113] C. Keresszegi,
- Page 87 and 88:
2.6 References [169] Q. Zhu, Y. Lia
- Page 89 and 90:
2.6 References [223] M. Fetizon, M.
- Page 91 and 92:
Chapter 3 Selective Liquid-Phase Ox
- Page 93 and 94:
3.2 Experimental 3.2.1 Catalyst pre
- Page 95 and 96:
3.3 Results Scattering amplitudes a
- Page 97 and 98:
Absorption (a.u.) 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0
- Page 99 and 100:
Conversion (%) 100 90 80 70 60 50 4
- Page 101 and 102:
3.3 Results Figure 3‐5: In situ X
- Page 103 and 104:
3.3 Results Table 3‐2: Conversion
- Page 105 and 106:
3.3 Results In order to gain insigh
- Page 107 and 108:
3.3 Results the cost of selectivity
- Page 109 and 110:
3.4 Discussion synergetic interacti
- Page 111 and 112:
3.5 Conclusions to corroborate the
- Page 113 and 114:
3.6 References [29] T. Mitsudome, Y
- Page 115 and 116:
Chapter 4 Selective Side-Chain Oxid
- Page 117 and 118:
4.2 Experimental single‐step flam
- Page 119 and 120:
4.2 Experimental alcohol (Aldrich,
- Page 121 and 122:
4.3 Results Scheme 4‐1: Oxidation
- Page 123 and 124:
4.3 Results Figure 4‐2: Formation
- Page 125 and 126:
4.3 Results oxidation by either 2,6
- Page 127 and 128:
Absorption (a.u.) Absorption (a.u.)
- Page 129 and 130:
4.3 Results atomic mixing of Ag and
- Page 131 and 132:
4.3 Results Figure 4‐7: Influence
- Page 133 and 134:
4.4 Discussion and mechanistic cons
- Page 135 and 136:
4.5 Conclusions heterogeneous radic
- Page 137 and 138:
4.6 References [29] S.I. Zabinsky,
- Page 139 and 140:
Chapter 5 Experimental Determinatio
- Page 141 and 142:
5.2 Experimental The most important
- Page 143 and 144:
5.2 Experimental Eurotherm 2216e te
- Page 145 and 146:
Figure 5-1: Schematic view of the e
- Page 147 and 148:
(Eq. 5‐5) AB i j ε AB i j β 5.2
- Page 149 and 150:
(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i)
- Page 151 and 152:
5.3 Results two association sites o
- Page 153 and 154:
Pressure (bar) 150 145 140 135 5.3
- Page 155 and 156:
5.3 Results Figure 5‐7: Oxidation
- Page 157 and 158:
Weight (g) 5.3 Results Figure 5‐8
- Page 159 and 160:
5.4 Discussion catalytic reactions
- Page 161 and 162:
5.4 Discussion corresponding CO2‐
- Page 163 and 164:
5.5 Conclusions 5.5 Conclusions The
- Page 165 and 166:
5.6 References [29] I. Tsivintzelis
- Page 167 and 168:
6.1 Introduction 6.1 Introduction A
- Page 169 and 170:
6.2 Experimental [38]. In a typical
- Page 171 and 172:
6.3 Results out in 1 mm quartz tube
- Page 173 and 174:
6.3 Results Figure 6‐2: Structure
- Page 175 and 176:
6.3 Results Figure 6‐4: Epoxidati
- Page 177 and 178:
6.3 Results Figure 6‐6: Compariso
- Page 179 and 180:
6.3 Results Figure 6‐8: Influence
- Page 181 and 182:
6.3 Results investigated the epoxid
- Page 183 and 184:
6.3 Results Figure 6‐10: Co‐epo
- Page 185 and 186:
6.3 Results Figure 6‐11: EXAFS an
- Page 187 and 188:
6.4 Discussion would need to be for
- Page 189 and 190:
6.5 Conclusions Formation of the ep
- Page 191 and 192:
6.6 References [28] J. Perles, N. S
- Page 193 and 194:
Chapter 7 Concluding Remarks 7.1 Co
- Page 195 and 196:
7.2 Final remarks and outlook speci
- Page 197 and 198:
Acknowledgements Acknowledgements T
- Page 199:
Curriculum Vitae Matthias Josef Bei