To the Graduate Council: I am submitting herewith a thesis written by ...
To the Graduate Council: I am submitting herewith a thesis written by ...
To the Graduate Council: I am submitting herewith a thesis written by ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
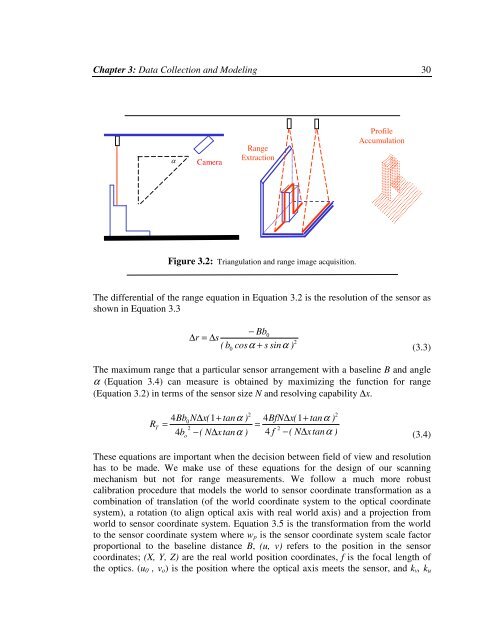
Chapter 3: Data Collection and Modeling 30αC<strong>am</strong>eraRangeExtractionProfileAccumulationFigure 3.2: Triangulation and range image acquisition.The differential of <strong>the</strong> range equation in Equation 3.2 is <strong>the</strong> resolution of <strong>the</strong> sensor asshown in Equation 3.3− Bb0∆ r = ∆s2( b cosα + s sinα)0(3.3)The maximum range that a particular sensor arrangement with a baseline B and angleα (Equation 3.4) can measure is obtained <strong>by</strong> maximizing <strong>the</strong> function for range(Equation 3.2) in terms of <strong>the</strong> sensor size N and resolving capability ∆x.RT4BbN∆x(1+tanα)20=224bo−(N∆xtanα)24BfN∆x(1+tanα)=4 f −(N∆xtanα)(3.4)These equations are important when <strong>the</strong> decision between field of view and resolutionhas to be made. We make use of <strong>the</strong>se equations for <strong>the</strong> design of our scanningmechanism but not for range measurements. We follow a much more robustcalibration procedure that models <strong>the</strong> world to sensor coordinate transformation as acombination of translation (of <strong>the</strong> world coordinate system to <strong>the</strong> optical coordinatesystem), a rotation (to align optical axis with real world axis) and a projection fromworld to sensor coordinate system. Equation 3.5 is <strong>the</strong> transformation from <strong>the</strong> worldto <strong>the</strong> sensor coordinate system where w p is <strong>the</strong> sensor coordinate system scale factorproportional to <strong>the</strong> baseline distance B, (u, v) refers to <strong>the</strong> position in <strong>the</strong> sensorcoordinates; (X, Y, Z) are <strong>the</strong> real world position coordinates, f is <strong>the</strong> focal length of<strong>the</strong> optics. (u 0 , v o ) is <strong>the</strong> position where <strong>the</strong> optical axis meets <strong>the</strong> sensor, and k v , k u