English Edition (6 MB pdf) - Saudi Aramco
English Edition (6 MB pdf) - Saudi Aramco
English Edition (6 MB pdf) - Saudi Aramco
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
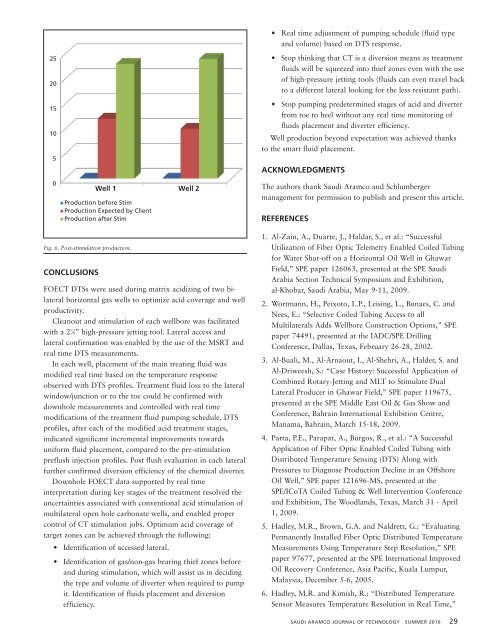
25<br />
20<br />
15<br />
10<br />
5<br />
0<br />
Well 1 Well 2<br />
Production before Stim<br />
Production Expected by Client<br />
Production after Stim<br />
• Real time adjustment of pumping schedule (fluid type<br />
and volume) based on DTS response.<br />
• Stop thinking that CT is a diversion means as treatment<br />
fluids will be squeezed into thief zones even with the use<br />
of high-pressure jetting tools (fluids can even travel back<br />
to a different lateral looking for the less resistant path).<br />
• Stop pumping predetermined stages of acid and diverter<br />
from toe to heel without any real time monitoring of<br />
fluids placement and diverter efficiency.<br />
Well production beyond expectation was achieved thanks<br />
to the smart fluid placement.<br />
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS<br />
The authors thank <strong>Saudi</strong> <strong>Aramco</strong> and Schlumberger<br />
management for permission to publish and present this article.<br />
REFERENCES<br />
Fig. 6. Post-stimulation production.<br />
CONCLUSIONS<br />
FOECT DTSs were used during matrix acidizing of two bilateral<br />
horizontal gas wells to optimize acid coverage and well<br />
productivity.<br />
Cleanout and stimulation of each wellbore was facilitated<br />
with a 2 7 ⁄8” high-pressure jetting tool. Lateral access and<br />
lateral confirmation was enabled by the use of the MSRT and<br />
real time DTS measurements.<br />
In each well, placement of the main treating fluid was<br />
modified real time based on the temperature response<br />
observed with DTS profiles. Treatment fluid loss to the lateral<br />
window/junction or to the toe could be confirmed with<br />
downhole measurements and controlled with real time<br />
modifications of the treatment fluid pumping schedule. DTS<br />
profiles, after each of the modified acid treatment stages,<br />
indicated significant incremental improvements towards<br />
uniform fluid placement, compared to the pre-stimulation<br />
preflush injection profiles. Post flush evaluation in each lateral<br />
further confirmed diversion efficiency of the chemical diverter.<br />
Downhole FOECT data supported by real time<br />
interpretation during key stages of the treatment resolved the<br />
uncertainties associated with conventional acid stimulation of<br />
multilateral open hole carbonate wells, and enabled proper<br />
control of CT stimulation jobs. Optimum acid coverage of<br />
target zones can be achieved through the following:<br />
• Identification of accessed lateral.<br />
• Identification of gas/non-gas bearing thief zones before<br />
and during stimulation, which will assist us in deciding<br />
the type and volume of diverter when required to pump<br />
it. Identification of fluids placement and diversion<br />
efficiency.<br />
1. Al-Zain, A., Duarte, J., Haldar, S., et al.: “Successful<br />
Utilization of Fiber Optic Telemetry Enabled Coiled Tubing<br />
for Water Shut-off on a Horizontal Oil Well in Ghawar<br />
Field,” SPE paper 126063, presented at the SPE <strong>Saudi</strong><br />
Arabia Section Technical Symposium and Exhibition,<br />
al-Khobar, <strong>Saudi</strong> Arabia, May 9-11, 2009.<br />
2. Wortmann, H., Peixoto, L.P., Leising, L., Bunaes, C. and<br />
Nees, E.: “Selective Coiled Tubing Access to all<br />
Multilaterals Adds Wellbore Construction Options,” SPE<br />
paper 74491, presented at the IADC/SPE Drilling<br />
Conference, Dallas, Texas, February 26-28, 2002.<br />
3. Al-Buali, M., Al-Arnaout, I., Al-Shehri, A., Halder, S. and<br />
Al-Driweesh, S.: “Case History: Successful Application of<br />
Combined Rotary-Jetting and MLT to Stimulate Dual<br />
Lateral Producer in Ghawar Field,” SPE paper 119675,<br />
presented at the SPE Middle East Oil & Gas Show and<br />
Conference, Bahrain International Exhibition Centre,<br />
Manama, Bahrain, March 15-18, 2009.<br />
4. Parta, P.E., Parapat, A., Burgos, R., et al.: “A Successful<br />
Application of Fiber Optic Enabled Coiled Tubing with<br />
Distributed Temperature Sensing (DTS) Along with<br />
Pressures to Diagnose Production Decline in an Offshore<br />
Oil Well,” SPE paper 121696-MS, presented at the<br />
SPE/ICoTA Coiled Tubing & Well Intervention Conference<br />
and Exhibition, The Woodlands, Texas, March 31 - April<br />
1, 2009.<br />
5. Hadley, M.R., Brown, G.A. and Naldrett, G.: “Evaluating<br />
Permanently Installed Fiber Optic Distributed Temperature<br />
Measurements Using Temperature Step Resolution,” SPE<br />
paper 97677, presented at the SPE International Improved<br />
Oil Recovery Conference, Asia Pacific, Kuala Lumpur,<br />
Malaysia, December 5-6, 2005.<br />
6. Hadley, M.R. and Kimish, R.: “Distributed Temperature<br />
Sensor Measures Temperature Resolution in Real Time,”<br />
SAUDI ARAMCO JOURNAL OF TECHNOLOGY SUMMER 2010 29