soil - Lublin
soil - Lublin
soil - Lublin
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
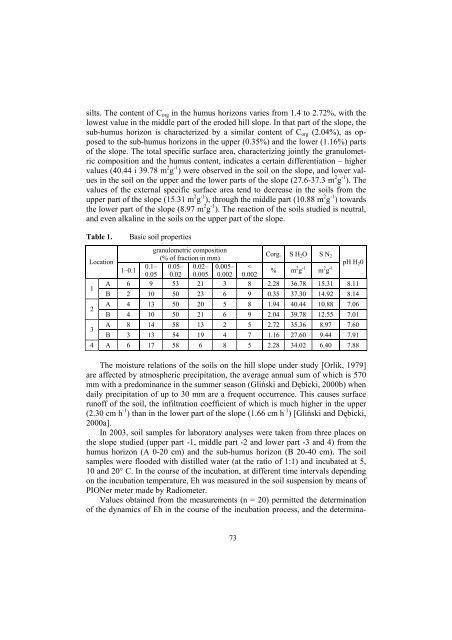
silts. The content of C org in the humus horizons varies from 1.4 to 2.72%, with the<br />
lowest value in the middle part of the eroded hill slope. In that part of the slope, the<br />
sub-humus horizon is characterized by a similar content of C org (2.04%), as opposed<br />
to the sub-humus horizons in the upper (0.35%) and the lower (1.16%) parts<br />
of the slope. The total specific surface area, characterizing jointly the granulometric<br />
composition and the humus content, indicates a certain differentiation – higher<br />
values (40.44 i 39.78 m 2 g -1 ) were observed in the <strong>soil</strong> on the slope, and lower values<br />
in the <strong>soil</strong> on the upper and the lower parts of the slope (27.6-37.3 m 2 g -1 ). The<br />
values of the external specific surface area tend to decrease in the <strong>soil</strong>s from the<br />
upper part of the slope (15.31 m 2 g -1 ), through the middle part (10.88 m 2 g -1 ) towards<br />
the lower part of the slope (8.97 m 2 g -1 ). The reaction of the <strong>soil</strong>s studied is neutral,<br />
and even alkaline in the <strong>soil</strong>s on the upper part of the slope.<br />
Table 1.<br />
Basic <strong>soil</strong> properties<br />
granulometric composition<br />
Corg. S H<br />
(% of fraction in mm)<br />
2 O S N 2<br />
Location<br />
pH H<br />
0.1– 0.05– 0.02– 0.005– <<br />
2 0<br />
1–0.1<br />
% m 2 g -1 m 2 g -1<br />
0.05 0.02 0.005 0.002 0.002<br />
A 6 9 53 21 3 8 2.28 36.78 15.31 8.11<br />
1<br />
B 2 10 50 23 6 9 0.35 37.30 14.92 8.14<br />
2<br />
3<br />
A 4 13 50 20 5 8 1.94 40.44 10.88 7.06<br />
B 4 10 50 21 6 9 2.04 39.78 12.55 7.01<br />
A 8 14 58 13 2 5 2.72 35.36 8.97 7.60<br />
B 3 13 54 19 4 7 1.16 27.60 9.44 7.91<br />
4 A 6 17 58 6 8 5 2.28 34.02 6.40 7.88<br />
The moisture relations of the <strong>soil</strong>s on the hill slope under study [Orlik, 1979]<br />
are affected by atmospheric precipitation, the average annual sum of which is 570<br />
mm with a predominance in the summer season (Gliński and Dębicki, 2000b) when<br />
daily precipitation of up to 30 mm are a frequent occurrence. This causes surface<br />
runoff of the <strong>soil</strong>, the infiltration coefficient of which is much higher in the upper<br />
(2.30 cm h -1 ) than in the lower part of the slope (1.66 cm h -1 ) [Gliński and Dębicki,<br />
2000a].<br />
In 2003, <strong>soil</strong> samples for laboratory analyses were taken from three places on<br />
the slope studied (upper part -1, middle part -2 and lower part -3 and 4) from the<br />
humus horizon (A 0-20 cm) and the sub-humus horizon (B 20-40 cm). The <strong>soil</strong><br />
samples were flooded with distilled water (at the ratio of 1:1) and incubated at 5,<br />
10 and 20° C. In the course of the incubation, at different time intervals depending<br />
on the incubation temperature, Eh was measured in the <strong>soil</strong> suspension by means of<br />
PIONer meter made by Radiometer.<br />
Values obtained from the measurements (n = 20) permitted the determination<br />
of the dynamics of Eh in the course of the incubation process, and the determina-<br />
73