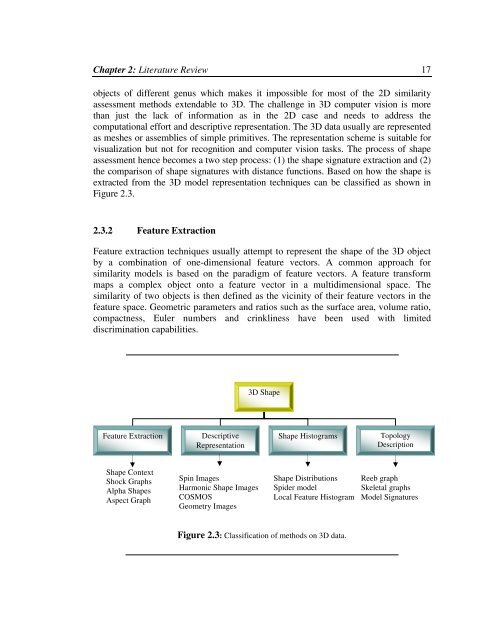
Chapter 2: Literature Review 17objects of different genus which makes it impossible for most of <strong>the</strong> 2D similarityassessment methods extendable to 3D. The challenge in 3D computer vision is morethan just <strong>the</strong> lack of information as in <strong>the</strong> 2D case and needs to address <strong>the</strong>computational effort and descriptive representation. The 3D data usually are representedas meshes or assemblies of simple primitives. The representation scheme is suitable forvisualization but not for recognition and computer vision tasks. The process of shapeassessment hence becomes a two step process: (1) <strong>the</strong> shape signature extraction and (2)<strong>the</strong> comparison of shape signatures with distance functions. Based on how <strong>the</strong> shape isextracted from <strong>the</strong> 3D model representation techniques can be classified as shown inFigure 2.3.2.3.2 Feature ExtractionFeature extraction techniques usually attempt to represent <strong>the</strong> shape of <strong>the</strong> 3D object<strong>by</strong> a combination of one-dimensional feature vectors. A common approach forsimilarity models is based on <strong>the</strong> paradigm of feature vectors. A feature transformmaps a complex object onto a feature vector in a multidimensional space. Thesimilarity of two objects is <strong>the</strong>n defined as <strong>the</strong> vicinity of <strong>the</strong>ir feature vectors in <strong>the</strong>feature space. Geometric par<strong>am</strong>eters and ratios such as <strong>the</strong> surface area, volume ratio,compactness, Euler numbers and crinkliness have been used with limiteddiscrimination capabilities.3D ShapeFeature ExtractionDescriptiveRepresentationShape Histogr<strong>am</strong>s<strong>To</strong>pologyDescriptionShape ContextShock GraphsAlpha ShapesAspect GraphSpin ImagesHarmonic Shape ImagesCOSMOSGeometry ImagesShape DistributionsSpider modelLocal Feature Histogr<strong>am</strong>Reeb graphSkeletal graphsModel SignaturesFigure 2.3: Classification of methods on 3D data.
Chapter 2: Literature Review 18Kortgen et al. [Kortgen et al., 2003] achieves shape matching <strong>by</strong> extending <strong>the</strong> 2Dshape contexts [Belongie, 2003] to 3D. They use <strong>the</strong> shape context at a point on <strong>the</strong>surface as <strong>the</strong> summary of <strong>the</strong> global shape characteristics invariant to rotation,translation and scaling. Vranic and Saupe [Vranic and Saupe, 2001] propose a newmethod for shape similarity search on polygonal meshes. They characterize spatialproperties of 3D objects such that similar objects are mapped as close points in <strong>the</strong>feature space. They <strong>the</strong>n perform a coarse voxelization of <strong>the</strong> object in <strong>the</strong> canonicalcoordinate fr<strong>am</strong>e and compute <strong>the</strong> absolute value of <strong>the</strong> 3D Fourier coefficients as <strong>the</strong>feature vector. Vranic improves it fur<strong>the</strong>r in [Vranic, 2003]. Ohbuchi et al. [Obhuchi etal., 2003] describe a multi-resolution analysis technique for <strong>the</strong> task of shapesimilarity comparison. They use 3D alpha shapes to generate a multi-resolutionhierarchy of shapes of a given query object. They <strong>the</strong>n follow that <strong>by</strong> applying asimple shape descriptor such as <strong>the</strong> D 2 shape function introduced <strong>by</strong> [Osada et al.,2002] on each of <strong>the</strong> multi-resolution representations and call it <strong>the</strong> multi-resolutionshape descriptor.Automated feature recognition has also been attempted <strong>by</strong> extracting instances ofmanufactured features from engineering designs. Henderson [Henderson et al., 1993]is an extensive survey of such methods that make use of a library of machiningfeatures for description. With <strong>the</strong> assumption of primitives, procedural methodsproposed <strong>by</strong> Elinson et al. [Elinson et al., 1997] and Mukai et al. [Mukai et al., 2002]have applied constructive solid geometry (CSG’s) to classify CAD models ofmechanical parts. Their methods however cannot be extended to a more general classof shapes represented as point sets and meshes. Biermann et al. in [Biermann et al.,2001] propose Boolean operations of primitives for shape description. However, directassessment of similarity between 3D models using Boolean operations iscomputationally slow due to <strong>the</strong> difficulty in aligning <strong>the</strong> models before performing<strong>the</strong> operation. With a large database, it is not a pragmatic solution. Zhang and Chen[Zhang and Chen, 2001] discuss efficient global feature extraction methods from <strong>the</strong>mesh representation.Duda and Hart [Duda and Hart, 1973] have been extended <strong>by</strong> Khotanzad et al.[Khotanzad et al., 1980] to a subset of 3D moments that are invariant to rotation,translation and scaling that can be used as feature vectors for shapes as shown inEquation 2.6.∞∞∞ m = x y z ρ (x, y,z) dxdydzpqr−∞ −∞ -∞pqrwhere ρ (x, y, z) represents <strong>the</strong> point cloud of <strong>the</strong> model. (2.6)Cybenko et al. [Cybenko et al., 1997] use second-order moments, spherical kernelmoment invariants, bounding-box dimensions, object centroid and surface area alongwith a correlation metric for shape-similarity measurement. Elad et al. [Elad et al.,