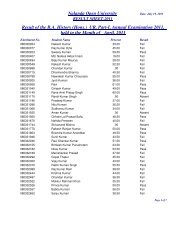
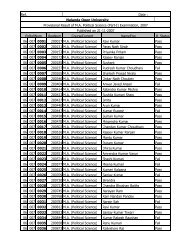
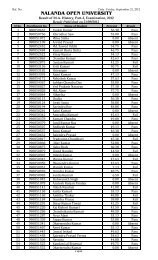
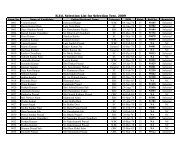
BABSc, B.Com & BCA Questions _III - Nalanda Open University
BABSc, B.Com & BCA Questions _III - Nalanda Open University
BABSc, B.Com & BCA Questions _III - Nalanda Open University
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
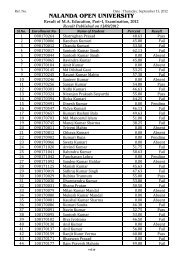
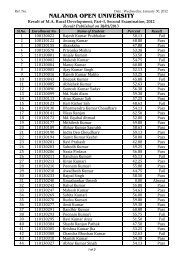
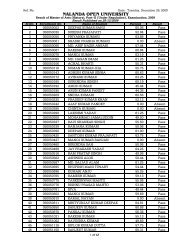
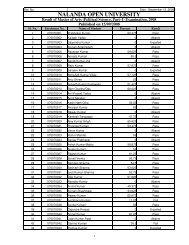
<strong>Nalanda</strong> <strong>Open</strong> <strong>University</strong><br />
Annual Exam-2010,<br />
Bachelor of Science (Botany) Hons, Part-<strong>III</strong><br />
Paper-V<strong>III</strong> (Genetics)<br />
Time: 3Hrs Full Marks: 75<br />
Answer any five questions. Question no. 1 is compulsory.<br />
All questions are of equal marks.<br />
1. Multiple Choice <strong>Questions</strong>:<br />
(xlvi) A ratio of 9:3:3:1 is modified in inhibitory factors to:-<br />
(a) 15:1 (b) 9:7 (c) 12:3:1 (d) 13:3<br />
(xlvii) Genes, which in homozygous conditions results in a non-viable progeny is called as:-<br />
(a) Duplicate gene (b) Linked gene (c) Lethal gene (d)<br />
Epistatic gene.<br />
(xlviii) The duplicate factors show the ratio:<br />
(a) 9:7 (b) 15:1 (c) 13:3 (d) 9:6:1<br />
(xlix) Additive factors or polymerism contain modified ratio as:-<br />
(a) 1:4:6:4:1 (b) 9:6:1 (c) 9:3:4 (d) 12:3:1<br />
(l) Datura is a classic example of:-<br />
(a) trisomy (b) triploid (c) monosomy (d) monoploid<br />
(li) Allopoyploid is:-<br />
(lii)<br />
(a) intraspecific (b) interspecific (c) both (d) none<br />
Down's syndrome in human beings is due to:-<br />
(a) monosomy (b) nullisomy (c) triploidy (d) trisomy<br />
(liii) If haploid number of chromosome is 10, what is the tetrasomic no:-<br />
(a) 10 (b) 20 (c) 22 (d) 40<br />
(liv) If haploid number of chromosomes in a cell is 12, the monosomic number will be:-<br />
(a) 24 (b) 25 (c) 23 (d) 21<br />
(lv)<br />
The bread wheat, Triticum aestivum is:-<br />
(a) haploid (b) diploid (c) tetraploid (d) hexaploid<br />
(lvi) Genetic code is:<br />
(a) Universal (b) Degenerate (c) Non-overlapping<br />
(d) <strong>Com</strong>maless (e) All of the above<br />
(lvii) Genetic engineering aims at:<br />
(a) Destroying wild genes<br />
(b) Preserving<br />
wild gene<br />
(c) Curing human disease by troducing new genes<br />
(d) None of the<br />
above<br />
(lviii) Which of the following techniques is used by forensic Scientists in crime detection?<br />
(a) DNA Sequencing (b) DNA nicking (c) Gene therapy (d) DNA finger<br />
printing<br />
(xiv) The technique of artificial synthesis of a new gene and its successful transplantation<br />
in the genome of a component organism comes under the perview of:<br />
(a) Gene therapy<br />
counselling<br />
(c) Genetic Engineering<br />
printing<br />
(xv) Which of the following is an 'ochre'codon?<br />
(a) UAA (b) UAG (c) UGA (d) AUG<br />
(b) Genetic<br />
(d) DNA finger<br />
2. Describe the type and cause of chromosomal disease in man.<br />
3. What is genetic counselling? Discuss its significance and role in human life.<br />
4. Write short notes on<br />
(a) aneuploidy (b) euploidy<br />
5. What is genetic code? Describe the characteristic of genetic code. What are initiator<br />
and non- sense codon?<br />
6. What are mutagen? Discuss the mutagenic action of some chemical and physical<br />
mutagen.