E N S W - Human Development Reports - United Nations ...
E N S W - Human Development Reports - United Nations ...
E N S W - Human Development Reports - United Nations ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
The base case scenario<br />
The base case scenario implies continuity with historical<br />
patterns (including development policies pursued in recent<br />
decades). However, the model’s complex dynamics—including<br />
a wide range of nonlinear relationships—provide a structure<br />
that can also generate nonlinear future patterns that differ<br />
considerably from historical trajectories.<br />
The accelerated progress scenario<br />
Under the accelerated progress scenario, resources and policy<br />
ambition increase substantially compared with the base case.<br />
Table A2 lists choices and targets for appropriate (aggressive but<br />
reasonable) magnitudes of intervention in poverty reduction,<br />
infrastructure and governance, among others. Changes are<br />
relative to the underlying values for each country in the base<br />
case scenario and therefore take into account different national<br />
starting points and patterns.<br />
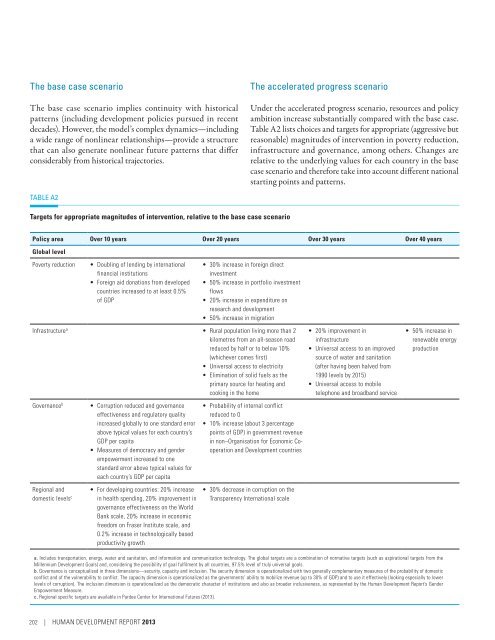
Table A2<br />
Targets for appropriate magnitudes of intervention, relative to the base case scenario<br />
Policy area Over 10 years Over 20 years Over 30 years Over 40 years<br />
Global level<br />
Poverty reduction<br />
• Doubling of lending by international<br />
financial institutions<br />
• Foreign aid donations from developed<br />
countries increased to at least 0.5%<br />
of GDP<br />
• 30% increase in foreign direct<br />
investment<br />
• 50% increase in portfolio investment<br />
flows<br />
• 20% increase in expenditure on<br />
research and development<br />
• 50% increase in migration<br />
Infrastructure a • Rural population living more than 2<br />
kilometres from an all-season road<br />
reduced by half or to below 10%<br />
(whichever comes first)<br />
• Universal access to electricity<br />
• Elimination of solid fuels as the<br />
primary source for heating and<br />
cooking in the home<br />
Governance b<br />
Regional and<br />
domestic levels c<br />
• Corruption reduced and governance<br />
effectiveness and regulatory quality<br />
increased globally to one standard error<br />
above typical values for each country’s<br />
GDP per capita<br />
• Measures of democracy and gender<br />
empowerment increased to one<br />
standard error above typical values for<br />
each country’s GDP per capita<br />
• For developing countries: 20% increase<br />
in health spending, 20% improvement in<br />
governance effectiveness on the World<br />
Bank scale, 20% increase in economic<br />
freedom on Fraser Institute scale, and<br />
0.2% increase in technologically based<br />
productivity growth<br />
• Probability of internal conflict<br />
reduced to 0<br />
• 10% increase (about 3 percentage<br />
points of GDP) in government revenue<br />
in non–Organisation for Economic Cooperation<br />
and <strong>Development</strong> countries<br />
• 30% decrease in corruption on the<br />
Transparency International scale<br />
• 20% improvement in<br />
infrastructure<br />
• Universal access to an improved<br />
source of water and sanitation<br />
(after having been halved from<br />
1990 levels by 2015)<br />
• Universal access to mobile<br />
telephone and broadband service<br />
• 50% increase in<br />
renewable energy<br />
production<br />
a. Includes transportation, energy, water and sanitation, and information and communication technology. The global targets are a combination of normative targets (such as aspirational targets from the<br />
Millennium <strong>Development</strong> Goals) and, considering the possibility of goal fulfilment by all countries, 97.5% level of truly universal goals.<br />
b. Governance is conceptualized in three dimensions—security, capacity and inclusion. The security dimension is operationalized with two generally complementary measures of the probability of domestic<br />
conflict and of the vulnerability to conflict. The capacity dimension is operationalized as the governments’ ability to mobilize revenue (up to 30% of GDP) and to use it effectively (looking especially to lower<br />
levels of corruption). The inclusion dimension is operationalized as the democratic character of institutions and also as broader inclusiveness, as represented by the <strong>Human</strong> <strong>Development</strong> Report’s Gender<br />
Empowerment Measure.<br />
c. Regional specific targets are available in Pardee Center for International Futures (2013).<br />
202 | HUMAN DevELoPMENt REPort 2013