Download Guidebook as .pdf (1.8 Mb) - Carolina Geological Society
Download Guidebook as .pdf (1.8 Mb) - Carolina Geological Society
Download Guidebook as .pdf (1.8 Mb) - Carolina Geological Society
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
ROLF K. AADLAND, PAUL A. THAYER, AND ANDREW D. SMITS<br />
confining unit (Figs. 1 and 2). The two aquifers can be traced<br />
northward, where they constitute an integral part of the Floridan<br />
Midville aquifer system.<br />
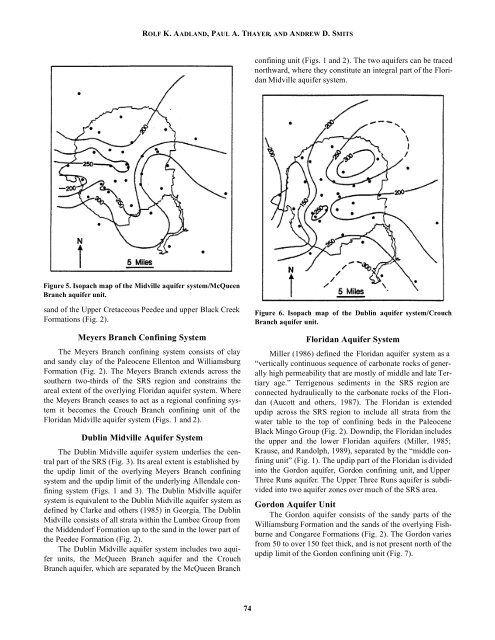
Figure 5. Isopach map of the Midville aquifer system/McQueen<br />
Branch aquifer unit.<br />
sand of the Upper Cretaceous Peedee and upper Black Creek<br />
Formations (Fig. 2).<br />
Meyers Branch Confining System<br />
The Meyers Branch confining system consists of clay<br />
and sandy clay of the Paleocene Ellenton and Williamsburg<br />
Formation (Fig. 2). The Meyers Branch extends across the<br />
southern two-thirds of the SRS region and constrains the<br />
areal extent of the overlying Floridan aquifer system. Where<br />
the Meyers Branch ce<strong>as</strong>es to act <strong>as</strong> a regional confining system<br />
it becomes the Crouch Branch confining unit of the<br />
Floridan Midville aquifer system (Figs. 1 and 2).<br />
Dublin Midville Aquifer System<br />
The Dublin Midville aquifer system underlies the central<br />
part of the SRS (Fig. 3). Its areal extent is established by<br />
the updip limit of the overlying Meyers Branch confining<br />
system and the updip limit of the underlying Allendale confining<br />
system (Figs. 1 and 3). The Dublin Midville aquifer<br />
system is equivalent to the Dublin Midville aquifer system <strong>as</strong><br />
defined by Clarke and others (1985) in Georgia. The Dublin<br />
Midville consists of all strata within the Lumbee Group from<br />
the Middendorf Formation up to the sand in the lower part of<br />
the Peedee Formation (Fig. 2).<br />
The Dublin Midville aquifer system includes two aquifer<br />
units, the McQueen Branch aquifer and the Crouch<br />
Branch aquifer, which are separated by the McQueen Branch<br />
Figure 6. Isopach map of the Dublin aquifer system/Crouch<br />
Branch aquifer unit.<br />
Floridan Aquifer System<br />
Miller (1986) defined the Floridan aquifer system <strong>as</strong> a<br />
“vertically continuous sequence of carbonate rocks of generally<br />
high permeability that are mostly of middle and late Tertiary<br />
age.” Terrigenous sediments in the SRS region are<br />
connected hydraulically to the carbonate rocks of the Floridan<br />
(Aucott and others, 1987). The Floridan is extended<br />
updip across the SRS region to include all strata from the<br />
water table to the top of confining beds in the Paleocene<br />
Black Mingo Group (Fig. 2). Downdip, the Floridan includes<br />
the upper and the lower Floridan aquifers (Miller, 1985;<br />
Krause, and Randolph, 1989), separated by the “middle confining<br />
unit” (Fig. 1). The updip part of the Floridan is divided<br />
into the Gordon aquifer, Gordon confining unit, and Upper<br />
Three Runs aquifer. The Upper Three Runs aquifer is subdivided<br />
into two aquifer zones over much of the SRS area.<br />
Gordon Aquifer Unit<br />
The Gordon aquifer consists of the sandy parts of the<br />
Williamsburg Formation and the sands of the overlying Fishburne<br />
and Congaree Formations (Fig. 2). The Gordon varies<br />
from 50 to over 150 feet thick, and is not present north of the<br />
updip limit of the Gordon confining unit (Fig. 7).<br />
74