Vendetta Final Proposal Part 2 - Cal Poly
Vendetta Final Proposal Part 2 - Cal Poly
Vendetta Final Proposal Part 2 - Cal Poly
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
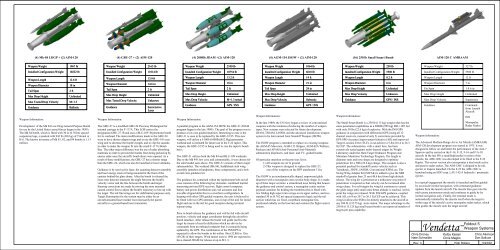
(4) Mk-84 LDGP + (2) AIM-120<br />
(4) GBU-27 + (2) AIM-120<br />
(4) 2000lb JDAM +(2) AIM-120<br />
(4) AGM-154 JSOW + (2) AIM-120<br />
(16) 250 lb Small Smart Bomb<br />
AIM-120 C AMRAAM<br />
Weapon Weight<br />
1967 lb<br />
Weapon Weight<br />
2165 lb<br />
Weapon Weight<br />
2100 lb<br />
Weapon Weight<br />
1064 lb<br />
Weapon Weight<br />
250 lb<br />
Weapon Weight<br />
327 lb<br />
Installed Configuration Weight<br />
10222 lb<br />
Installed Configuration Weight<br />
11014 lb<br />
Installed Configuration Weight<br />
10754 lb<br />
Installed Configuration Weight<br />
6610 lb<br />
Installed Configuration Weight<br />
5500 lb<br />
Installed Configuration Weight<br />
5500 lb<br />
Weapon Length<br />
Weapon Diameter<br />
Tail Span<br />
Max Drop Height<br />
Max Tested Drop Velocity<br />
Guidance<br />
Weapon Information:<br />
12.6 ft<br />
18 in<br />
2 ft<br />
Unlimited<br />
M=1.3<br />
Ballistic<br />
Development of the Mk 84 Low Drag General Purpose Bomb<br />
for use by the United States armed forces began in the 1950's.<br />
The Mk 84 bomb, which is fitted with 30 in (0.762m) spaced<br />
suspension lugs, is packed with 942 lb (426 kg) of Tritonal or<br />
H-6. The known inventory of Mk 81, 82, and 84 bombs is 1.13<br />
million.<br />
Weapon Length<br />
Weapon Diameter<br />
Tail Span<br />
Max Drop Height<br />
Max Tested Drop Velocity<br />
Guidance<br />
Weapon Information:<br />
13.9 ft<br />
14.6 in<br />
2 ft<br />
Unlimited<br />
Unknown<br />
Semi-Active<br />
Laser<br />
The GBU-27 is a modified GBU-24 Paveway III designed for<br />
internal carriage in the F-117A. This LGB carries the<br />
designation GBU-27 /B and uses a BLU-109 /B penetrator bomb<br />
for its warhead. The main modifications made to the GBU-24<br />
were to have shorter adaptor rings and to use the GBU-10's rear<br />
wing unit to decrease the bomb's length, and to clip the canards<br />
in order to make the weapon fit into the small F-117A Bomb<br />
Bay. The other major difference was the use of radar absorbing<br />
materials in order to prevent the bombs from being picked up by<br />
enemy radar once the aircraft's bomb doors were opened. As a<br />
result of these modifications, the GBU-27 has a shorter range<br />
than the GBU-24, which can also be launched at lower altitudes.<br />
Guidance is by semi-active laser, the scanning detector assembly<br />
and laser energy receiver being mounted in the front of the<br />
canister behind the glass dome. After the bomb is released the<br />
laser error detector measures the angle between the bomb's<br />
velocity vector and the line between the bomb and target.<br />
Steering corrections are made by moving the nose mounted<br />
canard control fins to adjust the bomb's trajectory to line up with<br />
the target. The tail fins/wings are for stabilization purposes only.<br />
Target illumination for the system may be either by an<br />
aircraft-mounted laser marker (not necessarily the parent<br />
aircraft) or a ground-based laser transmitter.<br />
Weapon Length<br />
Weapon Diameter<br />
Tail Span<br />
Max Drop Height<br />
Max Drop Velocity<br />
Guidance<br />
Weapon Information:<br />
13.2 ft<br />
18 in<br />
2 ft<br />
Unlimited<br />
M=1.3 tested<br />
GPS / INS<br />
A parallel program to the AGM-154 JSOW the GBU-31 JDAM<br />
program began in the late 1980's. The goal of the program was to<br />
produce a low cost guided munition. Interesting to note is the<br />
GBU-31 is soon to be replaced by the GBU-32/35. This new<br />
weapon, will utilize a I-1000 (1000lb)(452.5kg) penetrator<br />
warhead and is intended for future use in the F-22 raptor. This<br />
weapon, the GBU-32/35 is being used to size the raptor's bomb<br />
bay's.<br />
The GBU-31 utilizes both the Mk 84 and BLU-109 warheads.<br />
Due to the Mk 84's low cost, and commonality, it was chosen for<br />
the solid model seen above. The GBU-31 consists of three major<br />
subassemblies. The warhead (Mk 84), Saddleback stub wing<br />
assembly (attaches at hardpoints, three components), and a bolt<br />
on tail cone guidance kit.<br />
The guidance kit, contained within the replacement bolt-on tail<br />
cone consists of the following key elements: combined inertial<br />
measuring unit and GPS receiver; flight control computer;<br />
battery and power distribution unit; tail actuators and four<br />
movable clipped delta fins in a cruciform configuration. In<br />
keeping with other GPS guided weapons, the unit is believed to<br />
be fitted with two GPS antennas, one on top of the unit for initial<br />
flight and one in the tail for good reception during terminal<br />
maneuvering.<br />
Prior to bomb release the guidance unit will be fed with aircraft<br />
position, velocity and target coordinates through the aircraft to<br />
bomb interface. After release the bomb will guide itself to the<br />
target by means of rear fin deflection which are driven by<br />
commands from an onboard computer that is constantly being<br />
updated by the GPS. The combination of the INS/GPS is<br />
expected to allow the bombs to hit within 10m (32.8ft) to 15m<br />
(49.2ft) of their targets. Wind tunnel tests in 1996 are reported to<br />
have cleared JDAM for release at up to M 1.3.<br />
Weapon Length<br />
Weapon Diameter<br />
Tail Span<br />
Max Drop Height<br />
Max Drop Velocity<br />
Guidance<br />
Weapon Information:<br />
14 ft<br />
21 in<br />
24 in<br />
Unlimited<br />
Subsonic<br />
GPS / INS<br />
In the late 1980's the US Navy began a review of conventional<br />
weapons with the intention of reducing the number of weapon<br />
types. New systems were selected for future development:<br />
JDAM, TSSAM, JASSM, and the advanced interdiction weapon<br />
system to be later named Joint Standoff Weapon (JSOW).<br />
The JSOW program is intended to replace six existing weapons:<br />
the AGM-65 Maverick, AGM-123 Skipper, AGM-62A Walleye,<br />
Rockeye and APAM (Anti-Personnel/Anti-Material)<br />
submunition dispensers, and laser- and TV- guided bombs.<br />
Of particular attention on the previous list is:<br />
1) All weapons are air to ground.<br />
2) This weapon is designed to replace the GBU-27,<br />
one of the weapons on the RFP attachment 3 list.<br />
The JSOW is an aerodynamically shaped, unpowered glide<br />
dispenser with a rectangular cross-section body shape. It is made<br />
up of three major sections: a streamlined nose fairing that houses<br />
the guidance and control system, a rectangular center section<br />
payload container for holding the bomblets (this is fitted with<br />
two folding high aspect ratio wings on its upper surface, and two<br />
standard 30 in (0.762 m) spaced suspension lugs); and the tail<br />
section which has six fixed, sweptback rectangular fins<br />
positioned radially on the boat tail and contains the flight control<br />
system.<br />
Weapon Length<br />
Weapon Diameter<br />
Max Drop Height<br />
Max Drop Velocity<br />
Guidance<br />
Weapon Information:<br />
8.2 ft<br />
6 in<br />
Unlimited<br />
Unknown<br />
GPS / INS<br />
The Small Smart Bomb is a 250 lb (113 kg) weapon that has the<br />
same penetration capabilities as a 2000lb (905 kg) BLU-109, but<br />
with only 50 lbs (22.6 kg) of explosive. With the INS/GPS<br />
guidance in conjunction with differential GPS (using all 12<br />
channel receivers, instead of only 5) corrections provided by<br />
GPS SPO Accuracy Improvement Initiative (AII) and improved<br />
Target Location Error (TLE), it can achieve a 5-8m (16.4 to 26.3<br />
ft) CEP. The submunition, with a smart fuze, has been<br />
extensively tested against multi-layered targets by Wright<br />
Laboratory under the Hard Target Ordnance Program and<br />
Miniature Munitions Technology Program. The length to<br />
diameter ratio and nose shape are designed to optimize<br />
penetration for a 50lb (22.6 kg) charge. This weapon is also a<br />
potential payload for standoff carrier vehicles such as<br />
Tomahawk, JSOW, JASSM, Conventional ICBM, etc. The<br />
Swing Wing Adapter Kit (SWAK) is added to give the SSB<br />
standoff of greater than 25 nm (48.6 km) from high altitude<br />
release. The wing kit is jettisoned at a midcourse way point if<br />
penetration is required so that velocity can be increased after<br />
wing release. For soft targets the wing kit continues to extend<br />
the glide range until small arms threat altitude is reached. At this<br />
point the wings are released. With INS/GPS guidance, coupled<br />
with AII, a 6-8 m (19.7 to 26.3 ft) CEP can be achieved. This<br />
wing kit allows the SSB to be directly attached to the aircraft at<br />
any 300 lb (135.75 kg) store station. The major advantage to the<br />
250 lb (113.125 kg) small smart bomb is an improved number of<br />
targets per pass capability.<br />
Weapon Information:<br />
The Advanced Medium-Range Air to Air Missile (AMRAAM)<br />
AIM-120 development program was started in 1975. It was<br />
designed to follow on and better the performance of the Aim-7<br />
Sparrow and be carried on the F-14, F-15, F-16 and F/A-18<br />
aircraft. In the late 90's a modified(smaller) version of the<br />
missile, the AIM-120C was developed to be fitted to the F-22<br />
Raptor. This newer version also incorporates a dual mode active<br />
and passive radar seeker. The AIM-120C is deigned to be rail,<br />
ejector or trapeze launched. On the F-22 the AIM-120C is<br />
launched using an EDO corp. LAU-142/A hydraulic / pneumatic<br />
ejector.<br />
In a typical engagement the missile is launched and first guided<br />
by on-missile inertial navigation, with command guidance<br />
updates from the launch aircraft. The missile then goes into the<br />
mid-course autonomous mode and continues to guide by by<br />
inertial navigation only. <strong>Final</strong>ly, the terminal mode is<br />
automatically initiated by the missile itself when the target is<br />
within rage of the missile's active monopulse radar seeker, which<br />
then guides the missile onto the target aircraft.<br />
<strong>Vendetta</strong><br />
Chris Droney<br />
Nate Schnaible<br />
Rev. 3<br />
Weapon Length<br />
Weapon Diameter<br />
Fin Span<br />
Max Drop Height<br />
Max Drop Velocity<br />
Guidance<br />
Kolby Keiser<br />
Chris Maglio<br />
12 ft<br />
7 in<br />
INS<br />
High Rollers<br />
1 ft 6 in<br />
Unlimited<br />
Supersonic<br />
Command<br />
from Launch<br />
Aircraft<br />
Monopulse<br />
Radar Seeker<br />
Foldout 5<br />
Weapon Systems<br />
Chris Atkinson<br />
Dan Salluce<br />
5/23/02