Radar Technology for Level Gauging - Krohne
Radar Technology for Level Gauging - Krohne
Radar Technology for Level Gauging - Krohne
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
3. <strong>Radar</strong>-Füllstandsmesssysteme<br />
7.3.5 Bulk (particulate) materials<br />
The effective relative permittivity of particulate materials (with air in the interstices) can be<br />
much lower than that of the homogeneous solid body. For instance, a material with εr = 2<br />
and 50% air content has an effective εr, eff of 1.5. The rule of thumb:<br />
εr, eff = 1 + (εr –1) · (1 –0.01·L[%]); L = volumetric air content in %.<br />
Also to be borne in mind is the fact that with bulk materials having a particle size range in<br />
the order of the wavelength, the microwaves will disperse (see next chapter) and so greatly<br />
decrease reflectivity.<br />
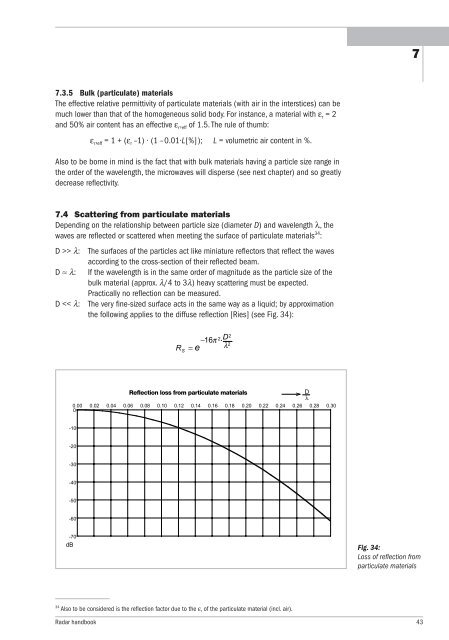
7.4 Scattering from particulate materials<br />
Depending on the relationship between particle size (diameter D) and wavelength λ, the<br />
waves are reflected or scattered when meeting the surface of particulate materials34 :<br />
D >> λ: The surfaces of the particles act like miniature reflectors that reflect the waves<br />
according to the cross-section of their reflected beam.<br />
D ≈ λ: If the wavelength is in the same order of magnitude as the particle size of the<br />
bulk material (approx. λ/4 to 3λ) heavy scattering must be expected.<br />
Practically no reflection can be measured.<br />
D