- Page 1: A 5/2006 Deformation behaviour of r
- Page 4 and 5: Finnish Rail Administration Publica
- Page 6 and 7: 4 Past investigations have shown cl
- Page 8 and 9: 6 Brecciaroli, Fabrizio - Kolisoja,
- Page 10 and 11: 8 kuvataan jakamalla jännitykset j
- Page 12 and 13: 10 TABLE OF CONTENTS ABSTRACT .....
- Page 14 and 15: 12 8.9 Trondheim NTNU/SINTEF’s re
- Page 16 and 17: 14 combination of resilient strains
- Page 18 and 19: 16 Modelling is an important necess
- Page 20 and 21: 18 Figure 2.1:2 Two-dimensional sta
- Page 22 and 23: 20 σ xx − σ 3 2 det τ yx σ yy
- Page 24 and 25: 22 stresses. As it can be seen from
- Page 26 and 27: 24 grains. The resistance to partic
- Page 28 and 29: 26 The reason was argued to be that
- Page 30 and 31: 28 term matric suction implies the
- Page 32 and 33: 30 Figure 3.2.1:1 Idealisation of t
- Page 34 and 35: 32 ε ε 2 ν = , (Eq. 3.2.2:4) whe
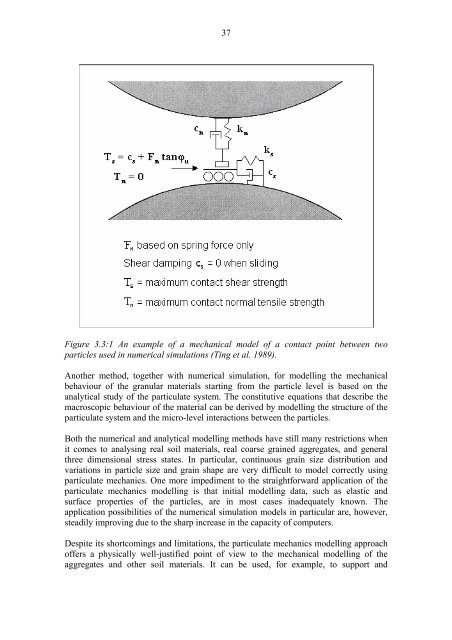
- Page 36 and 37: 34 where sij = σ −σ , (Eq. 3.2.
- Page 40 and 41: 38 supplement continuum mechanics m
- Page 42 and 43: 40 Figure 4.2:1 A typical variation
- Page 44 and 45: 42 Figure 4.2:3 Modulus of resilien
- Page 46 and 47: 44 provided that the applied stress
- Page 48 and 49: 46 material (Uzan 1985). Dilation i
- Page 50 and 51: 48 Figure 4.5:1 Resilient modulus o
- Page 52 and 53: 50 The grain size distribution of g
- Page 54 and 55: 52 The grain sizes that determine t
- Page 56 and 57: 54 4.6.3 Fines content A simple cha
- Page 58 and 59: 56 grained than for fine-grained ag
- Page 60 and 61: 58 and the shape of the particles a
- Page 62 and 63: 60 Figure 4.7:1 Effect of the wetti
- Page 64 and 65: 62 Figure 4.7:3 Modulus of resilien
- Page 66 and 67: 64 Figure 4.7:6 Dry -density as a f
- Page 68 and 69: 66 Figure 4.7:7 Resilient response
- Page 70 and 71: 68 The form index can be measured u
- Page 72 and 73: 70 Hovinmoen are gravel materials.
- Page 74 and 75: 72 5 MODELLING OF RESILIENT DEFORMA
- Page 76 and 77: 74 5.2.2 Resilient modulus as a fun
- Page 78 and 79: 76 M r k2 k3 ⎛ θ ⎞ ⎛ q ⎞ =
- Page 80 and 81: 78 the model showed good representa
- Page 82 and 83: 80 discussed. However it can be exp
- Page 84 and 85: 82 et al. (2003) calculated the res
- Page 86 and 87: 84 p u = unit pressure (1 kPa), δp
- Page 88 and 89:
86 Figure 5.2.5:2 Vertical resilien
- Page 90 and 91:
88 2 1 ⎛ ⎞ = A q ε ν p ⎜1
- Page 92 and 93:
90 Figure 5.3:2 An example of the c
- Page 94 and 95:
92 by incorporating a coefficient o
- Page 96 and 97:
94 6 FACTORS AFFECTING PERMANENT DE
- Page 98 and 99:
96 cycles. He drew the general conc
- Page 100 and 101:
98 accumulated strain, ε p , is co
- Page 102 and 103:
100 Figure 6.3:1 Effect of loading
- Page 104 and 105:
102 load” is not equal to the fai
- Page 106 and 107:
104 Chan (1990) noticed, in his stu
- Page 108 and 109:
106 Youd (1972) studied the behavio
- Page 110 and 111:
108 Figure 6.5:2 Comparison of plas
- Page 112 and 113:
110 ample fine-grained fractions th
- Page 114 and 115:
112 of a dolomitic limestone with a
- Page 116 and 117:
114 Fuller curve (Equation 4.6.2:3)
- Page 118 and 119:
116 Figure 6.6:7 Elastic and plasti
- Page 120 and 121:
118 Figure 6.7:1 Dependence of the
- Page 122 and 123:
120 0,7 0,6 Elastic limit Failure s
- Page 124 and 125:
122 Figure 6.8.1:1 Influence of fin
- Page 126 and 127:
124 explain why the differences in
- Page 128 and 129:
126 was then argued that the variat
- Page 130 and 131:
128 7 MODELLING OF PERMANENT DEFORM
- Page 132 and 133:
130 Figure 7.2:1 Mohr-Coulomb repre
- Page 134 and 135:
132 where K p (N) = bulk modulus wi
- Page 136 and 137:
134 1993)) have reported that at le
- Page 138 and 139:
136 ε 1,p = accumulated permanent
- Page 140 and 141:
138 Barksdale (1972) conducted repe
- Page 142 and 143:
140 Figure 7.6:2 Relationship betwe
- Page 144 and 145:
142 also be employed for pavement d
- Page 146 and 147:
144 repeated loads, although adapta
- Page 148 and 149:
146 series of specimens (or in a mu
- Page 150 and 151:
148 Figure 7.7:5 S-N design models
- Page 152 and 153:
150 In conclusion, both Huurman (19
- Page 154 and 155:
152 aim to simulate as closely as p
- Page 156 and 157:
154 by the American Association of
- Page 158 and 159:
156 Confining pressure is applied t
- Page 160 and 161:
158 particles. During the test, the
- Page 162 and 163:
160 method takes the average value
- Page 164 and 165:
162 Figure 8.7.2:2 Schematic illust
- Page 166 and 167:
164 through each platen is provided
- Page 168 and 169:
166 measured for the 600 mm central
- Page 170 and 171:
168 displayed on the monitor in gra
- Page 172 and 173:
170 unbound granular materials. The
- Page 174 and 175:
172 Figure 8.8.2:2 Permanent axial
- Page 176 and 177:
174 performance-related (functional
- Page 178 and 179:
176 the six supports of the vertica
- Page 180 and 181:
178 under the same isotropic stress
- Page 182 and 183:
180 9 CONCLUSIONS 9.1 Resilient def
- Page 184 and 185:
182 − Permanent deformation resis
- Page 186 and 187:
184 Balay J., Gomes Correia A., Jou
- Page 188 and 189:
186 Cheung, L.W. (1994). Laboratory
- Page 190 and 191:
188 El abd, A., Hornych, P., Breyss
- Page 192 and 193:
190 Hoff, I., Nordal, S., and Norda
- Page 194 and 195:
192 Kolisoja, P. (1996b) Large Scal
- Page 196 and 197:
194 Mitry, F.G. (1964). Determinati
- Page 198 and 199:
196 Plaistow, N.C. (1994). Non-Line
- Page 200 and 201:
198 Tam, W.A. and Brown, S.F. (1988
- Page 202 and 203:
200 Wellner, F. (1996). Influence o
- Page 204 and 205:
Liite RHK:n julkaisuun A 5/2006 1 L
- Page 206 and 207:
Liite RHK:n julkaisuun A 5/2006 3 2
- Page 208 and 209:
Liite RHK:n julkaisuun A 5/2006 5 R
- Page 210 and 211:
Liite RHK:n julkaisuun A 5/2006 7 4
- Page 212 and 213:
Liite RHK:n julkaisuun A 5/2006 9 4
- Page 214 and 215:
RATAHALLINTOKESKUKSEN JULKAISUJA A-