soil - Lublin
soil - Lublin
soil - Lublin
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Cumulative CO 2<br />
(kg C ha -1 )<br />
600<br />
FALL<br />
500<br />
400<br />
300<br />
200<br />
Moldboard<br />
100<br />
Not tilled<br />
0<br />
0 5 10 15 20 25 30<br />
Cumulative CO 2<br />
(kg C ha -1 )<br />
800<br />
700<br />
600<br />
500<br />
400<br />
300<br />
200<br />
100<br />
SPRING<br />
0<br />
0 5 10 15 20 25 30<br />
2500<br />
SUMMER<br />
Cumulative CO 2<br />
(kg C ha -1 )<br />
2000<br />
1500<br />
1000<br />
500<br />
0<br />
0 20 40 60 80<br />
Time since plow ing (d)<br />
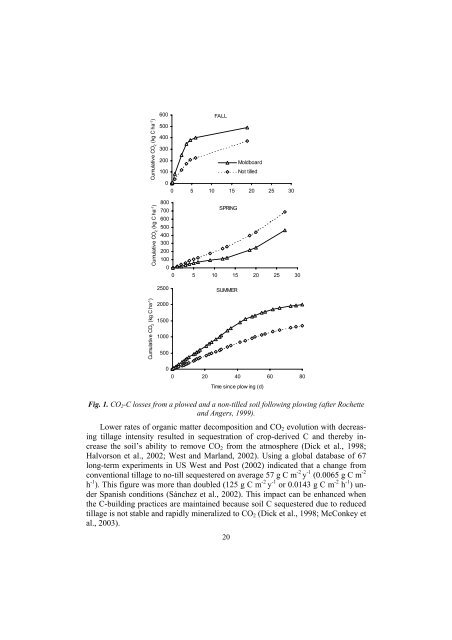
Fig. 1. CO 2 -C losses from a plowed and a non-tilled <strong>soil</strong> following plowing (after Rochette<br />
and Angers, 1999).<br />
Lower rates of organic matter decomposition and CO 2 evolution with decreasing<br />
tillage intensity resulted in sequestration of crop-derived C and thereby increase<br />
the <strong>soil</strong>’s ability to remove CO 2 from the atmosphere (Dick et al., 1998;<br />
Halvorson et al., 2002; West and Marland, 2002). Using a global database of 67<br />
long-term experiments in US West and Post (2002) indicated that a change from<br />
conventional tillage to no-till sequestered on average 57 g C m -2 y -1 (0.0065 g C m -2<br />
h -1 ). This figure was more than doubled (125 g C m -2 y -1 or 0.0143 g C m -2 h -1 ) under<br />
Spanish conditions (Sánchez et al., 2002). This impact can be enhanced when<br />
the C-building practices are maintained because <strong>soil</strong> C sequestered due to reduced<br />
tillage is not stable and rapidly mineralized to CO 2 (Dick et al., 1998; McConkey et<br />
al., 2003).<br />
20