Download the publication - Tropenbos International
Download the publication - Tropenbos International
Download the publication - Tropenbos International
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Plant diversity in a Central African rain forest: Implications for biodiversity conservation in Cameroon<br />
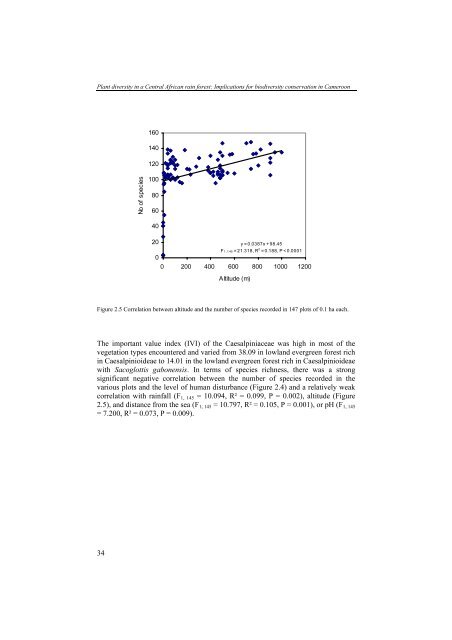
Figure 2.5 Correlation between altitude and <strong>the</strong> number of species recorded in 147 plots of 0.1 ha each.<br />
The important value index (IVI) of <strong>the</strong> Caesalpiniaceae was high in most of <strong>the</strong><br />
vegetation types encountered and varied from 38.09 in lowland evergreen forest rich<br />
in Caesalpinioideae to 14.01 in <strong>the</strong> lowland evergreen forest rich in Caesalpinioideae<br />
with Sacoglottis gabonensis. In terms of species richness, <strong>the</strong>re was a strong<br />
significant negative correlation between <strong>the</strong> number of species recorded in <strong>the</strong><br />
various plots and <strong>the</strong> level of human disturbance (Figure 2.4) and a relatively weak<br />
correlation with rainfall (F1, 145 = 10.094, R² = 0.099, P = 0.002), altitude (Figure<br />
2.5), and distance from <strong>the</strong> sea (F1, 145 = 10.797, R² = 0.105, P = 0.001), or pH (F1, 145<br />
= 7.200, R² = 0.073, P = 0.009).<br />
34<br />
No of species<br />
160<br />
140<br />
120<br />
100<br />
80<br />
60<br />
40<br />
20<br />
y = 0.0387x + 98.45<br />
F1,145 = 21.318, R 2 = 0.188, P < 0.0001<br />
0<br />
0 200 400 600<br />
Altitude (m)<br />
800 1000 1200