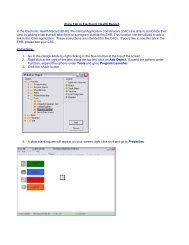
Public Health Nursing Documentation Guidelines - Indian Health ...
Public Health Nursing Documentation Guidelines - Indian Health ...
Public Health Nursing Documentation Guidelines - Indian Health ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Documentation</strong> and Coding <strong>Guidelines</strong> for <strong>Public</strong> <strong>Health</strong> Nurses<br />
Table 1.1.2 <strong>Indian</strong> <strong>Health</strong> Manual Vis-à-Vis the <strong>Nursing</strong> Process<br />
<strong>Health</strong> Information Management Requirements in<br />
the <strong>Indian</strong> <strong>Health</strong> Manual<br />
Chief complaint or reason for visit<br />
Relevant history and examination of findings<br />
Clinical impression or diagnosis<br />
Plan of care<br />
Identification of appropriate risk factors<br />
<strong>Nursing</strong> Process<br />
Assessment—subjective data<br />
Assessment—objective data<br />
<strong>Nursing</strong> diagnosis<br />
Outcome (goals) and planning<br />
Implementation, nursing interventions, and evaluation<br />
of progress<br />
Refusals<br />
Documenting services refused is just as important as documenting services provided.<br />
If a patient refuses a service, the health care provider must document that refusal to<br />
show that the provider did his or her best to offer a service according to standards of<br />
care. This documentation is an important risk management activity, because it will<br />
help protect the provider if any legal issues arise from a negative outcome to the patient.<br />
It is also very important that these refusals are recorded in the Electronic<br />
<strong>Health</strong> Record (which is explained below). Refusals must be documented.<br />
1.2 Understanding the Data Collection Process<br />
In the <strong>Indian</strong> health system, patient databases are managed by the Resource and<br />
Patient Management System (RPMS), which is a set of integrated computer applications<br />
designed to support clinical and administrative functions of a health care program.<br />
Most public health nurses and other health care providers use the Electronic<br />
<strong>Health</strong> Record (EHR)—a user-friendly application that interfaces with the RPMS—<br />
to enter and manage patient information. The EHR replaces paper forms that record<br />
visit information and activities. However, public health nurses at some facilities are<br />
still filling out Patient Care Component (PCC) forms.<br />
The <strong>Indian</strong> <strong>Health</strong> Service (IHS) PHN program compiles data into the PHN data<br />
mart, which generates reports on level of activity, performance, and other measurements.<br />
(See http://www.ihs.gov/NonMedicalPrograms/ihpes/phn/.) The <strong>Indian</strong> <strong>Health</strong><br />
Service’s PHN budget justification for the fiscal year is based on outcome measures<br />
of performance specific to the PHN program. The performance measurement is the<br />
total number of public health nurse activities captured by the PHN data mart with<br />
an emphasis on primary, secondary, and tertiary prevention activities to individuals,<br />
Page 1-8