Abstracts of the Academy of Dental Materials Annual ... - IsiRed
Abstracts of the Academy of Dental Materials Annual ... - IsiRed
Abstracts of the Academy of Dental Materials Annual ... - IsiRed
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
e58 dental materials 26S (2010) e1–e84<br />
124<br />
Zirconium oxy-fluoride surface activation for improved bonding<br />
to zirconia substrates<br />
J.R. Piascik 1 , S.D. Wolter 2 , B.R. Stoner 1,2<br />
1 RTI International, Durham, NC, USA<br />
2 Duke University, Durham, NC, USA<br />
Objectives: The purpose <strong>of</strong> this study was to compare an<br />
oxy-fluoride surface activation process to o<strong>the</strong>r techniques<br />
used to enhance adhesion <strong>of</strong> dental materials to zirconia surfaces.<br />
The effect <strong>of</strong> this novel pre-treatment on <strong>the</strong> adhesive<br />
strength to both as-received and mechanically roughened surfaces<br />
will be presented along with a discussion <strong>of</strong> bonding<br />
mechanisms, <strong>the</strong>ir advantages and limitations.<br />
<strong>Materials</strong> and methods: The study leverages a novel gasphase<br />
fluorination process that creates a thin oxy-fluoride<br />
conversion layer on <strong>the</strong> surface <strong>of</strong> zirconia, making it more<br />
reactive to conventional adhesive bonding protocols. Zirconia<br />
specimens, polished and roughened, were pre-treated and<br />
both composite and zirconia cylinders were bonded to <strong>the</strong>m<br />
using conventional adhesive techniques. All specimens were<br />
subjected to a shear force at a crosshead speed <strong>of</strong> 0.5 mm/min<br />
in an electro-mechanical testing device. Single factor analysis<br />
<strong>of</strong> variance (ANOVA) at a 5% confidence level was performed<br />
for <strong>the</strong> bonding strength data. Optical and scanning electron<br />
microscopy was used to evaluate and quantify failure surfaces.<br />
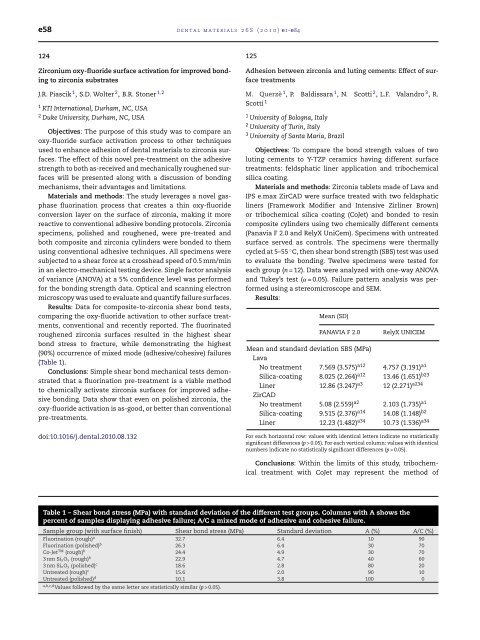
Results: Data for composite-to-zirconia shear bond tests,<br />
comparing <strong>the</strong> oxy-fluoride activation to o<strong>the</strong>r surface treatments,<br />
conventional and recently reported. The fluorinated<br />
roughened zirconia surfaces resulted in <strong>the</strong> highest shear<br />
bond stress to fracture, while demonstrating <strong>the</strong> highest<br />
(90%) occurrence <strong>of</strong> mixed mode (adhesive/cohesive) failures<br />
(Table 1).<br />
Conclusions: Simple shear bond mechanical tests demonstrated<br />
that a fluorination pre-treatment is a viable method<br />
to chemically activate zirconia surfaces for improved adhesive<br />
bonding. Data show that even on polished zirconia, <strong>the</strong><br />
oxy-fluoride activation is as-good, or better than conventional<br />
pre-treatments.<br />
doi:10.1016/j.dental.2010.08.132<br />
125<br />
Adhesion between zirconia and luting cements: Effect <strong>of</strong> surface<br />
treatments<br />
M. Querzè 1 , P. Baldissara 1 , N. Scotti 2 , L.F. Valandro 3 ,R.<br />
Scotti 1<br />
1 University <strong>of</strong> Bologna, Italy<br />
2 University <strong>of</strong> Turin, Italy<br />
3 University <strong>of</strong> Santa Maria, Brazil<br />
Objectives: To compare <strong>the</strong> bond strength values <strong>of</strong> two<br />
luting cements to Y-TZP ceramics having different surface<br />
treatments: feldsphatic liner application and tribochemical<br />
silica coating.<br />
<strong>Materials</strong> and methods: Zirconia tablets made <strong>of</strong> Lava and<br />
IPS e.max ZirCAD were surface treated with two feldsphatic<br />
liners (Framework Modifier and Intensive Zirliner Brown)<br />
or tribochemical silica coating (CoJet) and bonded to resin<br />
composite cylinders using two chemically different cements<br />
(Panavia F 2.0 and RelyX UniCem). Specimens with untreated<br />
surface served as controls. The specimens were <strong>the</strong>rmally<br />
cycled at 5–55 ◦ C, <strong>the</strong>n shear bond strength (SBS) test was used<br />
to evaluate <strong>the</strong> bonding. Twelve specimens were tested for<br />
each group (n = 12). Data were analyzed with one-way ANOVA<br />
and Tukey’s test (˛ = 0.05). Failure pattern analysis was performed<br />
using a stereomicroscope and SEM.<br />
Results:<br />
Mean (SD)<br />
PANAVIA F 2.0 RelyX UNICEM<br />
Mean and standard deviation SBS (MPa)<br />
Lava<br />
No treatment 7.569 (3.575) a12 4.757 (3.191) a1<br />
Silica-coating 8.025 (2.264) a12 13.46 (1.651) b23<br />
Liner 12.86 (3.247) a3 12 (2.271) a234<br />
ZirCAD<br />
No treatment 5.08 (2.559) a2 2.103 (1.735) a1<br />
Silica-coating 9.515 (2.376) a14 14.08 (1.148) b2<br />
Liner 12.23 (1.482) a34 10.73 (1.536) a34<br />
For each horizontal row: values with identical letters indicate no statistically<br />
significant differences (p > 0.05). For each vertical column: values with identical<br />
numbers indicate no statistically significant differences (p > 0.05).<br />
Conclusions: Within <strong>the</strong> limits <strong>of</strong> this study, tribochemical<br />
treatment with CoJet may represent <strong>the</strong> method <strong>of</strong><br />
Table 1 – Shear bond stress (MPa) with standard deviation <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> different test groups. Columns with A shows <strong>the</strong><br />
percent <strong>of</strong> samples displaying adhesive failure; A/C a mixed mode <strong>of</strong> adhesive and cohesive failure.<br />
Sample group (with surface finish) Shear bond stress (MPa) Standard deviation A (%) A/C (%)<br />
Fluorination (rough) a 32.7 6.4 10 90<br />
Fluorination (polished) b 26.3 6.4 30 70<br />
Co-JetTM (rough) b 24.4 4.9 30 70<br />
3nmSixOy (rough) b 22.9 4.7 40 60<br />
3nmSixOy (polished) c 18.6 2.8 80 20<br />
Untreated (rough) c 15.6 2.0 90 10<br />
Untreated (polished) d 10.1 3.8 100 0<br />
a,b,c,dValues followed by <strong>the</strong> same letter are statistically similar (p > 0.05).