What Is A Free Radical - Ãstav lékaÅské chemie a biochemie
What Is A Free Radical - Ãstav lékaÅské chemie a biochemie
What Is A Free Radical - Ãstav lékaÅské chemie a biochemie
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
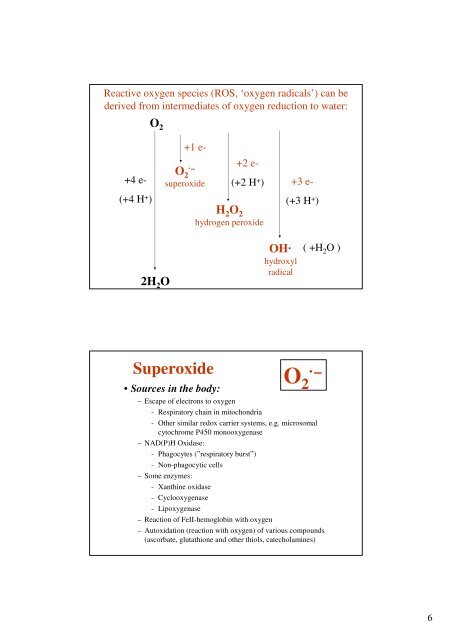
Reactive oxygen species (ROS, ‘oxygen radicals’) can be<br />
derived from intermediates of oxygen reduction to water:<br />
O 2<br />
+4 e-<br />
(+4 H + )<br />
+1 e-<br />
O 2·–<br />
superoxide<br />
+2 e-<br />
(+2 H + )<br />
H 2 O 2<br />
hydrogen peroxide<br />
+3 e-<br />
(+3 H + )<br />
2H 2 O<br />
OH·<br />
hydroxyl<br />
radical<br />
( +H 2 O )<br />
Superoxide<br />
O 2·–<br />
• Sources in the body:<br />
– Escape of electrons to oxygen<br />
- Respiratory chain in mitochondria<br />
- Other similar redox carrier systems, e.g. microsomal<br />
cytochrome P450 monooxygenase<br />
– NAD(P)H Oxidase:<br />
- Phagocytes (”respiratory burst”)<br />
- Non-phagocytic cells<br />
– Some enzymes:<br />
- Xanthine oxidase<br />
- Cyclooxygenase<br />
- Lipoxygenase<br />
– Reaction of FeII-hemoglobin with oxygen<br />
– Autoxidation (reaction with oxygen) of various compounds<br />
(ascorbate, glutathione and other thiols, catecholamines)<br />
6





![(Microsoft PowerPoint - ATP angl.ppt [Re\236im kompatibility])](https://img.yumpu.com/46799556/1/190x134/microsoft-powerpoint-atp-anglppt-re236im-kompatibility.jpg?quality=85)