Contents Chapter Topic Page Neonatology Respiratory Cardiology
Contents Chapter Topic Page Neonatology Respiratory Cardiology
Contents Chapter Topic Page Neonatology Respiratory Cardiology
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
NEONATAL SEIZURES<br />
Seizures are the most frequent manifestation of neonatal neurological diseases.<br />
It is important to recognize seizures, determine their etiology and treat them because:<br />
1. the seizures may be related to significant diseases and may require specific<br />
treatment<br />
2. the seizures may interfere with supportive measures e.g. feeding and assisted<br />
respiration for associated disorders<br />
3. the seizures per se may be a cause of brain injury.<br />
Clinical<br />
A seizure is defined as a paroxysmal alteration in neurologic function that is behavioral,<br />
motor or autonomic function. This includes clinical phenomena that are associated with<br />
or without surface recorded EEG seizure activity.<br />
Epileptic phenomena can be generated at subcortical (deep limbic, diencephalic, brain<br />
stem) levels in the absence of surface recorded EEG discharges.<br />
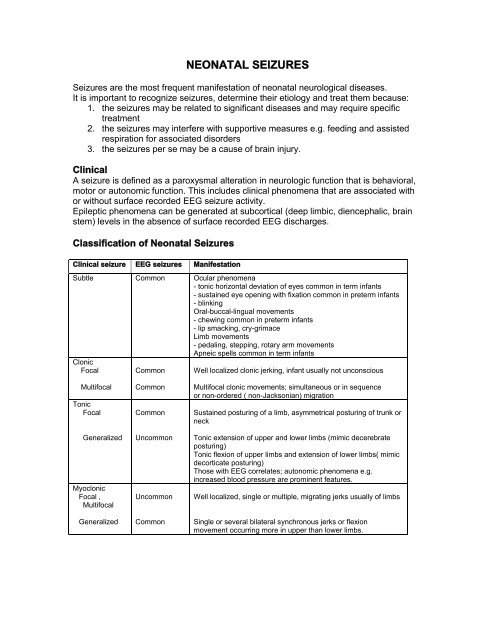
Classification of Neonatal Seizures<br />
Clinical seizure EEG seizures Manifestation<br />
Subtle<br />
Clonic<br />
Common Ocular phenomena<br />
- tonic horizontal deviation of eyes common in term infants<br />
- sustained eye opening with fixation common in preterm infants<br />
- blinking<br />
Oral-buccal-lingual movements<br />
- chewing common in preterm infants<br />
- lip smacking, cry-grimace<br />
Limb movements<br />
- pedaling, stepping, rotary arm movements<br />
Apneic spells common in term infants<br />
Focal<br />
Common Well localized clonic jerking, infant usually not unconscious<br />
Multifocal<br />
Tonic<br />
Focal<br />
Generalized<br />
Myoclonic<br />
Focal ,<br />
Multifocal<br />
Generalized<br />
Common<br />
Common<br />
Uncommon<br />
Uncommon<br />
Common<br />
Multifocal clonic movements; simultaneous or in sequence<br />
or non-ordered ( non-Jacksonian) migration<br />
Sustained posturing of a limb, asymmetrical posturing of trunk or<br />
neck<br />
Tonic extension of upper and lower limbs (mimic decerebrate<br />
posturing)<br />
Tonic flexion of upper limbs and extension of lower limbs( mimic<br />
decorticate posturing)<br />
Those with EEG correlates; autonomic phenomena e.g.<br />
increased blood pressure are prominent features.<br />
Well localized, single or multiple, migrating jerks usually of limbs<br />
Single or several bilateral synchronous jerks or flexion<br />
movement occurring more in upper than lower limbs.