Max Planck Institute for Astronomy - Annual Report 2007
Max Planck Institute for Astronomy - Annual Report 2007
Max Planck Institute for Astronomy - Annual Report 2007
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
50 II. Highlights<br />
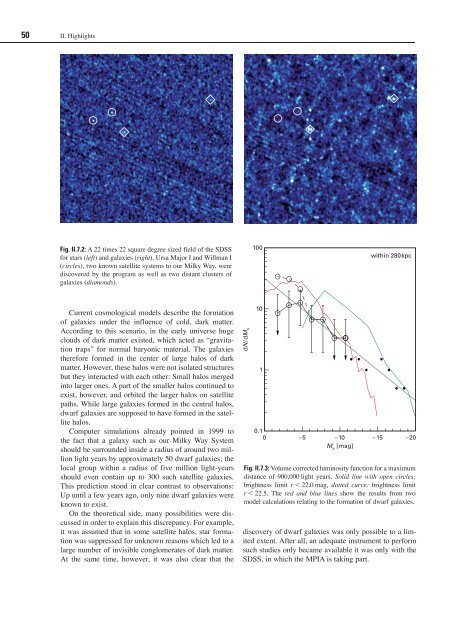
Fig. II.7.2: A 22 times 22 square degree sized field of the SDSS<br />
<strong>for</strong> stars (left) and galaxies (right). Ursa Major I and Willman I<br />
(circles), two known satellite systems to our Milky Way, were<br />
discovered by the program as well as two distant clusters of<br />
galaxies (diamonds).<br />
Current cosmological models describe the <strong>for</strong>mation<br />
of galaxies under the influence of cold, dark matter.<br />
According to this scenario, in the early universe huge<br />
clouds of dark matter existed, which acted as “gravitation<br />
traps” <strong>for</strong> normal baryonic material. The galaxies<br />
there<strong>for</strong>e <strong>for</strong>med in the center of large halos of dark<br />
matter. However, these halos were not isolated structures<br />
but they interacted with each other: Small halos merged<br />
into larger ones. A part of the smaller halos continued to<br />
exist, however, and orbited the larger halos on satellite<br />
paths. While large galaxies <strong>for</strong>med in the central halos,<br />
dwarf galaxies are supposed to have <strong>for</strong>med in the satellite<br />
halos.<br />
Computer simulations already pointed in 1999 to<br />
the fact that a galaxy such as our Milky Way System<br />
should be surrounded inside a radius of around two million<br />
light years by approximately 50 dwarf galaxies; the<br />
local group within a radius of five million light-years<br />
should even contain up to 300 such satellite galaxies.<br />
This prediction stood in clear contrast to observations:<br />
Up until a few years ago, only nine dwarf galaxies were<br />
known to exist.<br />
On the theoretical side, many possibilities were discussed<br />
in order to explain this discrepancy. For example,<br />
it was assumed that in some satellite halos, star <strong>for</strong>mation<br />
was suppressed <strong>for</strong> unknown reasons which led to a<br />
large number of invisible conglomerates of dark matter.<br />
At the same time, however, it was also clear that the<br />
dN/dM v<br />
100<br />
10<br />
1<br />
0.1<br />
0<br />
within 280kpc<br />
–5 –10<br />
Mv [mag]<br />
–15 –20<br />
Fig. II.7.3: Volume corrected luminosity function <strong>for</strong> a maximum<br />
distance of 900,000 light years. Solid line with open circles:<br />
brightness limit r 22.0 mag, dotted curve: brightness limit<br />
r 22.5. The red and blue lines show the results from two<br />
model calculations relating to the <strong>for</strong>mation of dwarf galaxies.<br />
discovery of dwarf galaxies was only possible to a limited<br />
extent. After all, an adequate instrument to per<strong>for</strong>m<br />
such studies only became available it was only with the<br />
SDSS, in which the MPIA is taking part.