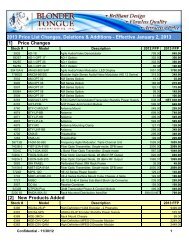
Functional Block Diagram - Blonder Tongue Laboratories Inc.
Functional Block Diagram - Blonder Tongue Laboratories Inc.
Functional Block Diagram - Blonder Tongue Laboratories Inc.
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Broadband Specification Guide<br />
CATV Terms & Definitions<br />
Reflection<br />
1. Reflected energy which substantially covers the spectrum occupied by<br />
the originating signal.<br />
2. The abrupt change in direction of a light beam at an interface between<br />
two dissimilar media so that the light beam returns into the medium<br />
from which it originated.<br />
Refraction<br />
The bending of a beam of light at an interface between two dissimilar<br />
media or in a medium whose refractive index is a continuous function of<br />
position (graded-index medium).<br />
Refractive Index<br />
The ratio of the velocity of light in a vacuum to the velocity of light in the<br />
specified medium.<br />
Remote Local Origination<br />
Closed-circuit program generated some place other than the headend.<br />
Example: Sub-channel origination.<br />
Repeater<br />
A signal amplification device, often used along cables to extend<br />
transmission distances.<br />
Response<br />
The fidelity with which the output of a system, device, or network<br />
corresponds to its input.<br />
Responsivity<br />
The ratio of an optical detector's electrical output to its optical input, the<br />
precise definition depending on the detector type; generally expressed in<br />
Amperes per Watt or Volts per Watt of incident radiant power.<br />
Return Loss<br />
A ratio expressed in dB between the reflected signal and the total<br />
signal applied to a device. In 75 ohm systems, the closer the device’s<br />
impedance is to 75 ohms, the higher the return loss.<br />
Return Loss, Structural<br />
The return loss of coaxial cable as established by discrete discontinuities<br />
introduced during the manufacturing process.<br />
RF<br />
Radio Frequency (10 KHz-100GHz).<br />
RFI<br />
Radio Frequency Interference. Undesired RF signals.<br />
Ribbon Cable<br />
A cable whose conductors lie side by side in a single plane. Usually has a<br />
molded polyethylene insulation.<br />
Rise Time<br />
For an emitter, the time it takes for light intensity to rise from 10% to 90%<br />
of peak output. Detector rise time, also called response time, is the time<br />
in which the detector output goes from 10% to 90% of peak.<br />
Riser<br />
Term generally used to describe a simplified single line distribution<br />
drawing. In buildings, a riser refers to a location where cable routing can<br />
pass from floor to floor.<br />
Second-order Distortion<br />
Spurious signals generated when two or more carriers are passed<br />
through a nonlinear circuit. The spurious signals are sum and difference<br />
products of any two carriers. Sometimes referred to as second-order<br />
"beats." Second order distortion is calculated as a power addition.<br />
Second Window<br />
Characteristic of an optical fiber having a region of relatively high<br />
transmittance surrounded by regions of low transmittance in the<br />
wavelength range of 1200 to 1350 nanometers.<br />
Semiconductor<br />
A material whose resistivity is between that of conductors and insulators,<br />
and whose resistivity can sometimes be changed by light, an electric<br />
field, or a magnetic field. Current flow is sometimes by movement of<br />
negative electrons, and sometimes by transfer of positive holes. Used<br />
in transistors, diodes, photodiodes, photocells, and thermistors. Some<br />
examples are: silicon, germanium, selenium, and lead sulfide.<br />
Semiconductor, n-type<br />
A semiconductor material, such as germanium or silicon, which has a<br />
small amount of impurity, such as antimony, arsenic, or phosphorous<br />
added to increase the supply of free electrons. Such a material conducts<br />
electricity through movement of electrons.<br />
Semiconductor, p-type<br />
A semiconductor material which has been doped so that it has a net<br />
deficiency of free electrons. It therefore conducts electricity through<br />
movement of "holes," which see.<br />
Sensitivity<br />
Imprecise synonym for responsivity. In optical system receivers, the<br />
minimum power required to achieve a specified quality of performance<br />
in terms of output signal-to-noise ratio or other measure.<br />
Scattering<br />
The change in direction of light rays or photons after striking a small<br />
particle or particles. It may also be regarded as the diffusion of a light<br />
beam caused by the inhomogeneity of the transmitting medium.<br />
Signal Level Meter (SLM)<br />
A tuned radio frequency voltmeter, usually calibrated in decibels per<br />
millivolt (dBmV) as well as voltage.<br />
Signal-to-noise Ratio (S/N ratio)<br />
The difference in amplitude of a signal (before modulation or after<br />
detection of a modulated carrier), and the noise present in the spectrum<br />
occupied by the signal, when both are measured at the same point in<br />
the system.<br />
92