pdf - SRON
pdf - SRON
pdf - SRON
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
CHAPTER 3: SOURCE COUNTS OF THE AXIS SOURCES<br />
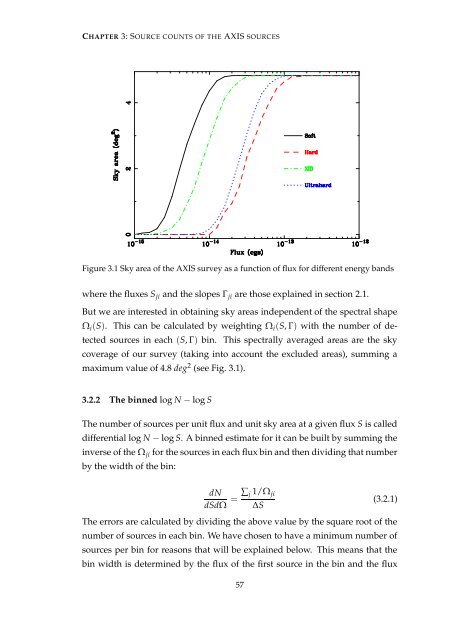
Figure 3.1 Sky area of the AXIS survey as a function of flux for different energy bands<br />
where the fluxes S ji and the slopes Γ ji are those explained in section 2.1.<br />
But we are interested in obtaining sky areas independent of the spectral shape<br />
Ω i (S). This can be calculated by weighting Ω i (S, Γ) with the number of detected<br />
sources in each (S, Γ) bin. This spectrally averaged areas are the sky<br />
coverage of our survey (taking into account the excluded areas), summing a<br />
maximum value of 4.8 deg 2 (see Fig. 3.1).<br />
3.2.2 The binned log N − log S<br />
The number of sources per unit flux and unit sky area at a given flux S is called<br />
differential log N − log S. A binned estimate for it can be built by summing the<br />
inverse of the Ω ji for the sources in each flux bin and then dividing that number<br />
by the width of the bin:<br />
dN<br />
dSdΩ = ∑ j 1/Ω ji<br />
∆S<br />
(3.2.1)<br />
The errors are calculated by dividing the above value by the square root of the<br />
number of sources in each bin. We have chosen to have a minimum number of<br />
sources per bin for reasons that will be explained below. This means that the<br />
bin width is determined by the flux of the first source in the bin and the flux<br />
57