October 31, 1975 - Gerald R. Ford Presidential Library and Museum
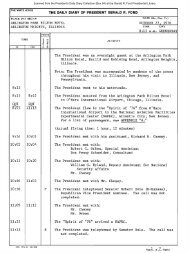
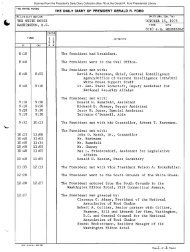
October 31, 1975 - Gerald R. Ford Presidential Library and Museum
October 31, 1975 - Gerald R. Ford Presidential Library and Museum
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
The West Cote Blanche Bay oil <strong>and</strong> gas field is located in West Cote<br />
Blanche Bay, St. Mary Parish in extreme southern Louisiana. The<br />
field is 65 miles south of Baton Rouge in the onshore Miocene Belt.<br />
The producing formations are s<strong>and</strong>s in a thick s<strong>and</strong>-shale sequence of<br />
Pliocene <strong>and</strong> Miocene age. Depths to the s<strong>and</strong>s range from 1,400 to<br />
10,200 feet.<br />
The structure at West Cote Blanche Bay is related to a shallow piercement<br />
type salt dome. The shallowest salt is at about 7,700 feet.<br />
There are numerous faults associated with the field <strong>and</strong> over 200<br />
separate reservoir segments are believed to exist. Some reservoirs<br />
are superdomal <strong>and</strong> are related entirely to the anticlinal structure.<br />
Other reservoirs are controlled by truncation of the s<strong>and</strong>s by salt or<br />
shale as the salt intruded. Some s<strong>and</strong>s pinch out stratigraphically<br />
as deposition approaches the salt mass. Faults <strong>and</strong> bottom water also<br />
delineate the accumulations in most instances. The field has about<br />
2,860 productive areas (4 square miles).<br />
Hydrocarbons orig'inally in place at West Cote Blanche Bay were estimated<br />
by means of a "broad" or 'coarse II volumetric analysis. A sampling<br />
of logs was examined to determine net oil <strong>and</strong> gas s<strong>and</strong> thickness <strong>and</strong><br />
a composite isopach map was prepared. Average reservoir <strong>and</strong> fluid<br />
characteristics were selected.<br />
The predominate recovery mechanism is a water drive. Also there are<br />
eleven active water floods, all of which have been in operation long<br />
enough to be assessed. The field has been on production decline since<br />
1971. The proved reserves have been estimated by analysis of production<br />
history <strong>and</strong> by analogy with overall performance characteristics<br />
of water drive reservoirs. The specific manner in which the shut-in<br />
reserves were estimated was not mentioned in the report. Presumably<br />
a method similar to that described in the Bay de Chene field summary<br />
was followed.<br />
The FEA report on the West Cote Blanche Bay Field was prepared by<br />
Keplinger <strong>and</strong> Associates, Inc., under Contract No. CO-05-50l84-00.<br />
168