Drivers of environmental innovation - Vinnova
Drivers of environmental innovation - Vinnova
Drivers of environmental innovation - Vinnova
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
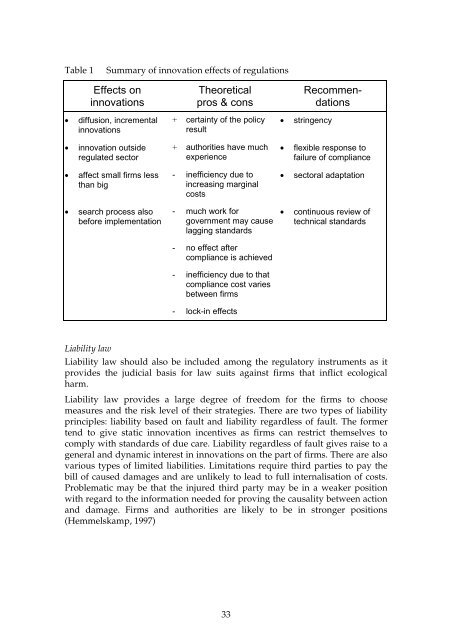
Table 1<br />
Summary <strong>of</strong> <strong>innovation</strong> effects <strong>of</strong> regulations<br />
Effects on<br />
<strong>innovation</strong>s<br />
• diffusion, incremental<br />
<strong>innovation</strong>s<br />
• <strong>innovation</strong> outside<br />
regulated sector<br />
• affect small firms less<br />
than big<br />
• search process also<br />
before implementation<br />
Theoretical<br />
pros & cons<br />
+ certainty <strong>of</strong> the policy<br />
result<br />
+ authorities have much<br />
experience<br />
- inefficiency due to<br />
increasing marginal<br />
costs<br />
- much work for<br />
government may cause<br />
lagging standards<br />
- no effect after<br />
compliance is achieved<br />
- inefficiency due to that<br />
compliance cost varies<br />
between firms<br />
- lock-in effects<br />
Recommendations<br />
• stringency<br />
• flexible response to<br />
failure <strong>of</strong> compliance<br />
• sectoral adaptation<br />
• continuous review <strong>of</strong><br />
technical standards<br />
Liability law<br />
Liability law should also be included among the regulatory instruments as it<br />
provides the judicial basis for law suits against firms that inflict ecological<br />
harm.<br />
Liability law provides a large degree <strong>of</strong> freedom for the firms to choose<br />
measures and the risk level <strong>of</strong> their strategies. There are two types <strong>of</strong> liability<br />
principles: liability based on fault and liability regardless <strong>of</strong> fault. The former<br />
tend to give static <strong>innovation</strong> incentives as firms can restrict themselves to<br />
comply with standards <strong>of</strong> due care. Liability regardless <strong>of</strong> fault gives raise to a<br />
general and dynamic interest in <strong>innovation</strong>s on the part <strong>of</strong> firms. There are also<br />
various types <strong>of</strong> limited liabilities. Limitations require third parties to pay the<br />
bill <strong>of</strong> caused damages and are unlikely to lead to full internalisation <strong>of</strong> costs.<br />
Problematic may be that the injured third party may be in a weaker position<br />
with regard to the information needed for proving the causality between action<br />
and damage. Firms and authorities are likely to be in stronger positions<br />
(Hemmelskamp, 1997)<br />
33