Contents Chapter Topic Page Neonatology Respiratory Cardiology
Contents Chapter Topic Page Neonatology Respiratory Cardiology
Contents Chapter Topic Page Neonatology Respiratory Cardiology
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
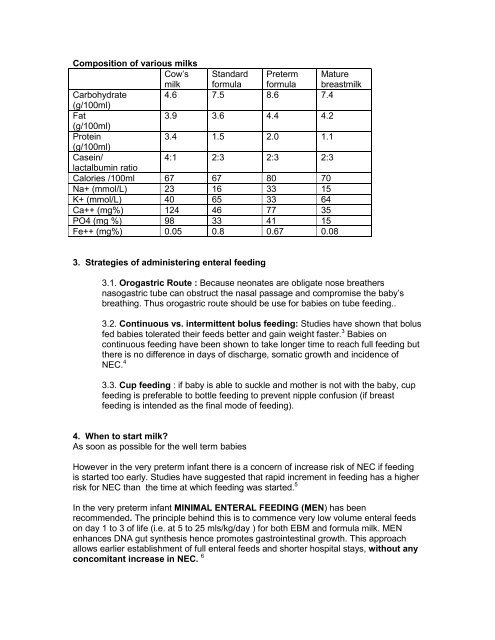
Composition of various milks<br />
Cow’s Standard Preterm Mature<br />
milk formula formula breastmilk<br />
Carbohydrate<br />
(g/100ml)<br />
4.6 7.5 8.6 7.4<br />
Fat<br />
(g/100ml)<br />
3.9 3.6 4.4 4.2<br />
Protein<br />
(g/100ml)<br />
3.4 1.5 2.0 1.1<br />
Casein/<br />
4:1 2:3 2:3 2:3<br />
lactalbumin ratio<br />
Calories /100ml 67 67 80 70<br />
Na+ (mmol/L) 23 16 33 15<br />
K+ (mmol/L) 40 65 33 64<br />
Ca++ (mg%) 124 46 77 35<br />
PO4 (mg %) 98 33 41 15<br />
Fe++ (mg%) 0.05 0.8 0.67 0.08<br />
3. Strategies of administering enteral feeding<br />
3.1. Orogastric Route : Because neonates are obligate nose breathers<br />
nasogastric tube can obstruct the nasal passage and compromise the baby’s<br />
breathing. Thus orogastric route should be use for babies on tube feeding..<br />
3.2. Continuous vs. intermittent bolus feeding: Studies have shown that bolus<br />
fed babies tolerated their feeds better and gain weight faster. 3 Babies on<br />
continuous feeding have been shown to take longer time to reach full feeding but<br />
there is no difference in days of discharge, somatic growth and incidence of<br />
NEC. 4<br />
3.3. Cup feeding : if baby is able to suckle and mother is not with the baby, cup<br />
feeding is preferable to bottle feeding to prevent nipple confusion (if breast<br />
feeding is intended as the final mode of feeding).<br />
4. When to start milk?<br />
As soon as possible for the well term babies<br />
However in the very preterm infant there is a concern of increase risk of NEC if feeding<br />
is started too early. Studies have suggested that rapid increment in feeding has a higher<br />
risk for NEC than the time at which feeding was started. 5<br />
In the very preterm infant MINIMAL ENTERAL FEEDING (MEN) has been<br />
recommended. The principle behind this is to commence very low volume enteral feeds<br />
on day 1 to 3 of life (i.e. at 5 to 25 mls/kg/day ) for both EBM and formula milk. MEN<br />
enhances DNA gut synthesis hence promotes gastrointestinal growth. This approach<br />
allows earlier establishment of full enteral feeds and shorter hospital stays, without any<br />
concomitant increase in NEC. 6