Policy Paper - Drama Improves Lisbon Key Competences in Education
Policy Paper - Drama Improves Lisbon Key Competences in Education
Policy Paper - Drama Improves Lisbon Key Competences in Education
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
R e s u l t s<br />
of questions that can be asked. The only limit is what practitioners and policy-makers<br />
are <strong>in</strong>terested <strong>in</strong>. Hopefully the DICE database will be a valuable resource for answer<strong>in</strong>g<br />
many questions like these <strong>in</strong> the near future, and we will have the opportunity to f<strong>in</strong>d out<br />
as much as possible about how educational theatre and drama works, and to help <strong>in</strong> the<br />
design<strong>in</strong>g of even more effective educational theatre and drama programmes.<br />
For the seriously curious, let us take a look at a very simplified example how the DICE<br />
database could be used to understand more about how educational theatre and drama<br />
works.<br />
We have seen that the assessments of teachers <strong>in</strong>crease on average for all five<br />
competences, and this <strong>in</strong>crease is always higher <strong>in</strong> the case of the research group than<br />
<strong>in</strong> the control group. But what is beh<strong>in</strong>d this <strong>in</strong>crease? Do teachers’ assessments of all<br />
students <strong>in</strong>crease, or this is just an average?<br />
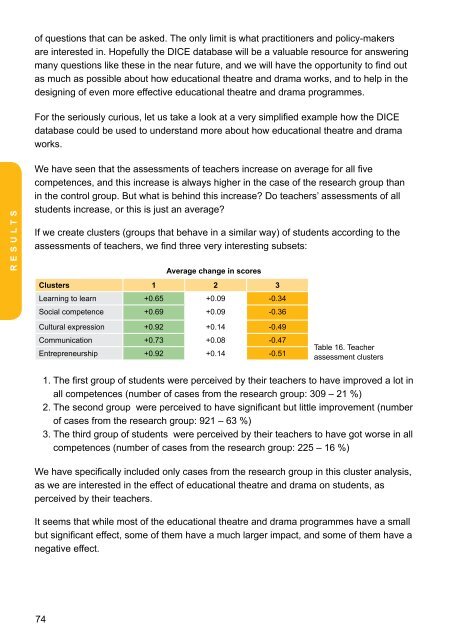
If we create clusters (groups that behave <strong>in</strong> a similar way) of students accord<strong>in</strong>g to the<br />
assessments of teachers, we f<strong>in</strong>d three very <strong>in</strong>terest<strong>in</strong>g subsets:<br />
Average change <strong>in</strong> scores<br />
Clusters 1 2 3<br />
Learn<strong>in</strong>g to learn +0.65 +0.09 -0.34<br />
Social competence +0.69 +0.09 -0.36<br />
Cultural expression +0.92 +0.14 -0.49<br />
Communication +0.73 +0.08 -0.47<br />
Entrepreneurship +0.92 +0.14 -0.51<br />
Table 16. Teacher<br />
assessment clusters<br />
The total average, when expressed as a s<strong>in</strong>gle number (and when these differences are<br />
masked), is slightly positive, as we have seen <strong>in</strong> chapter B.10.<br />
But what is beh<strong>in</strong>d this? If we can understand those factors that put the students of<br />
an educational theatre and drama programme <strong>in</strong>to one of these subgroups, we can<br />
understand much more about how an educational theatre and drama programme works<br />
and what makes it more effective.<br />
Look<strong>in</strong>g at the statistical analysis, it seems that the most important factors (among many)<br />
are:<br />
Relationship Significance Interpretation:<br />
...the more likely the programme will<br />
achieve better results<br />
The programme leader’s <strong>in</strong>tention to create an p < 0.000 The higher score this goal gets...<br />
artistic work<br />
The programme leader’s <strong>in</strong>tention to teach pupils<br />
The higher score this goal gets...<br />
p < 0.060<br />
about theatre and drama<br />
The programme leader’s <strong>in</strong>tention to learn about a p < 0.002 The higher score this goal gets...<br />
specific theme or topic through drama<br />
The programme leader’s <strong>in</strong>tention to develop<br />
p < 0.003<br />
The higher score this goal gets...<br />
pupils’ creativity and th<strong>in</strong>k<strong>in</strong>g skills<br />
The <strong>in</strong>tention of the programme leader(s) to<br />
offer voluntary participation, as observed by the<br />
<strong>in</strong>dependent observers<br />
The length of time the programme leader(s) have<br />
been work<strong>in</strong>g<br />
p < 0.000<br />
p